Abstract
Purpose
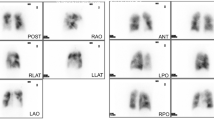
We aimed to investigate the response to balloon pulmonary angioplasty (BPA) in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) using semi-quantitative analysis of lung perfusion SPECT/CT.
Methods
This is a single-center retrospective study of patients with CTEPH who underwent BPA and pre- and post-BPA lung perfusion SPECT/CT between 2015 and 2022. Segmental defects on SPECT/CT were visually assessed and semi-quantitatively scored as 1 (large defect) or 0.5 (moderate defect) in accordance with modified PIOPED II criteria. The perfusion defect score was defined as (Σ segmental defect scores/18) × 100 (%). Associations between perfusion defect score and hemodynamic or functional parameters including WHO functional class, six-minute walking distance (6MWD), serum B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), mean arterial pulmonary pressure (mPAP), pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), and tricuspid regurgitation pressure gradient (TRPG) on echocardiography were statistically analyzed.
Results
A total of 24 consecutive patients were included. The perfusion defect score significantly improved after BPA (median 58.3% vs. 47.2%, P < 0.001), in conjunction with the WHO functional class, 6MWD, serum BNP, mPAP, and TRPG. Perfusion defect scores were significantly correlated with 6MWD (rho = − 0.583, P < 0.001), serum BNP (rho = 0.514, P < 0.001), mPAP (rho = 0.583, P < 0.001), and PVR (rho = 0.575, P < 0.001). The improvement in the perfusion defect score was significantly associated with improvement in mPAP (rho = 0.844, P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Our results suggest that semi-quantitative analysis of lung perfusion SPECT/CT can provide a potential imaging biomarker for monitoring the efficacy of BPA.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Contact the corresponding author for data requests.
References
Simonneau G, Gatzoulis MA, Adatia I, Celermajer D, Denton C, Ghofrani A, et al. Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:D34–41.
Valerio L, Mavromanoli AC, Barco S, Abele C, Becker D, Bruch L, et al. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension and impairment after pulmonary embolism: the FOCUS study. Eur Heart J. 2022;43:3387–98.
Gall H, Hoeper MM, Richter MJ, Cacheris W, Hinzmann B, Mayer E. An epidemiological analysis of the burden of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension in the USA, Europe and Japan. Eur Respir Rev. 2017;26.
Simonneau G, Torbicki A, Dorfmuller P, Kim N. The pathophysiology of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir Rev. 2017;26.
Galie N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Joint Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J. 2016;37:67–119.
Humbert M, Kovacs G, Hoeper MM, Badagliacca R, Berger RMF, Brida M, et al. 2022 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2022;43:3618–731.
Pepke-Zaba J, Delcroix M, Lang I, Mayer E, Jansa P, Ambroz D, et al. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH): results from an international prospective registry. Circulation. 2011;124:1973–81.
Rotzinger DC, Rezaei-Kalantari K, Aubert JD, Qanadli SD. Pulmonary angioplasty: a step further in the continuously changing landscape of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension management. Eur J Radiol. 2021;136:109562.
Mahmud E, Madani MM, Kim NH, Poch D, Ang L, Behnamfar O, et al. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: evolving therapeutic approaches for operable and inoperable disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71:2468–86.
Moradi F, Morris TA, Hoh CK. Perfusion scintigraphy in diagnosis and management of Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Radiographics. 2019;39:169–85.
Bajc M, Schumichen C, Gruning T, Lindqvist A, Le Roux PY, Alatri A, et al. EANM guideline for ventilation/perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) for diagnosis of pulmonary embolism and beyond. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:2429–51.
Koike H, Sueyoshi E, Sakamoto I, Uetani M, Nakata T, Maemura K. Comparative clinical and predictive value of lung perfusion blood volume CT, lung perfusion SPECT and catheter pulmonary angiography images in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension before and after balloon pulmonary angioplasty. Eur Radiol. 2018;28:5091–9.
Maruoka Y, Nagao M, Baba S, Isoda T, Kitamura Y, Yamazaki Y, et al. Three-dimensional fractal analysis of 99mTc-MAA SPECT images in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension for evaluation of response to balloon pulmonary angioplasty: association with pulmonary arterial pressure. Nucl Med Commun. 2017;38:480–6.
Derlin T, Kelting C, Hueper K, Weiberg D, Meyer K, Olsson KM, et al. Quantitation of perfused lung volume using hybrid SPECT/CT allows Refining the Assessment of Lung Perfusion and estimating Disease Extent in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Clin Nucl Med. 2018;43:e170–7.
Hashimoto H, Oka T, Nakanishi R, Mizumura S, Dobashi S, Hashimoto Y, et al. Evaluation of balloon pulmonary angioplasty using lung perfusion SPECT in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. J Nucl Cardiol. 2022;29:3392–400.
Ha S, Han S. The role of Lung Ventilation/Perfusion scan in the management of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Nucl Med Mol Imaging; 2023.
Oh DK, Song JM, Park DW, Oh SY, Ryu JS, Lee J, et al. The effect of a multidisciplinary team on the implementation rates of major diagnostic and therapeutic procedures of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Heart Lung. 2019;48:28–33.
Kang BJ, Lee SD, Oh YM, Lee JS. Improved survival of Korean patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension after the introduction of targeted therapies. Heart Lung. 2014;43:561–8.
Leblanc M, Leveillee F, Turcotte E. Prospective evaluation of the negative predictive value of V/Q SPECT using 99mTc-Technegas. Nucl Med Commun. 2007;28:667–72.
Elf JE, Jogi J, Bajc M. Home treatment of patients with small to medium sized acute pulmonary embolism. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2015;39:166–72.
Parker JA, Coleman RE, Grady E, Royal HD, Siegel BA, Stabin MG, et al. SNM practice guideline for lung scintigraphy 4.0. J Nucl Med Technol. 2012;40:57–65.
Skoro-Sajer N, Becherer A, Klepetko W, Kneussl MP, Maurer G, Lang IM. Longitudinal analysis of perfusion lung scintigrams of patients with unoperated chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Thromb Haemost. 2004;92:201–7.
Dickson JC, Armstrong IS, Gabina PM, Denis-Bacelar AM, Krizsan AK, Gear JM, et al. EANM practice guideline for quantitative SPECT-CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023;50:980–95.
Le Pennec R, Tromeur C, Orione C, Robin P, Le Mao R, Gut-Gobert C, et al. Quantification of the pulmonary vascular obstruction index on ventilation/perfusion lung scintigraphy: comparison of a segmental visual scoring to the Meyer score. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:970808.
Lang IM, Pesavento R, Bonderman D, Yuan JX. Risk factors and basic mechanisms of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a current understanding. Eur Respir J. 2013;41:462–8.
Dorfmuller P, Gunther S, Ghigna MR, Thomas de Montpreville V, Boulate D, Paul JF, et al. Microvascular disease in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a role for pulmonary veins and systemic vasculature. Eur Respir J. 2014;44:1275–88.
Lewczuk J, Piszko P, Jagas J, Porada A, Wojciak S, Sobkowicz B, et al. Prognostic factors in medically treated patients with chronic pulmonary embolism. Chest. 2001;119:818–23.
Ghofrani HA, Galiè N, Grimminger F, Grünig E, Humbert M, Jing ZC, et al. Riociguat for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:330–40.
Suh M. The COVID-19 era, is it OK to perform a perfusion-only SPECT/CT for the diagnosis of Pulmonary Embolism? Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022;56:67–70.
Wang L, Wang M, Yang T, Wu D, Xiong C, Fang W. A prospective, comparative study of Ventilation-Perfusion Planar Imaging and Ventilation-Perfusion SPECT for Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. J Nucl Med. 2020;61:1832–8.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
There is no source of funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Statement
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the respective Institutional Research Committee and with the 2013 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The local institutional review board approved this retrospective study (IRB No. 2022-1324).
Informed Consent
The requirement for obtaining informed consent was waived (IRB No. 2022-1324).
Consent for Publication
The Institutional Review Board at our institute approved this retrospective study, and the requirement to obtain informed consent was waived.
Conflict of Interest
Shin Ae Han, Sangwon Han, Jinho Lee, Do-Yoon Kang, Jae Seung Lee, Dae-Hee Kim, Duk-Woo Park, Jong-Min Song, Jin-Sook Ryu, Dae-Hyuk Moon declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, S.A., Han, S., Lee, J. et al. Semi-Quantitative Analysis of Lung Perfusion SPECT/CT for Evaluation of Response to Balloon Pulmonary Angioplasty in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Nucl Med Mol Imaging (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-024-00858-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-024-00858-1