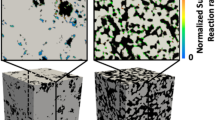
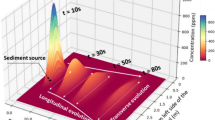
Abstract
Solute transport processes in heterogeneous porous media have been traditionally studied through the parameterization of macroscale properties using upscaling approaches over a representative elementary volume. As a result, our ability to accurately model solute transport at fine-scale is limited. Combining multiple transport and geometrical observations from the pore scale in a multiphysics framework can enhance the understanding of transport mechanisms that manifest at larger scales. In this paper, we predict conservative solute transport in three sandstone geometries (Castlegate, Bentheimer, and sandpack) that range across different degrees of heterogeneity using a machine learning approach. Our approach, which is based on the random forests (RF) algorithm, performs simulated transport predictions such as solute breakthrough curves. The RF algorithm used in our workflow is a tree-based ensemble method, which builds several different decision tree models independently and then computes a final prediction by combining the outputs of the individual trees. We employ observations, such as solute arrival time and distance traveled, as input to train the predictive model using random walk particle tracking (RWPT) simulations in the sandstones. We employ Bayesian optimization techniques to select the hyperparameter values controlling the structure of the RF model in order to avoid overfitting. Results of our workflow show accurate RF predictions of the RWPT breakthrough curves demonstrating the ability of the RF algorithm to capture the critical flow and transport properties of porous media. We also examine the sensitivity to geometrical sample effects in the training data, which can impact machine learning predictions. The RF algorithm used is able to provide accurate results in real rock samples spanning from unconsolidated granular to consolidated media, highlighting the ability of the model to generalize solute transport problems in porous media.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All datasets and codes generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmad, I., Ilyas, H., Urooj, A., et al.: Novel applications of intelligent computing paradigms for the analysis of nonlinear reactive transport model of the fluid in soft tissues and microvessels. Neural Comput. Appl. 31(12), 9041–9059 (2019)
Ahmmed, B., Mudunuru, M.K., Karra, S., et al.: A comparative study of machine learning models for predicting the state of reactive mixing. J. Comput. Phys. 432(110), 147 (2021)
Al-Farisi, O., Zhang, H., Raza, A., et al.: Machine learning for 3D image recognition to determine porosity and lithology of heterogeneous carbonate rock. In: SPE Reservoir Characterisation and Simulation Conference and Exhibition, OnePetro (2019)
Al-Salamah, I.S., Ghazaw, Y.M., Ghumman, A.R.: Groundwater modeling of Saq Aquifer Buraydah Al Qassim for better water management strategies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 173(1), 851–860 (2011)
Alizadeh, R., Allen, J.K., Mistree, F.: Managing computational complexity using surrogate models: a critical review. Res. Eng. Des. 31(3), 275–298 (2020)
Aquino, T., Aubeneau, A., Bolster, D.: Peak and tail scaling of breakthrough curves in hydrologic tracer tests. Adv. Water Resour. 78, 1–8 (2015)
Ben-Noah, I., Hidalgo, J.J., Jimenez-Martinez, J., et al.: Solute trapping and the mechanisms of non-Fickian transport in partially saturated porous media. Water Resources Res. 59(2):e2022WR033,613 (2023)
Bolster, D., Roche, K.R., Morales, V.L.: Recent advances in anomalous transport models for predicting contaminants in natural groundwater systems. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 26, 72–80 (2019)
Breiman, L.: Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 24, 123–140 (1996)
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45(1), 5–32 (2001)
Breiman, L., Cutler, A.: Random forest-manual (2004). http://www.statberkeleyedu/breiman/RandomForests/cc_manual.htm
Breiman, L., Friedman, J.H., Olshen, R.A., et al.: Classification and Regression Trees. Brooks. Wadsworth and Brooks, Monterey (1984)
Breiman, L., Friedman, J.H., Olshen, R.A., et al.: Classification and Regression Trees. Routledge, London (2017)
Brusseau, M.L., Anderson, R.H., Guo, B.: PFAS concentrations in soils: background levels versus contaminated sites. Sci. Total Environ. 740(140), 017 (2020)
Comolli, A., Hakoun, V., Dentz, M.: Mechanisms, upscaling, and prediction of anomalous dispersion in heterogeneous porous media. Water Resour. Res. 55(10), 8197–8222 (2019)
Cortis, A., Berkowitz, B.: Anomalous transport in “classical’’ soil and sand columns. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 68(5), 1539–1548 (2004)
De Lucia, M., Kempka, T., Jatnieks, J., et al.: Integrating surrogate models into subsurface simulation framework allows computation of complex reactive transport scenarios. Energy Procedia 125, 580–587 (2017)
Di Palma, P.R., Guyennon, N., Parmigiani, A., et al.: Impact of synthetic porous medium geometric properties on solute transport using direct 3d pore-scale simulations. Geofluids 2019 (2019)
DiGiovanni, A.A., Fredrich, J.T., Holcomb, D.J., et al. Micromechanics of compaction in an analogue reservoir sandstone. In: 4th North American Rock Mechanics Symposium, OnePetro (2000)
Edmunds, W., Smedley, P.: Residence time indicators in groundwater: the east midlands triassic sandstone aquifer. Appl. Geochem. 15(6), 737–752 (2000)
Engdahl, N.B., Aquino, T.: Upscaled models for time-varying solute transport: transient spatial-Markov dynamics. Adv. Water Resour. 166(104), 271 (2022)
Gouze, P., Puyguiraud, A., Roubinet, D., et al.: Pore-scale transport in rocks of different complexity modeled by random walk methods. Transp. Porous Med. 146(1–2), 139–158 (2023)
Guo, B., Zeng, J., Brusseau, M.L.: A mathematical model for the release, transport, and retention of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the vadose zone. Water Resour. Res. 56(2), e2019WR026667 (2020a)
Guo, Z., Henri, C.V., Fogg, G.E., et al.: Adaptive multirate mass transfer (aMMT) model: a new approach to upscale regional-scale transport under transient flow conditions. Water Resour. Res. 56(2), e2019WR026000 (2020b)
Haggerty, R., McKenna, S.A., Meigs, L.C.: On the late-time behavior of tracer test breakthrough curves. Water Resour. Res. 36(12), 3467–3479 (2000)
He, Q., Tartakovsky, A.M.: Physics-informed neural network method for forward and backward advection-dispersion equations. Water Resour. Res. 57(7), e2020WR029479 (2021)
He, Q., Barajas-Solano, D., Tartakovsky, G., et al.: Physics-informed neural networks for multiphysics data assimilation with application to subsurface transport. Adv. Water Resour. 141(103), 610 (2020)
Hidalgo, J.J., Neuweiler, I., Dentz, M.: Transport under advective trapping. J. Fluid Mech. 907, A36 (2021)
Hong, S., Lynn, H.S.: Accuracy of random-forest-based imputation of missing data in the presence of non-normality, non-linearity, and interaction. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 20(1), 1–12 (2020)
Icardi, M., Boccardo, G., Marchisio, D.L., et al.: Pore-scale simulation of fluid flow and solute dispersion in three-dimensional porous media. Phys. Rev. E 90(1), 013032 (2014)
Kamrava, S., Tahmasebi, P., Sahimi, M.: Linking morphology of porous media to their macroscopic permeability by deep learning. Transp. Porous Med. 131(2), 427–448 (2020)
Kamrava, S., Im, J., de Barros, F.P.J., et al.: Estimating dispersion coefficient in flow through heterogeneous porous media by a deep convolutional neural network. Geophys. Res. Lett. 48(18), e2021GL094443 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1029/2021GL094443
Kim, J.S., Kang, P.K.: Anomalous transport through free-flow-porous media interface: pore-scale simulation and predictive modeling. Adv. Water Resour. 135(103), 467 (2020)
Kowalek, P., Loch-Olszewska, H., Szwabiński, J.: Classification of diffusion modes in single-particle tracking data: feature-based versus deep-learning approach. Phys. Rev. E 100(3), 032410 (2019)
Kurotori, T., Zahasky, C., Benson, S.M., et al.: Description of chemical transport in laboratory rock cores using the continuous random walk formalism. Water Resour. Res. 56(9), e2020WR027511 (2020)
Lange, H., Sippel, S.: Machine learning applications in hydrology. In: Forest-Water Interactions, pp. 233–257. Springer, Cham (2020)
Leal, A.M., Kyas, S., Kulik, D.A., et al.: Accelerating reactive transport modeling: on-demand machine learning algorithm for chemical equilibrium calculations. Transp. Porous Med. 133(2), 161–204 (2020)
Lee, J.W., Lee, J.B., Park, M., et al.: An extensive comparison of recent classification tools applied to microarray data. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 48(4), 869–885 (2005)
Li, Y., Lu, P., Zhang, G.: An artificial-neural-network-based surrogate modeling workflow for reactive transport modeling. Pet. Res. 7(1), 13–20 (2021)
Mostaghimi, P., Bijeljic, B., Blunt, M.J.: Simulation of flow and dispersion on pore-space images. SPE J. 17(04), 1131–1141 (2012)
Muñoz-Gil, G., Garcia-March, M.A., Manzo, C., et al.: Single trajectory characterization via machine learning. New J. Phys. 22(1), 013010 (2020)
Naghibi, S.A., Ahmadi, K., Daneshi, A.: Application of support vector machine, random forest, and genetic algorithm optimized random forest models in groundwater potential mapping. Water Resour. Manag. 31(9), 2761–2775 (2017)
Peksa, A.E., Wolf, K.H.A., Zitha, P.L.: Bentheimer sandstone revisited for experimental purposes. Mar. Pet. Geol. 67, 701–719 (2015)
Perez, L.J., Hidalgo, J.J., Dentz, M.: Upscaling of mixing-limited bimolecular chemical reactions in Poiseuille flow. Water Resour. Res. 55(1), 249–269 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1029/2018WR022730
Perez, L.J., Parashar, R., Plymale, A., et al.: Contributions of biofilm-induced flow heterogeneities to solute retention and anomalous transport features in porous media. Water Res. 209, 117896 (2021a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117896
Perez, L.J., Puyguiraud, A., Hidalgo, J.J., et al.: Upscaling mixing-controlled reactions in unsaturated porous media. Transp. Porous Med. 146, 177–196 (2021b)
Poffenbarger, H., Castellano, M., Egli, D., et al.: Contributions of plant breeding to soil carbon storage: retrospect and prospects. Crop Sci. 63, 990–1018 (2023)
Pollock, D.W.: Semianalytical computation of path lines for finite-difference models. Ground Water 26(6), 743–750 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1988.tb00425.x
Popova, O.H., Small, M.J., McCoy, S.T., et al.: Comparative analysis of carbon dioxide storage resource assessment methodologies. Environ. Geosci. 19(3), 105–124 (2012)
Puyguiraud, A., Gouze, P., Dentz, M.: Stochastic dynamics of Lagrangian pore-scale velocities in three-dimensional porous media. Water Resour. Res. 55(2), 1196–1217 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1029/2018WR023702
Puyguiraud, A., Perez, L.J., Hidalgo, J.J., et al.: Effective dispersion coefficients for the upscaling of pore-scale mixing and reaction. Adv. Water Resour. 146(103), 782 (2020)
Puyguiraud, A., Gouze, P., Dentz, M.: Pore-scale mixing and the evolution of hydrodynamic dispersion in porous media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 126(16), 164501 (2021)
Qiao, C., Xu, Y., Zhao, W., et al.: Fractional derivative modeling on solute non-Fickian transport in a single vertical fracture. Front. Phys. 8, 378 (2020)
Rodriguez-Galiano, V., Mendes, M.P., Garcia-Soldado, M.J., et al.: Predictive modeling of groundwater nitrate pollution using random forest and multisource variables related to intrinsic and specific vulnerability: a case study in an agricultural setting (southern Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 476, 189–206 (2014)
Santos, J.E., Xu, D., Jo, H., et al.: Poreflow-net: a 3d convolutional neural network to predict fluid flow through porous media. Adv. Water Resour. 138(103), 539 (2020)
Schilders, W.H., Van der Vorst, H.A., Rommes, J.: Model Order Reduction: Theory, Research Aspects and Applications, vol. 13. Springer, Cham (2008)
Sharma, P.K., Agarwal, P., Mehdinejadiani, B.: Study on non-Fickian behavior for solute transport through porous media. ISH J. Hydraul. Eng. 28(sup1), 171–179 (2022)
Sherman, T., Engdahl, N.B., Porta, G., et al.: A review of spatial Markov models for predicting pre-asymptotic and anomalous transport in porous and fractured media. J. Contam. Hydrol. 236, 103734 (2020)
Shiri, J.: Improving the performance of the mass transfer-based reference evapotranspiration estimation approaches through a coupled wavelet-random forest methodology. J. Hydrol. 561, 737–750 (2018)
Singh, B., Sihag, P., Singh, K.: Modelling of impact of water quality on infiltration rate of soil by random forest regression. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 3(3), 999–1004 (2017)
Snoek J, Larochelle H, Adams RP (2012) Practical bayesian optimization of machine learning algorithms. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, vol. 25
Sun, L., Qiu, H., Wu, C., et al.: A review of applications of fractional advection-dispersion equations for anomalous solute transport in surface and subsurface water. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 7(4), e1448 (2020)
Swanson, R.D., Binley, A., Keating, K., et al.: Anomalous solute transport in saturated porous media: relating transport model parameters to electrical and nuclear magnetic resonance properties. Water Resour. Res. 51(2), 1264–1283 (2015)
Tang, M., Liu, Y., Durlofsky, L.J.: A deep-learning-based surrogate model for data assimilation in dynamic subsurface flow problems. J. Comput. Phys. 413(109), 456 (2020)
Vesper, D.J.: Contamination of cave waters by heavy metals. In: Encyclopedia of Caves, pp. 320–325. Elsevier, Netherlands (2019)
Wang, Z., Lai, C., Chen, X., et al.: Flood hazard risk assessment model based on random forest. J. Hydrol. 527, 1130–1141 (2015)
Weller, H.G., Tabor, G., Jasak, H., et al.: A tensorial approach to computational continuum mechanics using object-oriented techniques. Comput. Phys. 12(6), 620–631 (1998)
Wu, J., Chen, X.Y., Zhang, H., et al.: Hyperparameter optimization for machine learning models based on Bayesian optimization. J. Electron. Sci. Technol. 17(1), 26–40 (2019)
Yoon, S., Kang, P.K.: Mixing-induced bimolecular reactive transport in rough channel flows: pore-scale simulation and stochastic upscaling. Transp. Porous Med. 146, 329–350 (2021)
Zhang, Z., Cai, Z.: Permeability prediction of carbonate rocks based on digital image analysis and rock typing using random forest algorithm. Energy Fuels 35(14), 11271–11284 (2021)
Zhou, X., Zhu, X., Dong, Z., et al.: Estimation of biomass in wheat using random forest regression algorithm and remote sensing data. Crop J. 4(3), 212–219 (2016)
Funding
L.J.P. and R.P. acknowledges the support of the Desert Research Institute (DRI) through the Internal Project Assignment award (PG20133).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Perez, L.J., Bebis, G., McKenna, S.A. et al. Solute transport prediction in heterogeneous porous media using random walks and machine learning. Int J Geomath 14, 30 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13137-023-00240-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13137-023-00240-x
Keywords
- Machine learning
- Random forest algorithm
- Random walks model
- Solute transport
- Anomalous transport
- Heterogeneous porous media