Abstract
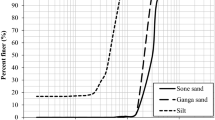
The wave-induced liquefaction of seabed is responsible for causing damage to marine structures. Particle composition and consolidation degree are the key factors affecting the pore water pressure response and liquefaction behavior of the seabed under wave action. The present study conducted wave flume experiments on silt and silty fine sand beds with varying particle compositions. Furthermore, a comprehensive analysis of the differences and underlying reasons for liquefaction behavior in two different types of soil was conducted from both macroscopic and microscopic perspectives. The experimental results indicate that the silt bed necessitates a lower wave load intensity to attain the liquefaction state in comparison to the silty fine sand bed. Additionally, the duration and development depth of liquefaction are greater in the silt bed. The dissimilarity in liquefaction behavior between the two types of soil can be attributed to the variation in their permeability and plastic deformation capacity. The permeability coefficient and compression modulus of silt are lower than those of silty fine sand. Consequently, silt is more prone to the accumulation of pore pressure and subsequent liquefaction under external loading. Prior research has demonstrated that silt beds with varying consolidation degrees exhibit distinct initial failure modes. Specifically, a dense bed undergoes shear failure, whereas a loose bed experiences initial liquefaction failure. This study utilized discrete element simulation to examine the microscopic mechanisms that underlie this phenomenon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biot M A. 1956. Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. I. low-frequency range. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 28(2): 168–178, doi: https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1908239
Cao Ruichen, Wang Shuya, Xu Guohui, et al. 2019. Characteristics of liquefied soil motion in wavy environment. Physics of Fluids, 31(7): 073102, doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5098507
Chen Changyun, Xu Guohui, Ren Yupeng, et al. 2019. Measurement of the viscosity coefficient of liquefied silty soil. Geo-Marine Letters, 39(2): 135–148, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-019-00563-5
de Groot M B, Kudella M, Meijers P, et al. 2006. Liquefaction phenomena underneath marine gravity structures subjected to wave loads. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 132(4): 325–335, doi: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(2006)132:4(325)
Duan Lunliang, Jeng D S, Wang Shaohua, et al. 2019. Numerical investigation of the wave/current-induced responses of transient soil around a square mono-pile foundation. Journal of Coastal Research, 35(3): 625–636, doi: https://doi.org/10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-18-00072.1
Duan Lunliang, Liao Chencong, Jeng D S, et al. 2017. 2D numerical study of wave and current-induced oscillatory non-cohesive soil liquefaction around a partially buried pipeline in a trench. Ocean Engineering, 135: 39–51, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2017.02.036
Foda M A, Tzang S Y. 1994. Resonant fluidization of silty soil by water waves. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 99(C10): 20463–20475, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/94JC02040
Gao Yufeng, Shen Yang, Zhang Jian, et al. 2011. Analysis of wave-induced liquefaction in seabed deposits of silt. China Ocean Engineering, 25(1): 31–44, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13344-011-0003-z
Gratchev I B, Sassa K, Osipov V I, et al. 2006. The liquefaction of clayey soils under cyclic loading. Engineering Geology, 86(1): 70–84, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2006.04.006
Guo Zhen, Jeng D S, Guo Wei. 2014. Simplified approximation of wave-induced liquefaction in a shallow porous seabed. International Journal of Geomechanics, 14(4): 06014008, doi: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000366
Jeng D S. 1997. Wave-induced seabed instability in front of a breakwater. Ocean Engineering, 24(10): 887–917, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0029-8018(96)00046-7
Jeng D S, Cha D H. 2003. Effects of dynamic soil behavior and wave non-linearity on the wave-induced pore pressure and effective stresses in porous seabed. Ocean Engineering, 30(16): 2065–2089, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0029-8018(03)00070-2
Jeng D S, Rahman M S. 2000. Effective stresses in a porous seabed of finite thickness: inertia effects. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 37(6): 1383–1392, doi: https://doi.org/10.1139/t00-063
Kirca V S O. 2013. Sinking of irregular shape blocks into marine seabed under wave-induced liquefaction. Coastal Engineering, 75: 40–51, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coastaleng.2013.01.006
Kirca V S O, Sumer B M. 2018. Sinking failure of drag embedment anchors due to wave-induced seabed liquefaction. International Journal of Ocean and Coastal Engineering, 1(4): 1850006, doi: https://doi.org/10.1142/S2529807018500069
Kirca V S O, Sumer B M, Fredsøe J. 2013. Residual liquefaction of seabed under standing waves. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 139(6): 489–501, doi: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WW.1943-5460.0000208
Kirca V S O, Sumer B M, Fredsøe J. 2014. Influence of clay content on wave-induced liquefaction. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 140(6): 04014024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WW.1943-5460.0000249
Liu Zhuangyi, Jeng D S, Chan A H C, et al. 2009. Wave - induced progressive liquefaction in a poro-elastoplastic seabed: a two - layered model. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 33(5): 591–610, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.734
Liu Bo, Jeng D S, Ye Guanlin, et al. 2015. Laboratory study for pore pressures in sandy deposit under wave loading. Ocean Engineering, 106: 207–219, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2015.06.029
Madsen O S. 1978. Wave-induced pore pressures and effective stresses in a porous bed. Géotechnique, 28(4): 377–393, doi: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1978.28.4.377
Miyamoto J, Sassa S, Sekiguchi H. 2004. Progressive solidification of a liquefied sand layer during continued wave loading. Géotechnique, 54(10): 617–629, doi: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2004.54.10.617
Miyamoto J, Sassa S, Tsurugasaki K, et al. 2020. Wave-induced liquefaction and floatation of a pipeline in a drum centrifuge. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 146(2): 04019039, doi: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WW.1943-5460.0000547
Okusa S. 1985. Wave-induced stresses in unsaturated submarine sediments. Géotechnique, 35(4): 517–532, doi: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1985.35.4.517
Peng Changsheng, Liu Hui, Zhang Qian, et al. 2015. Effects of particle size and solution properties on permeability of porous media. Periodical of Ocean University of China (in Chinese), 45(3): 107–115, doi: https://doi.org/10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20130409
Prior D B, Suhayda J N, Lu Nianzu, et al. 1989. Storm wave reactivation of a submarine landslide. Nature, 341(6237): 47–50, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/341047a0
Ren Yupeng, Xu Guohui, Xu Xingbei, et al. 2020a. The initial wave induced failure of silty seabed: liquefaction or shear failure. Ocean Engineering, 200: 106990, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.106990
Ren Yupeng, Xu Xingbei, Xu Guohui, et al. 2020b. Measurement and calculation of particle trajectory of liquefied soil under wave action. Applied Ocean Research, 101: 102202, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apor.2020.102202
Ren Yupeng, Zeng Yu, Xu Xingbei, et al. 2021. Sedimentary changes of a sand layer in liquefied silts. Journal of Ocean University of China, 20(5): 1046–1054, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4624-4
Sassa S, Sekiguchi H. 1999. Wave-induced liquefaction of beds of sand in a centrifuge. Géotechnique, 49(5): 621–638, doi: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1999.49.5.621
Sassa S, Sekiguchi H. 2001. Analysis of wave-induced liquefaction of sand beds. Géotechnique, 51(2): 115–126, doi: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2001.51.2.115
Sassa S, Sekiguchi H, Miyamoto J. 2001. Analysis of progressive liquefaction as a moving-boundary problem. Géotechnique, 51(10): 847–857, doi: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2001.51.10.847
Sassa S, Takayama T, Mizutani M, et al. 2006. Field observations of the build-up and dissipation of residual pore pressures in seabed sands under the passage of storm waves. Journal of Coastal Research, 39: 410–414
Sumer B M, Dixen F H, Fredsøe J. 2011. Stability of submerged rock berms exposed to motion of liquefied soil in waves. Ocean Engineering, 38(7): 849–859, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2010.09.009
Sumer B M, Fredsøe J, Christensen S, et al. 1999. Sinking/floatation of pipelines and other objects in liquefied soil under waves. Coastal Engineering, 38(2): 53–90, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3839(99)00024-1
Sumer B M, Hatipoglu F, Fredsøe J, et al. 2006a. Critical flotation density of pipelines in soils liquefied by waves and density of liquefied soils. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 132(4): 252–265, doi: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(2006)132:4(252)
Sumer B M, Hatipoglu F, Fredsøe J, et al. 2006b. The sequence of sediment behaviour during wave-induced liquefaction. Sedimentology, 53(3): 611–629, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3091.2006.00763.x
Sumer B M, Truelsen C, Fredsøe J. 2006c. Liquefaction around pipelines under waves. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 132(4): 266–275, doi: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(2006)132:4(266)
Tsai C P. 1995. Wave-induced liquefaction potential in a porous seabed in front of a breakwater. Ocean Engineering, 22(1): 1–18, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-8018(94)00042-5
Tzang S Y, Ou S H. 2006. Laboratory flume studies on monochromatic wave-fine sandy bed interactions: Part 1. Soil fluidization. Coastal Engineering, 53(11): 965–982, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coastaleng.2006.06.003
Wang Yuchen, Oh E, Zhan Jiemin. 2016. Examining the behaviors of sandy and silty seabed under wave actions. Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 24(4): 682–689, doi: https://doi.org/10.6119/JMST-015-1231-1
Wu Sheng, Jeng D S. 2019. Effects of dynamic soil permeability on the wave-induced seabed response around a buried pipeline. Ocean Engineering, 186: 106132, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106132
Xu Guohui, Liu Zhiqin, Sun Yongfu, et al. 2016. Experimental characterization of storm liquefaction deposits sequences. Marine Geology, 382: 191–199, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2016.10.015
Xu Guohui, Sun Yongfu, Wang Xin, et al. 2009. Wave-induced shallow slides and their features on the subaqueous Huanghe River delta. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 46(12): 1406–1417, doi: https://doi.org/10.1139/T09-068
Xu Guohui, Sun Yongfu, Yu Yueqian, et al. 2012. Discussion on storm-induced liquefaction of the superficial stratum in the Huanghe River subaqueous delta. Marine Science Bulletin, 14(1): 80–89
Xu Xingbei, Xu Guohui, Ren Yupeng, et al. 2019. Horizontal normal force on buried rigid pipelines in fluctuant liquefied silty soil. Journal of Ocean University of China, 18(1): 1–8, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-019-3526-1
Xu Xingbei, Xu Guohui, Yang Junjie, et al. 2021. Field observation of the wave-induced pore pressure response in a silty soil seabed. Geo-Marine Letters, 41(1): 13, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-020-00680-6
Yamamoto T, Koning H L, Sellmeijer H, et al. 1978. On the response of a poro-elastic bed to water waves. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 87(1): 193–206, doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112078003006
Yang Guoxiang, Ye Jianhong. 2017. Wave & current-induced progressive liquefaction in loosely deposited seabed. Ocean Engineering, 142: 303–314, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2017.07.027
Yang Guoxiang, Ye Jianhong. 2018. Nonlinear standing wave-induced liquefaction in loosely deposited seabed. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 77(1): 205–223, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1038-z
Ye Jianhong. 2012. 3D liquefaction criteria for seabed considering the cohesion and friction of soil. Applied Ocean Research, 37: 111–119, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apor.2012.04.004
Ye Jianhong, He Kunpeng. 2021. Dynamics of a pipeline buried in loosely deposited seabed to nonlinear wave & current. Ocean Engineering, 232: 109127, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.109127
Ye Jianhong, Jeng D, Wang Ren, et al. 2013. Validation of a 2-D semicoupled numerical model for fluid-structure-seabed interaction. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 42: 333–357, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2013.04.008
Ye Guanlin, Leng Jian, Jeng D S. 2018. Numerical testing on wave-induced seabed liquefaction with a poro-elastoplastic model. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 105: 150–159, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2017.11.026
Ye Jianhong, Wang Gang. 2015. Seismic dynamics of offshore breakwater on liquefiable seabed foundation. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 76: 86–99, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2015.02.003
Zen K, Yamazaki H. 1990a. Mechanism of wave-induced liquefaction and densification in seabed. Soils and Foundations, 30(4): 90–104, doi: https://doi.org/10.3208/sandf1972.30.4_90
Zen K, Yamazaki H. 1990b. Oscillatory pore pressure and liquefaction in seabed induced by ocean waves. Soils and Foundations, 30(4): 147–161, doi: https://doi.org/10.3208/sandf1972.30.4_147
Zen K, Yamazaki H. 1991. Field observation and analysis of wave-induced liquefaction in seabed. Soils and Foundations, 31(4): 161–179, doi: https://doi.org/10.3208/sandf1972.31.4_161
Zhang Jun, Jiang Qin, Jeng D, et al. 2020. Experimental study on mechanism of wave-induced liquefaction of sand-clay seabed. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(2): 66, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8020066
Zhao Hongyi, Jeng D S, Liao Chencong. 2016. Parametric study of the wave-induced residual liquefaction around an embedded pipeline. Applied Ocean Research, 55: 163–180, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apor.2015.12.005
Zhao Hongyi, Jeng D S, Liao Chencong, et al. 2018. Numerical modelling of liquefaction in loose sand deposits subjected to ocean waves. Applied Ocean Research, 73: 27–41, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apor.2018.01.011
Zienkiewicz O C, Chang C T, Bettess P. 1980. Drained, undrained, consolidating and dynamic behaviour assumptions in soils. Géotechnique, 30(4): 385–395, doi: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1980.30.4.385
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Natural Science Foundation of China under contract No. 41976049; the Opening Foundation of Marine Ecological Restoration and Smart Ocean Engineering Research Center of Hebei Province under contract No. HBMESO2306.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Ren, Y., Xu, G. et al. Effect of particle composition and consolidation degree on the wave-induced liquefaction of soil beds. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 43, 11–22 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-023-2223-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-023-2223-5