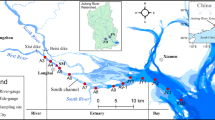
Abstract
The Zhujiang River Estuary is becoming eutrophic due to the impact of anthropogenic activities in the past decades. To understand nutrient dynamics and fluxes to the Lingdingyang water via four outlets (Humen, Jiaomen, Hongqimen and Hengmen), we investigated the spatial distribution and seasonal variation of dissolved nutrients in the Zhujiang River Estuary, based on fourteen cruises conducted from March 2015 to October 2017, covering both wet (April to September) and dry (October to March next year) seasons. Our results showed that riverine fluxes of dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) and dissolved silicate (DSi) into the Lingdingyang water through four outlets varied seasonally due to the influence of river discharge, with the highest in spring and the lowest in winter. However, riverine flux of phosphate exhibited little significant seasonal variability. Riverine nutrients into the Lingdingyang water most resulted through Humen Outlet. The estuarine export fluxes of DIN out of the Zhujiang River Estuary derived from a box model were higher than fluxes of riverine nutrients in May, likely due to the influence of local sewage, while lower than riverine flux in August. The export fluxes of phosphate were higher than the fluxes of riverine phosphate in May and August. In contrast, large amounts of DSi were buried in the estuary in May and August. Although excess DIN was delivered into the Zhujiang River Estuary, eutrophication effect was not as severe as expected in the Zhujiang River Estuary, since the light limitation restricted the utilization of nutrients by phytoplankton.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck A J, Rapaglia J P, Cochran J K, et al. 2008. Submarine groundwater discharge to Great South Bay, NY, estimated using Ra isotopes. Marine Chemistry, 109(3–4): 279–291, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2007.07.011
Billen G, Garnier J. 2007. River basin nutrient delivery to the coastal sea: assessing its potential to sustain new production of non-siliceous algae. Marine Chemistry, 106(1–2): 148–160, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2006.12.017
Cai Weijun, Dai Minhan, Wang Yongchen, et al. 2004. The biogeochemistry of inorganic carbon and nutrients in the Pearl River Estuary and the adjacent northern South China Sea. Continental Shelf Research, 24(12): 1301–1319, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2004.04.005
Cai Huayang, Huang Jingzheng, Niu Lixia, et al. 2018. Decadal variability of tidal dynamics in the Pearl River Delta: spatial patterns, causes, and implications for estuarine water management. Hydrological Process, 32(25): 3805–3819, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13291
Cloern J E. 1987. Turbidity as a control on phytoplankton biomass and productivity in estuaries. Continental Shelf Research, 7(11–12): 1367–1381, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-4343(87)90042-2
Cloern J E. 2001. Our evolving conceptual model of the coastal eutrophication problem. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 210: 223–253, doi: https://doi.org/10.3354/meps210223
Dai Minhan, Gan Jianping, Han Aiqin, et al. 2014. Physical dynamics and biogeochemistry of the Pearl River plume. In: Bianchi T, Allison M, Cai Weijun, eds. Biogeochemical Dynamics at Major River-Coastal Interfaces: Linkages with Global Change. New York: Cambridge University Press, 321–352
Dai Minhan, Guo Xianghui, Zhai Weidong, et al. 2006. Oxygen depletion in the upper reach of the Pearl River Estuary during a winter drought. Marine Chemistry, 102(1–2): 159–169, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2005.09.020
David V, Sautour B, Chardy P, et al. 2005. Long-term changes of the zooplankton variability in a turbid environment: the Gironde estuary (France). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 64(2–3): 171–184, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2005.01.014
Fisher T R, Harding Jr L W, Stanley D W, et al. 1988. Phytoplankton, nutrients, and turbidity in the Chesapeake, Delaware, and Hudson estuaries. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 27(1): 61–93
Gan Jianping, Lu Zhongming, Cheung Anson, et al. 2014. Assessing ecosystem response to phosphorus and nitrogen limitation in the Pearl River plume using the Regional Ocean Modeling System (ROMS). Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(12): 8858–8877, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JC009951
Glibert P M, Wilkerson F P, Dugdale R C, et al. 2016. Pluses and minuses of ammonium and nitrate uptake and assimilation by phytoplankton and implications for productivity and community composition, with emphasis on nitrogen-enriched conditions. Limnology and Oceanography, 61(1): 165–197, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10203
Gong Wenping, Lin Zhongyuan, Chen Yunzhen, et al. 2018. Effect of winds and waves on salt intrusion in the Pearl River Estuary. Ocean Science, 14(1): 139–159, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/os-14-139-2018
Gordon Jr D C, Boudreau P R, Mann K H, et al. 1996. LOICZ biogeochemical modelling guidelines. LOICZ/R&S/95–5. Texel, Netherlands: LOICZ-IGBP
Guo Xianghui, Dai Minhan, Zhai Weidong, et al. 2009. CO2 flux and seasonal variability in a large subtropical estuarine system, the Pearl River Estuary, China. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 114(G3): G03013, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JG000905
Guo Zhanrong, Huang Lei, Liu Huatai, et al. 2008. The estimation of submarine inputs of groundwater to a coastal bay using Radium isotopes (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 29(5): 647–652
Hansen H P, Koroleff F. 1999. Determination of nutrients. In: Grasshoff K, Kremling K, Ehrhardt M, eds. Methods of Seawater Analysis. Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH, 159–228
Harrison P J, Yin Kedong, Lee J H W, et al. 2008. Physical-biological coupling in the Pearl River Estuary. Continental Shelf Research, 28(12): 1405–1415, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2007.02.011
He Biyan, Dai Minhan, Zhai Weidong, et al. 2014. Hypoxia in the upper reaches of the Pearl River Estuary and its maintenance mechanisms: a synthesis based on multiple year observations during 2000–2008. Marine Chemistry, 167: 13–24, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2014.07.003
Hu Jiatang, Li Shiyu. 2009. Modeling the mass fluxes and transformations of nutrients in the Pearl River Delta, China. Journal of Marine Systems, 78(1): 146–167, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2009.05.001
Hu Jiatang, Li Shiyu, Geng Bingxu, et al. 2012. Modeling of CBOD, TN and TP fluxes in the river network and estuary of Pearl River Delta. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 43(1): 51–59
Huang Xiaoping, Huang Liangmin, Yue Weizhong. 2003. The characteristics of nutrients and eutrophication in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 47(1–6): 30–36, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00474-5
Jickells T D. 1998. Nutrient biogeochemistry of the coastal zone. Science, 281(5374): 217–222, doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.281.5374.217
Kot S C, Hu S L. 1995. Water flows and sediment transport in the Pearl River Estuary and wave in South China Sea near Hong Kong. In: Coastal Infrastructure Development in Hong Kong—A Review. Hong Kong, China: Hong Kong Government
Li Dou, Gan Jianping, Hui Rex, et al. 2020. Vortex and biogeochemical dynamics for the hypoxia formation within the coastal transition zone off the Pearl River Estuary. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 125(8): e2020JC016178, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JC016178
Li Ruihuan, Xu Jie, Li Xiangfu, et al. 2017. Spatiotemporal variability in phosphorus species in the Pearl River Estuary: influence of the river discharge. Scientific Reports, 7: 13649, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13924-w
Liang Cui, Xian Weiwei. 2018. Changjiang nutrient distribution and transportation and their impacts on the estuary. Continental Shelf Research, 165: 127–145, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2018.05.001
Liu Jingqin. 2006. Investigation of distribution and influx calculation of nutrients in the Eight Pearl River Openings (in Chinese)[dissertation]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China
Liu Bo, de Swart H E, de Jonge V N. 2018. Phytoplankton bloom dynamics in turbid, well-mixed estuaries: a model study. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 211: 137–151, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2018.01.010
Liu Sumei, Hong G H, Zhang Jing, et al. 2009. Nutrient budgets for large Chinese estuaries. Biogeosciences, 6(10): 2245–2263, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-6-2245-2009
Lu Zhongming, Gan Jianping. 2015. Controls of seasonal variability of phytoplankton blooms in the Pearl River Estuary. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 117: 86–96, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2013.12.011
Lu Zhongming, Gan Jianping, Dai Minhan, et al. 2018. Joint effects of extrinsic biophysical fluxes and intrinsic hydrodynamics on the formation of hypoxia west off the Pearl River Estuary. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 123(9): 6241–6259, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JC014199
Lu Fenghui, Ni Honggang, Liu Feng, et al. 2009. Occurrence of nutrients in riverine runoff of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Journal of Hydrology, 376(1–2): 107–115, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.07.018
Malakoff D. 1998. Death by suffocation in the Gulf of Mexico. Science, 281(5374): 190–192, doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.281.5374.190
McCarthy J J. 1981. The kinetics of nutrient utilization. In: Platt T, ed. Physiological Bases of Phytoplankton Ecology. Canadian Bulletin of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 210: 211–233
Moore W S. 1996. Large groundwater inputs to coastal waters revealed by 226Ra enrichments. Nature, 380(6575): 612–614, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/380612a0
Nixon S W. 1995. Coastal marine eutrophication: a definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia, 41(1): 199–219, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00785236.1995.10422044
Oudot C, Gerard R, Morin P, et al. 1988. Precise shipboard determination of dissolved oxygen (Winkler procedure) for productivity studies with a commercial system. Limnology and Oceanography, 33(1): 146–150, doi: https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1988.33.1.0146
Parsons T R, Maita Y, Lalli C M. 1984. A Manual of Chemical and Biological Methods for Seawater Analysis. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 173
Qian Wei, Gan Jianping, Liu Jinwen, et al. 2018. Current status of emerging hypoxia in a eutrophic estuary: the lower reach of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 205: 58–67, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2018.03.004
Qu Hongjuan, Kroeze C. 2010. Past and future trends in nutrients export by rivers to the coastal waters of China. Science of the Total Environment, 408(9): 2075–2086, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.12.015
Rabalais N N, Turner R E, Sen Gupta B K, et al. 2007. Hypoxia in the northern Gulf of Mexico: does the science support the plan to reduce, mitigate, and control hypoxia?. Estuaries and Coasts, 30(5): 753–772, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02841332
Savchuk O P. 2005. Resolving the Baltic Sea into seven subbasins: N and P budgets for 1991–1999. Journal of Marine Systems, 56(1–2): 1–15, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2004.08.005
Shen Pingping, Li Gang, Huang Liangmin, et al. 2011. Spatio-temporal variability of phytoplankton assemblages in the Pearl River Estuary, with special reference to the influence of turbidity and temperature. Continental Shelf Research, 31(16): 1672–1681, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2011.07.002
Strokal M, Kroeze C, Li Lili, et al. 2015. Increasing dissolved nitrogen and phosphorus export by the Pearl River (Zhujiang): a modeling approach at the sub-basin scale to assess effective nutrient management. Biogeochemistry, 125(2): 221–242, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-015-0124-1
Tang Danling, Kester D R, Ni I H, et al. 2003. In situ and satellite observations of a harmful algal bloom and water condition at the Pearl River Estuary in late autumn 1998. Harmful Algae, 2(2): 89–99, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1568-9883(03)00021-0
Turner R E, Rabalais N N. 1991. Changes in Mississippi River water quality this century: implications for coastal food webs. BioScience, 41(3): 140–147, doi: https://doi.org/10.2307/1311453
Turner R E, Rabalais N N. 1994. Coastal eutrophication near the Mississippi River Delta. Nature, 368(6472): 619–621, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/368619a0
Wai O W H, Wang C H, Li Y S, et al. 2004. The formation mechanisms of turbidity maximum in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 48(5–6): 441–448, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2003.08.019
Wang Jianing, Yan Weijin, Jia Xiaodong. 2006. Modeling the export of point sources of nutrients from the Yangtze River basin and discussing countermeasures. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 26(4): 658–666
Wei Xing, Wu Chaoyu. 2014. Long-term process-based morphodynamic modeling of the Pearl River Delta. Ocean Dynamics, 64(12): 1753–1765, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-014-0785-7
Xu Jie, Ho A Y T, He Lei, et al. 2012. Effects of inorganic and organic nitrogen and phosphorus on the growth and toxicity of two Alexandrium species from Hong Kong. Harmful Algae, 16: 89–97, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2012.02.006
Xu Jie, Ho A Y T, Yin Kedong, et al. 2008a. Temporal and spatial variations in nutrient stoichiometry and regulation of phytoplankton biomass in Hong Kong waters: influence of the Pearl River outflow and sewage inputs. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 57(6–12): 335–348, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2008.01.020
Xu Jie, Yin Kedong, He Lei, et al. 2008b. Phosphorus limitation in the northern South China Sea during late summer: influence of the Pearl River. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 55(10): 1330–1342, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2008.05.007
Yin Kedong, Harrison P J. 2008. Nitrogen over enrichment in subtropical Pearl River estuarine coastal waters: possible causes and consequences. Continental Shelf Research, 28(12): 1435–1442, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2007.07.010
Yin Kedong, Harrison P J, Goldblatt R H, et al. 1996. Spring bloom in the central Strait of Georgia: interactions of river discharge, winds and grazing. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 138: 255–263, doi: https://doi.org/10.3354/meps138255
Yin Kedong, Qian Peiyuan, Chen Jay C, et al. 2000. Dynamics of nutrients and phytoplankton biomass in the Pearl River Estuary and adjacent waters of Hong Kong during summer: preliminary evidence for phosphorus and silicon limitation. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 194: 295–305, doi: https://doi.org/10.3354/meps194295
Zhang Jing, Huang Weiwen, Létolle R, et al. 1995. Major element chemistry of the Huanghe (Yellow River), China-weathering processes and chemical fluxes. Journal of Hydrology, 168(1–4): 173–203, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(94)02635-O
Zhang Ling, Wang Lu, Yin Kedong, et al. 2014. Spatial and seasonal variations of nutrients in sediment profiles and their sediment-water fluxes in the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. Journal of Earth Science, 25(1): 197–206, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-014-0413-y
Zhao Yangyang, Liu Jing, Uthaipan K, et al. 2020. Dynamics of inorganic carbon and pH in a large subtropical continental shelf system: interaction between eutrophication, hypoxia, and ocean acidification. Limnology and Oceanography, 65(6): 1359–1379, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.11393
Acknowledgements
We thank colleagues for their help with sampling.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The Special Project for Marine Economic Development (Six Major Marine Industries) of Guangdong Province under contract No. GDNRC[2020]064; the Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou) under contract Nos GML2019ZD0303, GML2019ZD0305 and GML2019ZD0402; the Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences under contract Nos ISEE2019ZR02 and ISEE2019ZR03; the National Natural Science Foundation of China under contract Nos 41676075 and 41706085; the Department of Science and Technology of Guangdong Province under contract No. 2018B030320005.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Yang, Y., He, W. et al. Fluxes of riverine nutrient to the Zhujiang River Estuary and its potential eutrophication effect. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 41, 88–98 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-021-1919-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-021-1919-7