Abstract
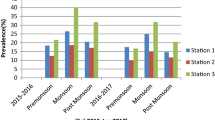
Investigation of four edible fishes (Etroplus suratensis, Oreochromis mossambicus, Lates calcarifer, Chanos chanos) collected from a fish landing center along Cochin Backwaters has done for caligid infestation. Of these, caligids were detected only from Etroplus suratensis and was identified to be Caligus rotundigenitalis. Parasites were attached to the inner side of operculum of host which indicates strong site preference. The annual observation of prevalence, mean intensity and abundance were found to be 19.21%, 1.051 and 0.202 respectively. Variation of prevalence with respect to the different length groups of E. suratensis has discussed in this paper. Damages of the inner side of operculum and increase in mucous production were noticed as a result of copepod attachment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arriagada G, Hamilton-West C, Nekouei O, et al. 2019. Caligus rogercresseyi infestation is associated with Piscirickettsia salmonis-attributed mortalities in farmed salmonids in Chile. Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 171: 10477
Balkhande J V. 2019. Cage culture of Oreochromis mossambicus (Tilapia) in back water of river Godavari, Nanded, Maharashtra India. Ecology & Environmental Sciences, 4(3): 100–105, doi: https://doi.org/10.15406/mojes.2019.04.00140
Bush A O, Lafferty K D, Lotz J M, et al. 1997. Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. Revisited. Journal of Parasitology, 83(4): 575–583, doi: https://doi.org/10.2307/3284227
Costello M J. 2009. The global economic cost of sea lice to the salmonid farming industry. Journal of Fish Diseases, 32(1): 115–118, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.2008.01011.x
Cruz-Lacierda E R, Erazo-Pagador G, Yamamoto A, et al. 2011. Parasitic caligid copepods of farmed marine fishes in the Philippines. In: Bondad-Reantaso M G, Jones J B, Corsin F, et al, eds. Diseases in Asian Aquaculture VII. Selangor, Malaysia: Fish Health Section, Asian Fisheries Society, 385
Del Mundo R C, Albaladejo J D, De Vera A. 1996. A parasite infestation of cage reared tilapia. Aquatic Animal Health Research Institute. Newsletter, 5: 3–4
Dinesh Kumar P K, Srinivas K, Muraleedharan K R, et al. 2009. Observed mixed standing-wave signatures in Cochin estuary on the southwest coast of India. Journal of Coastal Research, 25(5): 1106–1113
Fast M D, Ross N W, Mustafa A, et al. 2002. Susceptibility of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss, Atlantic salmon Salmo salar and Coho salmon Oncorhynchus kisutch to experimental infection with sea lice Lepeophtheirus salmonis. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 52(1): 57–68
Froese R, Pauly D. 2018. Fishbase. World Wide Web electronic publication. http://www.fishbase.org [2018-11-2]
González L, Carvajal J, George-Nascimento M. 2000. Differential infectivity of Caligus flexispina (Copepoda, Caligidae) in three farmed salmonids in Chile. Aquaculture, 183(1–2): 13–23, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00282-3
González M P, Marín S L, Vargas-Chacoff L. 2015. Effects of Caligus rogercresseyi (Boxshall and Bravo, 2000) infestation on physiological response of host Salmo salar (Linnaeus 1758): establishing physiological thresholds. Aquaculture, 438: 47–54, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.12.039
González M P, Vargas-Chacoff L, Marín S L. 2016. Stress response of Salmo salar (Linnaeus 1758) when heavily infested by Caligus rogercresseyi (Boxshall & Bravo 2000) copepodids. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 42(1): 263–274, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0134-x
Grobler N J, van As J G, Olivier P A S. 2004. New morphological information on the parasitic copepods Caligus epinepheli Yamaguti, 1936 and Caligus rotundigenitalis Yu, 1933 (Cope-poda, Caligidae) from South Africa. Crustaceana, 77(2): 187–196, doi: https://doi.org/10.1163/156854004774003547
Hamilton-West C, Arriagada G, Yatabe T, et al. 2012. Epidemiological description of the sea lice (Caligus rogercresseyi) situation in southern Chile in August 2007. Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 104(3–4): 341–345, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prevetmed.2011.12.002
Hayward C J, Aiken H M, Nowak B F. 2008. An epizootic of Caligus chiastos on farmed southern bluefin tuna Thunnus maccoyii off South Australia. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 79(1): 57–63, doi: https://doi.org/10.3354/dao01890
Ho J S. 2000. Major problem of cage aquaculture in Asia relating to sea lice. In: Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Cage Aquaculture in Asia. Bangkok: Asian Fisheries Society, 13–19
Ho J S. 2004. Invasiveness of sea lice (Copepoda, Caligidae) in marine aquaculture. Journal of the Fisheries Society of Taiwan, 31(2): 85–99
Ho J S, Kim I H, Cruz-Lucierda E R, et al. 2004. Sea lice (Copepoda, Caligidae) parasitic on marine cultured and wild fishes of the Philippines. Journal of the Fisheries Society of Taiwan, 31(4): 235–249
Ho J S, Lin Ching-Long, Chen Shiu-Nan. 2000. Species of Caligus Müller, 1785 (Copepoda: Caligidae) parasitic on marine fishes of Taiwan. Systematic Parasitology, 46(3): 159–179, doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006342120411
Jaikumar M, Suresh Kumar C, Robin R S, et al. 2013. Milkfish culture: alternative revenue for Mandapam Fisherfolk, Palk Bay, Southeast Coast of India. International Journal of Fisheries and Aquaculture Sciences, 3(1): 31–43
Jithendran K P, Natarajan M, Azad I S. 2008. Crustacean parasites and their management in brackish water finfish culture. Marine Finfish Aquaculture Network, 13: 47–50
Johnson S C, Treasurer J W, Bravo S, et al. 2004. A review of the impact of parasitic copepods on marine aquaculture. Zoological Studies, 43(2): 8–19
Khoa T N D, Mazelan S, Muda S, et al. 2019. Use of neem oil (Azadirachta indica) to control caligid copepod infestation on Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer). Aquaculture Research, 50(7): 1885–1892, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/are.14074
Kua B C, Muhd-Faizul H A H. 2010. Scanning electron microscopy of three species of Caligus (Copepoda: Caligidae) parasitized on cultured marine fish at Bukit Tambun, Penang. Malaysian Journal of Microscopy, 6(1): 9–13
Leaw Y Y, Faizah S, Anil C, et al. 2012. Prevalence, mean intensity and site preference of Caligus rotundigenitalis Yü, 1933 (Copepoda: Caligidae) on cage cultured crimson snapper (Lutjanus erythropterus Bloch, 1790) from Bukit Tambun, Penang, Malaysia. Veterinary Parasitology, 187(3–4): 505–510, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.02.003
Lin Ching-Long, Ho J S. 1993. Life history of Caligus epidemicus Hewitt parasitic on the Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambica) cultured in brackish water. In: Boxshall G A, Defaye D, eds. Pathogens of Wild and Farmed Fish: Sea Lice. London: Ellis Horwood
Lin Ching-Long, Ho J S. 2003. Two species of rare sea lice (Copepoda, Caligidae) on marine fishes of Taiwan. Journal of Fisheries Society of Taiwan, 30: 147–158
Maran B A V, Cruz-Lacierda E R, Ohtsuka S, et al. 2016. New records of caligidae (Copepoda, Siphonostomatoida) from the Philippines. Zootaxa, 4174(1): 237–248, doi: https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4174.1.16
Maran B A V, Seng L T, Ohtsuka S, et al. 2009. Records of Caligus (Crustacea: Copepoda: Caligidae) from marine fish cultured in floating cages in Malaysia with a redescription of the male of Caligus longipedis Bassett-Smith, 1898. Zoological Studies, 48(6): 797–807
Margolis L, Esch G W, Holmes J C, et al. 1982. The use of ecological terms in parasitology (report of an ad hoc committee of the American Society of Parasitologists). Journal of Parasitology, 68(1): 131–133, doi: https://doi.org/10.2307/3281335
Morales-Serna F N, Medina-Guerrero R M, Fajer-Avila E J. 2016. Sea lice (Copepoda: Caligidae) parasitic on fishes reported from the Neotropical region. Neotropical Biodiversity, 2(1): 141–150, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/23766808.2016.1236313
Morales-Serna F N, Pinacho-Pinacho C D, Gómez S, et al. 2014. Diversity of sea lice (Copepoda: Caligidae) parasitic on marine fishes with commercial and aquaculture importance in Chamela Bay, Pacific coast of Mexico by using morphology and DNA barcoding, with description of a new species of Caligus. Parasitology International, 63(1): 69–79, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2013.09.005
Muhd-Faizul H A H, Kua B C, Leaw Y Y. 2012. Caligidae infestation in Asian seabass, Lates calcarifer, Bloch 1790 cultured at different salinity in Malaysia. Veterinary Parasitology, 184(1): 68–72, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.08.008
Munilkumar S, Sundaray J K, Bhatacharya S B, et al. 2013. Biology and fisheries of some brackishwater food fishes of India. In: Goswami U C, ed. Advances in Fish Research. Delhi: Narendraâ Publishing House, 187–202
Nagasawa K. 2013. Caligus epidemicus (Copepoda: Caligidae), a pathogenic sea louse of wild and captive fish in Indo-West Pacific region: a review. Bulletin of the Hiroshima University Museum, 5: 71–86
Nikhila R M V, Drisya O K, Rijin K, et al. 2019. Copepod crustaceans parasitizing marine fish of the Kerala coast, India. Arthropoda Selecta, 28(4): 529–544
Noor El-Deen A E, Abdel Hady O K, Shalaby S I, et al. 2012. Field studies on Caligus Disease among cultured Mugil cephalus in brackish water fish farms. Life Science Journal, 9(3): 733–737
Okawachi H, Ohtsuka S, Ismail N B, et al. 2012. Seasonal occurrence and microhabitat of the hyperparasitic monogenean Udonella fugu on the caligid copepod Pseudocaligus fugu infecting the grass puffer Takifugu niphobles in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Ocean Science Journal, 47(3): 181–187, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-012-0018-2
Pandey P K, Sethi L N, Pholane L P, et al. 2014. Growth performance and economic analysis of Indian major carps and tilapia in rainwater ponds. Fishery Technology, 51(2): 71–77
Papapanagiotou E P, Trilles J P. 2001. Cymothoid parasite Ceratothoa parallela inflicts great losses on cultured gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata in Greece. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 45(3): 237–239
Papapanagiotou E P, Trilles J P, Photis G. 1999. First record of Emetha audouini, a cymothoid isopod parasite, from cultured sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax in Greece. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 38(3): 235–237
Pavoletti E, Fioravanti M L, Prearo M, et al. 1999. Osservazioni sulla Caligosi in spigole d’allevamento. Boll Soc Ital PatolIttica, 11: 2–9
Philipose K K, Sharma S R K, Loka J, et al. 2013. Culture of Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer, Bloch) in open sea floating net cages off Karwar, South India. Indian Journal of Fisheries, 60(1): 67–70
Pillai N K. 1985. The Fauna of India: Copepod Parasites of Marine Fishes. Calcutta: Zoological Society of India, 1–814
Pillai N K, Natarajan P. 1977. Copepods parasitic on fishes of the Kerala coast. Aquatic Biology, 2: 19–43
Rajkumar M, Perumal P, Trilles J P. 2005a. Cymothoa indica (Crustacea, Isopoda, Cymothoidae) parasitizes the cultured larvae of the Asian seabass Lates calcarifer under laboratory conditions. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 66(1): 87–90
Rajkumar M, Vasagam K P K, Perumal P, et al. 2005b. First record of Cymothoa indica (Crustacea, Isopoda, Cymothoidae) infecting the cultured catfish Mystus gulio in India. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 65(3): 269–272
Rangnekar M P. 1959. Parasitic copepods from fishes of the western coast of India with description of one new and redescription of four known species. Journal of the University of Bombay, 28: 43–58
Sanil N K, Vikas P A, Ratheesh T B, et al. 2009. Mortalities caused by the crustacean isopod, Cirolana fluviatilis, in tropical, cage-cultured Asian seabass, Lates calcarifer: a case study from the southwest coast of India. Aquaculture Research, 40(14): 1626–1633, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2009.02263.x
Solanki H G, Patil P K, Vanza J G, et al. 2016. Sea lice, Caligus rotundigenitalis infestations and its management in pond cultured pearlspot, Etroplus suratensis in Gujarat: a case study. Journal of Parasitic Diseases, 40(2): 565–567, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-014-0539-y
Tully O, Nolan D T. 2002. A review of the population biology and host-parasite interactions of the sea louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Copepoda: Caligidae). Parasitology, 124(7): 165–182, doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182002001889
Vijayaraghavan S, Kumari L K, Gopinathan V G, et al. 1981. Aquaculture of pearl spot (Etroplus suratensis) in an Estuarine Pond: environmental characteristics, primary production, growth and cost-benefit ratio. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 10: 82–89
Vinoth R, Ajith Kumar T T, Ravichandran S, et al. 2010. Infestation of copepod parasites in the food fishes of Vellar Estuary, Southeast coast of India. Acta Parasitologica Globalis, 1(1): 1–5
Yuasa K, Zafran, Koesharyani I, et al. 1998. Diseases in Marine Fishes reared at Gondol Research Station for Coastal Fisheries. Bali: Prosid Semin Teknol Perikanan Pantai, 94–98
Yuniar A T, Palm H W, Walter T. 2007. Crustacean fish parasites from Segara Anakan Lagoon, Java, Indonesia. Parasitology Research, 100(6): 1193–1204, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0391-9
Zafran, Roza D, Johnny F, et al. 2000. Diagnosis and Treatments for Parasitic Diseases, Humpback Grouper, Cromileptes altivelis Brood Stock. Japan: Indonesia and Japan International Cooperation Agency, 1–8
Acknowledgements
We thankfully acknowledge Head of the Department of Marine Biology, Microbiology and Biochemistry, Cochin University of Science and Technology for providing facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jemi Job, N., Hatha, A.A.M. & Radhakrishnan, C.K. Seasonal variation of Caligus rotundigenitalis infestation on the host fish Etroplus suratensis from the Cochin Backwaters, southwest coast of India. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 41, 132–136 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-021-1904-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-021-1904-1