Abstract
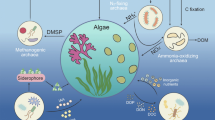
Specific bacterial communities interact with phytoplankton in laboratory algal cultures. These communities influence phytoplankton physiology and metabolism by transforming and exchanging phytoplankton-derived organic matter. Functional bacterial groups may participate in various critical nutrients fluxes within these associations, including nitrogen (N) metabolism. However, it is unclear how bacterial communities and the associated algae respond to changes of phycosphere N conditions. This response may have far-reaching implications for global nutrient cycling, algal bloom formation, and ecosystem function. Here, we identified changes in the bacterial communities associated with Phaeodactylum tricornutum when co-cultured with different forms and concentrations of N based on the Illumina HiSeq sequencing of 16S rRNA amplicons. Phylogenetic analysis identified Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes as the dominant phyla, accounting for 99.5% of all sequences. Importantly, bacterial abundance and community structure were more affected by algal abundance than by the form or concentration of inorganic N. The relative abundance of three gammaproteobacterial genera (Marinobacter, Algiphilus and Methylophaga) markedly increased in N-deficient cultures. Thus, some bacterial groups may play a role in the regulation of N metabolism when co-cultured with P. tricornutum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alavi M, Miller T, Erlandson K, et al. 2001. Bacterial community associated with Pfiesteria-like dinoflagellate cultures. Environmental Microbiology, 3(6): 380–396
Amin S A, Green D H, Hart M C, et al. 2009. Photolysis of iron-siderophore chelates promotes bacterial-algal mutualism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(40): 17071–17076
Amin S A, Hmelo L R, Van Tol H M, et al. 2015. Interaction and signalling between a cosmopolitan phytoplankton and associated bacteria. Nature, 522(7554): 98–101
Amin S A, Parker M S, Armbrust E V. 2012. Interactions between diatoms and bacteria. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 76(3): 667–684
Balvanera P, Pfisterer A B, Buchmann N, et al. 2006. Quantifying the evidence for biodiversity effects on ecosystem functioning and services. Ecology Letters, 9(10): 1146–1156
Behringer G, Ochsenkühn M A, Fei Cong, et al. 2018. Bacterial communities of diatoms display strong conservation across strains and time. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9: 659
Bell W, Mitchell R. 1972. Chemotactic and growth responses of marine bacteria to algal extracellular products. The Biological Bulletin, 143(2): 265–277
Bell W H. 1984. Bacterial adaptation to low-nutrient conditions as studied with algal extracellular products. Microbial Ecology, 10(3): 217–230
Bolch C J S, Bejoy T A, Green D H. 2017. Bacterial associates modify growth dynamics of the dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8: 670
Borcard D, Gillet F, Legendre P. 2011. Numerical Ecology with R. New York: Springer, 115–151
Bowler C, Allen A E, Badger J H, et al. 2008. The Phaeodactylum genome reveals the evolutionary history of diatom genomes. Nature, 456(7219): 239–244
Buchan A, Collier L S, Neidle E L, et al. 2000. Key aromatic-ringcleaving enzyme, protocatechuate 3,4-Dioxygenase, in the ecologically important marine Roseobacter Lineage. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66(11): 4662–4672
Buchan A, LeCleir G R, Gulvik C A, et al. 2014. Master recyclers: features and functions of bacteria associated with phytoplankton blooms. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 12(10): 686–698
Capone D G, Bronk D A, Mulholland M R, et al. 2008. Nitrogen in the Marine Environment. 2nd ed. San Diego: Academic Press, 757
Caporaso J G, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, et al. 2010. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods, 7(5): 335–336
Caporaso J G, Lauber C L, Walters W A, et al. 2011. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(Suppl 1): 4516–4522
Casciotti K L. 2016. Nitrogen and oxygen isotopic studies of the marine nitrogen cycle. Annual Review of Marine Science, 8: 379–407
Chapin III F S I, Zavaleta E S, Eviner V T, et al. 2000. Consequences of changing biodiversity. Nature, 405(6783): 234–242
Chiu H C, Levy R, Borenstein E. 2014. Emergent biosynthetic capacity in simple microbial communities. PLoS Computational Biology, 10(7): e1003695
Croft M T, Lawrence A D, Raux-Deery E, et al. 2005. Algae acquire vitamin B12 through a symbiotic relationship with bacteria. Nature, 438(7064): 90–93
de-Bashan L E, Antoun H, Bashan Y. 2008. Involvement of indole-3-acetic acid produced by the growth-promoting bacterium Azospirillum spp. in promoting growth of Chlorella vulgaris. Journal of Phycology, 44(4): 938–947
De La Haba R R, Sánchez-Porro C, Marquez M C, et al. 2011. Taxonomy of halophiles. In: Horikoshi K, ed. Extremophiles Handbook. Tokyo: Springer, 255–265
De Martino A, Bartual A, Willis A, et al. 2011. Physiological and molecular evidence that environmental changes elicit morphological interconversion in the model diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Protist, 162(3): 462–481
Donald D B, Bogard M J, Finlay K, et al. 2011. Comparative effects of urea, ammonium, and nitrate on phytoplankton abundance, community composition, and toxicity in hypereutrophic freshwaters. Limnology and Oceanography, 56(6): 2161–2175
Edgar R C. 2013. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nature Methods, 10(10): 996–998
Edgar R C, Haas B J, Clemente J C, et al. 2011. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics, 27(16): 2194–2200
Foster R A, Kuypers M M M, Vagner T, et al. 2011. Nitrogen fixation and transfer in open ocean diatom-cyanobacterial symbioses. ISME Journal, 5(9): 1484–1493
Fowler D, Coyle M, Skiba U, et al. 2013. The global nitrogen cycle in the twenty-first century. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 368(1621): 20130164
Gauthier M J, Lafay B, Christen R, et al. 1992. Marinobacter hydrocarbonoclasticus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new, extremely halotolerant, hydrocarbon-degrading marine bacterium. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 42(4): 568–576
González J M, Kiene R P, Moran M A. 1999. Transformation of sulfur compounds by an abundant lineage of marine bacteria in the α-subclass of the class Proteobacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65(9): 3810–3819
Green D H, Echavarri-Bravo V, Brennan D, et al. 2015. Bacterial diversity associated with the coccolithophorid algae Emiliania huxleyi and Coccolithus pelagicus f. braarudii. BioMed Research International, 2015: 194540
Green D H, Hart M C, Blackburn S I, et al. 2010. Bacterial diversity of Gymnodinium catenatum and its relationship to dinoflagellate toxicity. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 61(1): 73–87
Green D H, Llewellyn L E, Negri A P, et al. 2004. Phylogenetic and functional diversity of the cultivable bacterial community associated with the paralytic shellfish poisoning dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 47(3): 345–357
Grossart H P, Levold F, Allgaier M, et al. 2010. Marine diatom species harbour distinct bacterial communities. Environmental Microbiology, 7(6): 860–873
Guillard R R L. 1975. Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Smith W L, Chanley M H, ed. Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals. Boston, MA: Springer, 29–60
Guillard R R L, Ryther J H. 1962. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms: I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (cleve) Gran. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 8(2): 229–239
Gutierrez T, Green D H, Whitman W B, et al. 2012. Algiphilus aromaticivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., an aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium isolated from a culture of the marine dinoflagellate Lingulodinium polyedrum, and proposal of Algiphilaceae fam. nov.. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 62(11): 2743–2749
Haas B J, Gevers D, Earl A M, et al. 2011. Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Research, 21(3): 494–504
Haines K C, Guillard R R L. 1974. Growth of vitamin B12-requiring marine diatoms in mixed laboratory cultures with vitamin B12-producing marine bacteria. Journal of Phycology, 10(3): 245–252
Hatton A D, Shenoy D M, Hart M C, et al. 2012. Metabolism of DMSP, DMS and DMSO by the cultivable bacterial community associated with the DMSP-producing dinoflagellate Scrippsiella trochoidea. Biogeochemistry, 110(1–3): 131–146
Jasti S, Sieracki M E, Poulton N J, et al. 2005. Phylogenetic diversity and specificity of bacteria closely associated with Alexandrium spp. and other phytoplankton. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71(7): 3483–3494
Kaczmarska I, Ehrman J M, Bates E S S, et al. 2005. Diversity and distribution of epibiotic bacteria on Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries (Bacillariophyceae) in culture, and comparison with those on diatoms in native seawater. Harmful Algae, 4(4): 725–741
Kuo R C, Lin Senjie. 2013. Ectobiotic and endobiotic bacteria associated with Eutreptiella sp. isolated from Long Island Sound. Protist, 164(1): 60–74
Langille M G I, Zaneveld J, Caporaso J G, et al. 2013. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nature Biotechnology, 31(9): 814–821
Li Yang, Wang Zhen, Lin Xuezheng. 2016. Microbial community structure of Arctic seawater as revealed by pyrosequencing. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 35(6): 78–84
Little A E F, Robinson C J, Peterson S B, et al. 2008. Rules of engagement: interspecies interactions that regulate microbial communities. Annual Review of Microbiology, 62: 375–401
Liu Lemian, Yang Jun, Lv Hong, et al. 2015. Phytoplankton communities exhibit a stronger response to environmental changes than bacterioplankton in three subtropical reservoirs. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(18): 10850–10858
Løvdal T, Eichner C, Grossart H P, et al. 2008. Competition for inorganic and organic forms of nitrogen and phosphorous between phytoplankton and bacteria during an Emiliania huxleyi spring bloom. Biogeosciences, 5(2): 371–383
Lupette J, Lami R, Krasovec M, et al. 2016. Marinobacter dominates the bacterial community of the Ostreococcus tauri phycosphere in culture. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7: 1414
Ma Yuexin, Tao Wei, Liu Changfa, et al. 2017. Response of microbial biomass and bacterial community composition to fertilization in a salt marsh in China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 36(6): 80–88
Magoč T, Salzberg S L. 2011. FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics, 27(21): 2957–2963
Maheswari U, Jabbari K, Petit J L, et al. 2010. Digital expression profiling of novel diatom transcripts provides insight into their biological functions. Genome Biology, 11(8): R85
Martens-Habbena W, Berube P M, Urakawa H, et al. 2009. Ammonia oxidation kinetics determine niche separation of nitrifying archaea and bacteria. Nature, 461(7266): 976–979
Maruyama A, Maeda M, Simidu U. 1986. Occurrence of plant hormone (cytokinin)-producing bacteria in the sea. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 61(6): 569–574
Mayali X, Azam F. 2004. Algicidal bacteria in the sea and their impact on algal blooms. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 51(2): 139–144
Miller T R, Belas R. 2004. Dimethylsulfoniopropionate metabolism by Pfiesteria-associated Roseobacter spp.. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70(6): 3383–3391
Paerl H W, Dyble J, Moisander P H, et al. 2003. Microbial indicators of aquatic ecosystem change: current applications to eutrophication studies. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 46(3): 233–246
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, et al. 2013. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and webbased tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 41(D1): D590–D596
Ramanan R, Kim B H, Cho D H, et al. 2016. Algae-bacteria interactions: Evolution, ecology and emerging applications. Biotechnology Advances, 34(1): 14–29
Ramirez K S, Lauber C L, Knight R, et al. 2010. Consistent effects of nitrogen fertilization on soil bacterial communities in contrasting systems. Ecology, 91(12): 3463–3470
Risgaard-Petersen N, Nicolaisen M H, Revsbech N P, et al. 2004. Competition between ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and benthic microalgae. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70(9): 5528–5537
Rooney-Varga J N, Giewat M W, Savin M C, et al. 2005. Links between phytoplankton and bacterial community dynamics in a coastal marine environment. Microbial Ecology, 49(1): 163–175
Sapp M, Wichels A, Wiltshire K H, et al. 2007. Bacterial community dynamics during the winter-spring transition in the North Sea. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 59(3): 622–637
Sasaki K, Ikeda S, Ohkubo T, et al. 2013. Effects of plant genotype and nitrogen level on bacterial communities in rice shoots and roots. Microbes and Environments, 28(3): 391–395
Schäfer H, Abbas B, Witte H, et al. 2002. Genetic diversity of ‘satellite’ bacteria present in cultures of marine diatoms. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 42(1): 25–35
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, et al. 2011. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biology, 12(6): R60
Seymour J R, Amin S A, Raina J B, et al. 2017. Zooming in on the phycosphere: the ecological interface for phytoplankton-bacteria relationships. Nature Microbiology, 2: 17065
Seibold A, Wichels A, Schütt C. 2001. Diversity of endocytic bacteria in the dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 25(3): 229–235
Villeneuve C, Martineau C, Mauffrey F, et al. 2013. Methylophaga nitratireducenticrescens sp. nov. and Methylophaga frappieri sp. nov., isolated from the biofilm of the methanol-fed denitrification system treating the seawater at the Montreal Biodome. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 63(6): 2216–2222
Wang Qiong, Garrity G M, Tiedje J M, et al. 2007. Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73(16): 5261–5267
Wang Xin, Li Zhijiang, Su Jianqiang, et al. 2010. Lysis of a red-tide causing alga, Alexandrium tamarense, caused by bacteria from its phycosphere. Biological Control, 52(2): 123–130
Wemheuer B, Güllert S, Billerbeck S, et al. 2014. Impact of a phytoplankton bloom on the diversity of the active bacterial community in the southern North Sea as revealed by metatranscriptomic approaches. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 87(2): 378–389
Yang Caiyun, Li Yi, Zhou B, et al. 2015. Illumina sequencing-based analysis of free-living bacterial community dynamics during an Akashiwo sanguine bloom in Xiamen sea, China. Scientific Reports, 5: 8476
Zehr J P, Kudela R M. 2010. Nitrogen cycle of the open ocean: from genes to ecosystems. Annual Review of Marine Science, 3: 197–225
Zehr J P, Ward B B. 2002. Nitrogen cycling in the ocean: new perspectives on processes and paradigms. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68(3): 1015–1024
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under contract No. 31470536; the National Key Research and Development Program of China under contract No. 2018YFC1406403.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, F., Wei, X., Feng, J. et al. Variation of bacterial community associated with Phaeodactylum tricornutum in response to different inorganic nitrogen concentrations. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 37, 118–128 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-018-1272-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-018-1272-7