Abstract
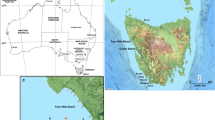
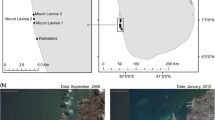
The coast of the Dapeng Peninsula has been honored as one of “the eight most beautiful coasts in China”. The most precious tourism resource for the peninsula is headland bay beaches, among which the beach at Xichong on the southern coast of the peninsula is the longest and the most important one. The information of the stability, sedimentary source and shape change of the beach is very important for maintaining the beach in terms of sustainable development of the peninsula. Heavy minerals in the sand of the beach and the inland stream at Xichong are compared with those of a nearby beach on the same coast to determine the beach sand source; with help of a computer software, MEPBAY, the equilibrium planforms of the beaches on the peninsula are compared with those of an island without rivers to evaluate the stream’s effects on the beach stability; cross shore profiles along the Xichong beach are also surveyed in different seasons of a year to assess the annual shore normal beach changes affected by the stream input, and the relation between the equilibrium planform state and cross shore changes of the beach. It is shown that (1) stream is the main sedimentary source of the beach and the weathering materials of the rocky headlands on both sides of the bay transported by waves are the second source for the beach but it is limited, sand from an inner shelf is not the sedimentary source for the beach at present and was not even during the Holocene transgression; (2) the Xichong beach cannot reach static equilibrium around the entire bay shoreline, the segment of the shoreline where a stream outlet is located is in dynamic equilibrium, and the unstable section occurs in the wave shadow region in the lee of an offshore island; (3) no matter whether the section of the beach shoreline at Xichong is in an equilibrium state or not, it is eroded in the typhoon season and recovered after the season, the maximum change in erosion and accretion occurs in the unstable segment; (4) the Xichong beach can only have small sand body since it is supplied with sand mainly form inland streams, resulting in a possible danger in which sand loss induced by human activities or huge storms cannot be replenished naturally.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bird E. 2005. Coastline changes. In: Schwartz M, ed. Encyclopedia of Coastal Science. Dordrecht: Springer, 319–323
Bird E. 2008. Coastal Geomorphology: An Introduction. 2nd ed. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons, 201–222
Bruun P. 1962. Sea-level rise as a cause of shore erosion. In: Proceedings of the American Society of Civil Engineers. USA: Journal of Waterways and Harbors Division, 88 (1): 117–130
Chen Yaotai. 1990. Heavy mineral characteristics in near-shore sediment of Shuidong of Western Guangdong and significance of their environments. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni (in Chinese), 29(1): 89–96
Chen Zishen. 1995. Analysis of the dynamic characteristics and stochastic simulation on variations of beach volumes. Haiyang Xuebao (in Chinese), 14(3): 393–403
Chen Zishen. 1996. Response characteristics of beach morphologies in an arc-shaped coast to typhoon waves. Chinese Science Bulletin, 41(12): 1015–1019
Chinese National Geography. 2005. Scenic splendor of China: China’ s eight most beautiful coasts. http://cng.dili360.com/cng/zzfm/2008/0612133.shtml [2013-11-29]
Dai Zhijun, Chen Jinhui, Ren Jie. 2007. Analysis of the stable states in the nearshore sea-floor of bar-lagoon coast in Bohe, Yuexi. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait (in Chinese), 26(1): 1–6
Dai Zhijun, Li Chunchu. 2004. Coastline configuration and geomorphologic development mode of arc-shaped coast in South China. Journal of Geographical Sciences (in Chinese), 14(4): 473–480
Dai Zhijun, Lui J T, Lei Yaping, et al. 2010. Patterns of sediment transport pathways on a headland bay beach-Nanwan Beach, South China: a case study. Journal of Coastal Research, 26(6): 1096–1103
Hsu J R C, Benedet L, Klein A H F, et al. 2008. Appreciation of static bay beach concept for coastal management and protection. Journal of Coastal Research, 24(1): 198–215
Hsu J R C, Evans C. 1989. Parabolic bay shapes and applications. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers, 87(4): 557–570
Hsu J R C, Uda T, Silvester R. 2000. Shoreline protection methods-Japanese Experience. In: Herbich J B, ed. Handbook of Coastal Engineering. New York: McGraw-Hill
Hsu J R C, Yu M J, Lee F C, et al. 2010. Static bay beach concept for scientists and engineers: a review. Coastal Engineering, 57(2): 76–91
Huang Fang, Ye Chunchi. 1995. Ocean Hydrology of Islands off the Coast of Guangdong (in Chinese). Guangzhou: Guangdong Science and Technology Press, 10–77
Huang Zhenguo, Li Pingri, Zhang Zhongyin, et al. 1983. Shenzhen Geomorphology (in Chinese). Guangzhou: Guangdong Science and Technology Press, 64–105
Hubert J F. 1962. A zircon-tourmaline-rutile maturity index and the interdependence of the composition of heavy mineral assemblages with the gross composition and texture of sandstones. Journal of Sediment Petrology, 32(3): 440–450
Inman D L, Nordstrom C F. 1971. On the tectonic and morphologic classification of coasts. The Journal of Geology, 79(1): 1–21
IPCC. 1996. Climate change 1995. The Science of Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1–572
Jackson D W T, Cooper J A G. 2010. Application of the equilibrium planform concept to natural beaches in Northern Ireland. Coastal Engineering, 57(2): 112–123
Klein A H F. 2004. Morphodynamics of Headland-bay beaches: examples from the coast of Santa Catarina State, Brazil [dissertation]. Algarve, Portugal: University of Algarve
Klein A H F, Raabe A L A, Pelz F D, et al. 2007. MepBay. http://siaiacad17.univali.br/mepbay/?pagina=home/ [2013-11-29]
Klein A H F, Vargas A, Raabe A L A, et al. 2003. Visual assessment of bayed beach stability with computer software. Computers & Geosciences, 29(10): 1249–1257
Kraft J C. 1971. Sedimentary facies patterns and geologic history of a Holocene marine transgression. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 82(8): 2131–2158
Krumbein W C. 1944. Shore processes and beach characteristics. Technical Memorandum, Vol. 3. Washington D C, U. S.: Beach Erosion Board
Kuang Cuiping, Pan Yi, Zhang Yu, et al. 2010. Shoreline change modeling on emergency beach nourishment project on West Beach of Beidaihe, China. China Ocean Engineering, 24(2): 277–289
Lee T L, Jeng D S, Chen B R. 2007. An engineering application tool for visual assessment of the equilibrium beach. China Ocean Engineering (in Chinese), 21(4): 701–713
Li Bing, Cao Lihua, Zhuang Zhenye, et al. 2012. The application of static bay beach concept to the east bank of Laizhou Bay. Periodical of Ocean University of China (in Chinese), 42(12): 77–82
Li Chunchu. 1986. Geomorphic characteristics of the harbor-coasts in South China. Acta Geographica Sinica (in Chinese), 41(4): 311–319
Li Chunchu, Luo Xianlin, Zhang Zhenyun, et al. 1986. Formation and evolution of the barrier-lagoon systems in Shuidong, Western Guangdong. Chinese Science Bulletin, 31(20): 1579–1582
Lužar-Oberiter B, Mikul i Pavlakovi S, Crnjakovi M, et al. 2008. Variable sources of beach sands of north Adriatic Lslands: examples from Rab and Susak. Geologia Croatica, 61(2–3): 379–384
Moreno L J, Kraus N C. 1999. Equilibrium shape of headland-bay beaches for engineering design. In: Proceedings of Coastal Sediments’ 99. Long Island: American Society of Civil Engineers, 860–875
Morton A C, Johnsson M J. 1993. Factors influencing the composition of detrital heavy mineral suites in Holocene sands of the Apure River drainage basin, Venezuela. In: Johnesson M J Basu A, eds. Processes Controlling the Composition of Clastic Sediments. Geological Society of America Special Paper, Vol. 284, Boulder, Colorado: American Society of Civil Engineers
Niedoroda A W, Swift D J P, Hopkins T S, et al. 1985. The shore face. In: Davis R A Jr, ed. Coastal Sedimentary Environments. New York: Springer Verlag, 533–624
Pierce J W, Colquhoun D J. 1970. Holocene evolution of a portion of the North Carolina coast. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 81(12): 3697–3714
Ren Yingxin, Zhu Baohua. 1987. Heavy Placer Mineral Separation and Identification (in Chinese). Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 17–36
Roy P S. 1984. New South Wales estuaries: their origin and evolution. In: Thom B G, ed. Developments in Coastal Geomorphology in Australia. London: Academic Press, 99–121
Roy P S, Cowell P J, Ferland M A, et al. 1994. Wave-dominated coasts. In: Carter R W G, Woodroffe C D, eds. Coastal Evolution: Later Quaternary Shoreline Morphodynamics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 121–186
Scoffin T P, Stoddart D R. 1983. Beach rock and intertidal cements. In: Goudie A S, Kenneth P, eds. Chemical Sediments and Geomorphology. London: Academic
Shepard F P. 1950. Longshore-bars and longshore-troughs. Beach Erosion Board Technical Memorandum, 15: 1–31
Short A D, Masselink G. 1999. Embayed and structurally controlled beaches. In: Short A D, ed. Handbook of Beach and Shoreface Morphodynamics. Chichester: John Willey and Sons, 230–250
Silvester R, Hsu J R C. 1993. Coastal Stabilization: Innovative Concepts. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, 215–221
So C L. 1972. The Effect of Typhoons on Beaches in Hong Kong. In: Adams W P, Helleiner F M, eds. International Geography. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 1018–1019
Thom B G. 1984. Sand barriers of Eastern Australia: Gippsland—A case study. In: Thom B G, ed. Coastal Geomorphology in Australia. London: Academic Press, 233–261
Uda T, Serizawa M. 2011. Model for predicting formation of bay barrier in Flat Shallow Sea. Coastal Engineering Proceedings, 32: 1176–1189
UASCE. 2002, Coastal Engineering Manual (CEM), Engineer Manual 1110-2-1100. Washington, D.C., U.S.: American Society of Civil Engineers Army Corps of Engineers
Wang Wei. 2000. The sediment sources for the bay barrier on the Hong Kong coasts—A case study in Pui O Bay in Lantau Island, Hong Kong. Scientia Geographica Sinica (in Chinese), 20(1): 45–50
Wang Wenjian. 1985. Development of the arc-shaped sandy beach at bays on the crenulate coast of east Guangdong. Tropic Oceanology (in Chinese), 4(2): 15–21
Wang Ying, Zhu Dakui. 1994. Coastal Geomorphology (in Chinese). Beijing: Higher Education Press, 101–126
Wang Zhongbo, Yang Shouye, Zhang Zhixun, et al. 2012. The heavy mineral assemblages of the surface sediments on the northeast shelf of the East China Sea and their environmental implication. Haiyang Xuebao (in Chinese), 34(6): 114–125
Williams A T, Grant C J, Leatherman S P. 1977. Sedimentation patterns in Repulse Bay, Hong Kong. Proceedings of the Geologists’ Association, 88(3): 183–200
Writing Group for Shenzhen Geology. 2009. Shenzhen Geology (in Chinese). Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 53–97
Xiang Xuhong, Shao Lei, Qiao Peijun, et al. 2011. Characteristics of heavy minerals in Pearl River sediments and their implications for provenance. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology (in Chinese), 31(6): 27–35
Yang Yanxiong, Zheng Jiabo. 2007. Static equilibrium headland-bay coast theory and its application to coasts of the Yellow and Bohai Seas. Coastal Engineering (in Chinese), 26(2): 38–46
Yu Jitao, Chen Zishen. 2011. Study on headland-bay sandy coast stability in South China coasts. China Ocean Engineering (in Chinese), 25(1): 1–13
Zeng Zhenwen. 2013. Why did the tourism of Dapeng Peninsula have a growth only in the number of tourists but not in the amount of wealth (in Chinese). http://wb.sznews.com/html/2013-04/27/content_2461844.htm [2013-11-26]
Zhang Yu, He Lulu, Kuang Cuiping, et al. 2010. Numerical study of shoreline changes by emergency beach nourishment project at the Middle Beach of Beidaihe, China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 31(1): 125–133
Zhang Song, Sun Xianling, Wang Wei, et al. 2013. Features of coastal landforms in Dapeng Peninsula of Shenzhen, China. Tropical Geography (in Chinese), 33(6): 647–658
Zhuang Lihua, Yan Jun, Chang Fengming, et al. 2009. Short-term morphological changes after sand-digging during a sand sculpture activity. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 27(4): 966–974
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Shenzhen Dapeng Peninsula National Geopark Project of China under contract No. 340775; the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province of China unde contract No. S2012010008610; the National Natural Science Foundation of China under contract No. 40871020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Wang, W., Huang, R. et al. The sedimentary source, planform stability and shore normal morphological change of the Xichong beach on the southern coast of the Dapeng Peninsula of Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 34, 76–89 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-015-0635-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-015-0635-6