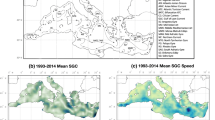
Abstract
Deep water in the Nordic seas is the major source of Atlantic deep water and its formation and transport play an important role in the heat and mass exchange between polar and the North Atlantic. A monthly hydrological climatology—Hydrobase II—is used to estimate the deep ocean circulation pattern and the deep water distribution in the Nordic seas. An improved P-vector method is applied in the geostrophic current calculation which introduces sea surface height gradient to solve the issue that a residual barotropic flow cannot be recognized by traditional method in regions where motionless level does not exist. The volume proportions, spatial distributions and seasonal variations of major water masses are examined and a comparison with other hydrological dataset is carried out. The variations and transports of deep water are investigated based on estimated circulation and water mass distributions. The seasonal variation of deep water volume in the Greenland Basin is around 22×103 km3 whereas significantly weaker in the Lofoten and Norwegian Basins. Annual downstream transports of about 1.54×103 and 0.64×103 km3 are reported between the Greenland/Lofoten and Lofoten/Norwegian Basins. The deep water transport among major basins is generally in the Greenland-Lofoten-Norwegian direction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aagaard K, Fahrbach E, Meincke J, et al. 1991. Saline outflow from the Arctic Ocean: its contribution to the Deep Waters of the Greenland, Norwegian, and Iceland Seas. Journal of Geophysical Research, 96(C11): 20433–20441
Blindheim J. 1990. Arctic intermediate water in the Norwegian Sea. Deep-Sea Research, 37(9): 1475–1489
Blindheim J, èsterhus S. 2005. The Nordic seas, main oceanographic features. In: Drange H, Dokken T, Furevik T, et al., eds. The Nordic seas: An Integrated Perspective. Washington D C: AGU, 11–37
Carmack E, Aagaard K. 1973. On the deep water of the Greenland Sea. Deep-Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 20(8): 687–715
Chu P C. 1995. P-vector method for determining absolute velocity from hydrographic data. Marine Technology Society Journal, 29(2): 3–14
Chu P C. 1996. The S-transform for obtaining localized spectra. Marine Technology Society Journal, 29(4): 28–38
Curry R. 2001. HydroBase 2—A database of hydrographic profiles and tools for climatological analysis. Massachusetts: Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, 81
Gascard J C, Watson A J, Messias M J, et al. 2002. Long-lived vortices as a mode of deep ventilation in the Greenland Sea. Nature, 416(6880): 525–527
Hansen B, èsterhus S. 2000. North Atlantic-Nordic seas exchanges. Progress in Oceanography, 45(2): 109–208
Helland-Hansen B, Nansen F. 1909. The Norwegian Sea, its physical oceanography based upon the Norwegian researches 1900–1904. Report on Norwegian Fishery and Marine-Investigations Vol. 11 No. 2. Norway: Geophysical Institute, University of Bergen
Hopkins T S. 1991. The GIN Sea—A synthesis of its physical oceanography and literature review 1972–1985. Earth-Science Reviews, 30(3–4): 175–318
Hunegnaw A, Siegismund F, Hipkin R, et al. 2009. Absolute flow field estimation for the Nordic seas from combined gravimetric, altimetric, and in situ data. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans (1978–2012), 114(C2), doi:10.1029/2008JC004797
Meincke J, Jonsson S, Swift J H. 1992. Variability of convective conditions in the Greenland Sea. In: Dickson R R, Maelkki P, Radach G et al., eds. Hydrobiological variability in the ICES area, 1980–1989. Copenhagen (Denmark): ICES, 32–39
Meincke J, Rudels B, Friedrich H J. 1997. The Arctic Ocean-Nordic seas thermohaline system. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 54(3): 283–299
Nøst O A, Isachsen P E. 2003. The large-scale time-mean ocean circulation in the Nordic seas and Arctic Ocean estimated from simplified dynamics. Journal of Marine Research, 61(2):175–210
Orvik K A, Niiler P. 2002. Major pathways of Atlantic water in the northern North Atlantic and Nordic seas toward Arctic. Geophysical Research Letters, 29(19): 2-1–2-4
Piacsek S, Allard R, McClean J. 2008. Water mass census in the Nordic seas using climatological and observational data sets. Nuovo Cimento Della Societa Italiana Di Fisica C-Geophysics and Space Physics, 31(2): 215–240
Poulain P M, Warn-Varnas A, Niiler P P. 1996. Near-surface circulation of the Nordic seas as measured by Lagrangian drifters. Journal of Geophysical Research, 101(C8):18237–18258
Rudels B, Friedrich H J, Quadfasel D. 1999. The arctic circumpolar boundary current. Deep-Sea Res II 46(6–7): 1023–1062
Smethie Jr W M, Ostlund H G, Loosli H H. 1986. Ventilation of the deep Greenland and Norwegian seas: evidence from krypton-85, tritium, carbon-14 and argon-39. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers, 33(5): 675–703
Stommel H, Schott F. 1977. The beta spiral and the determination of the absolute velocity field from hydrographic station data. Deep Sea Research, 24(3): 325–329
Swift J H, Koltermann K P. 1988. The origin of Norwegian Sea Deep Water. Journal of Geophysical Research, 93(C4): 3563–3569
Voet G, Quadfasel D, Mork K, et al. 2010. The mid-depth circulation of the Nordic seas derived from profiling float observations. Tellus A, 62(4): 516–529
Zhang Z, Yuan D, Chu P C. 2013. Geostrophic meridional transport in tropical Northwest Pacific based on Argo profiles. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 31(3): 656–664
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The Key Project of Chinese Natural Science Fundation under contract No. 41330960; the Chinese Polar Environment Comprehensive Investigation and Assessment Programmes, State Oceanic Administration of China under contract Nos CHINARE2014-03-01 and CHINARE2014-04-03; the Public Science and Technology Research Funds Projects of Ocean under contract No. 201205007-4.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Zhao, J., Liu, N. et al. Deep water distribution and transport in the Nordic seas from climatological hydrological data. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 34, 9–17 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-015-0629-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-015-0629-4