Abstract
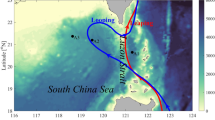
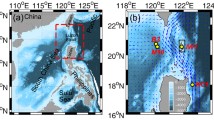
On the basis of the time series observations from a temperature chain and an acoustic Doppler current profiler on the continental shelf of the northern South China Sea, a sequence of internal solitary waves (ISWs) and background waves (BWs, including internal tides and near-inertial waves) on the continental shelf were captured simultaneously after the transit of Typhoon Neast in October 2011. These measurementsprovided a unique opportunity to explore the influence of BWs on the ISWs. The BWs appeared a conversion on the current strength and vertical mode structure during the observational period. The BWs were dominated by weak and mode-one waves before October 2 and then turned to strong and high-mode waves after that time. Meanwhile, the ISWs displayed different wave structures before and after October 2, which was closely related to BWs’ changes. According to the current profiles of BWs, the high-mode wave structure with strong current could significantly strengthen the vertical shear of ISWs in the near-surface layer and promote the breaking of ISWs, and thus it may play an important role in affecting the background current condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alford Matthew H, Lien Ren-Chieh, Simmons Harper, et al. 2010. Speed and evolution of nonlinear internal waves transiting the South China Sea. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 40: 1338–1355
Cai Shuqun, Xie Jieshuo. 2010. A propagation model for the internal solitary waves in the northern South China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115: C12074
Chang Ming-Huei, Lien Ren-Chieh, Tang Tswen Yung, et al. 2006. Energy flux of nonlinear internal waves in northern South China Sea. Geophysical Research Letters, 33: L03607
Fu Ke-Hsien, Wang Yu-Huai, Laurent Louis St, et al. 2012. Shoaling of large-amplitude nonlinear internal waves at Dongsha Atoll in the northern South China Sea. Continental Shelf Research, 37: 1–7
Jackson Christopher R. 2009. An empirical model for estimating the geographic location of nonlinear internal solitary waves. J Atmos Ocean Technol, 26: 2243–2255
Vidal Javier, Xavier Casamitjana, Jordi Colomer, et al. 2005. The internal wave field in Sau reservoir: observation and modeling of a third vertical mode. Limnol Ocanogr, 50: 1326–1333
Lamb Kevin G. 2003. Shoaling solitary internal waves: on a criterion for the formation of waves with trapped cores. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 478: 81–100
Lamb Kevin G, Farmer David. 2011. Instabilities in an internal solitarylike wave on the Oregon shelf. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 41: 67–87
Lien Ren-Chieh, D’asaroEeric A, Henyey Frank, et al. 2012. Trapped core formation within a shoaling nonlinear internal wave. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 42: 511–525
Lien Ren-Chieh, Tang Tswen-Yung, Chang Ming-Huei, et al. 2005. Energy of nonlinear internal waves in the South China Sea. Geophysical Research Letters, 32: L05615
Liu Antony K, Chang Y Steve, Hsu Ming-K, et al. 1998. Evolution of nonlinear internal waves in the East and South China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research, 103: 7995–8008
Moum J N, Farmer D M, Smyth W D, et al. 2003. Structure and generation of turbulence at interfaces strained by internal solitary waves propagating shoreward over the continental shelf. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 33: 2093–2112
Nam Sung Hyun, Kim Duk-jin, Kim Hyong Rok, et al. 2007. Typhooninduced, highly nonlinear internal solitary waves off the east coast of Korea. Geophysical Research Letters, 34: L01607
Nash Jonathan D, Kelly Samuel M, Shroyer Emily L, et al. 2012. The unpredictable nature of internal tides on continental shelves. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 42: 1981–2000
Orr Marshall H, Mignerey Peter C. 2003. Nonlinear internal waves in the South China Sea: observation of the conversion of depression internal waves to elevation internal waves. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108(C3): 3064
Pawlowicz R, Beardsley R, Lentz S. 2002. Classical tidal harmonic analysis including error estimates in MATLAB using T_TIDE. Computers Geosci, 28: 929–937
Ramp Steven R, Tang Tswen Yung, Duda Timothy F, et al. 2004. Internal solitons in the northeastern South China Sea. Part I: Sources and deep water propagation. IEEE JOceanic Eng, 29(4): 1157–1181
Wiegand Ronald C, Chamberlain Vivian. 1987. Internal waves of the second vertical mode in a stratified lake. Limnol Oceanogr, 32: 29–42
Xu Zhenhua, Yin Baoshu, Hou Yijun. 2011. Response of internal solitary waves to tropical storm Washi in the northwestern South China Sea. AnnGeophys, 29: 2181–2187
Zhao Zhongxiang, Klemas Victor, Zheng Quanan, et al. 2004. Remote sensing evidence for baroclinic tide origin of internal solitary waves in the northeastern South China Sea. Geophysical Research Letters, 31: 1–4
Zhao Y, Liu A K, Hsu M-K. 2008. Internal wave refraction observed from sequential satellite images. Int J Remote Sens, 29(21): 6381–6390
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Nature Science Foundation of China under contract Nos U1133001, 41030855 and 2013AA09A502.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, F., Hou, Y., Liu, Z. et al. The influence of background waves on internal solitary waves after the transit of Typhoon Neast in the northern South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 33, 40–47 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-014-0511-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-014-0511-9