Abstract
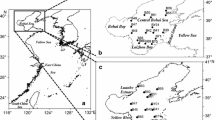
Heavy metals in the surface sediments and sediment core from the Xiangshan Bay, a mariculture base on the coast of the East China Sea, were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) in order to evaluate their levels and sources. The results showed that the levels of Cu, Pb, Zn, and Cr in the sediments of the bay have been generally influenced by anthropogenic inputs since the founding of the People’s Republic of China. In particular, Cu and Zn were polluted to some extent, as evidenced by high enrichment factors. Organic matter, grain size, wastewater discharge, and low energy hydrodynamic environment played dominant roles in the heavy metal enrichment in the sediments. The ratio of terrigenous source to marine biogenic deposit of trace metals in the sediments was calculated, revealing that terrigenous inputs were the main source of Cu, Pb, and Zn, while biological pellets contributed much more to the enrichment of Cr and Cd. Considering the influence of biological sources on the enrichment of Cd and Cr, and the fact that the sediment has been polluted by Cu and Zn, the development of mariculture and discharge of wastewater into the Bay should be restricted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai Minghong, Lin Jing, Hong Qingquan, et al. 2011. Content and distribution of trace metals in surface sediments from the northern Bering Sea, Chukchi Sea and adjacent Arctic areas. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 63: 523–527
Compilation Committee of Gulf topography of China. 1993. Gulf Topography of China: Part 5. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 293
Dong Aiguo, Zhai Shikui, Zabel M, et al. 2009. The distribution of heavy metal contents in surface sediments of the Changjiang Estuary in China and surrounding coastal areas. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 31(6): 54–68
Duan Liqin, Song Jinming, Li Xuegang, et al. 2012. Thallium concentrations and sources in the surface sediments of Bohai Bay. Marine Environmental Research, 73: 25–31
Durán I, Sánchez-Marín P, Beiras R. 2012. Dependence of Cu, Pb and Zn remobilization on physicochemical properties of marine sediments. Marine Environmental Research, 77: 43–49
Fang Jie. 2007. Persistent organic pollutants and heavy metals in surface sediments and marine organisms from coastal areas of Zhejiang Province [dissertation]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University
Fernandes L, Nayak G N, Ilangovan D, et al. 2011. Accumulation of sediment, organic matter and trace metals with space and time, in a creek along Mumbai coast, India. Estuarine, Coastal, and Shelf Science, 91: 388–399
Förstner U, Wittmann G T W. 1983. Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 698
Giordano R, Lombard G, Ciaralli L, et al. 1999. Major and trace elements in sediments from Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica. Science of The Total Environment, 227: 29–40
Guo Binghuo, Huang Zhenzong, Li Peying, et al. 2004. Marine Environment of Offshore and Adjacent Areas, China. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 446
Huang Xiuqing, Wang Jinhui, Jiang Xiaoshan. 2008. Study of the Marine Environmental Capacity and Total Amount Control of Pollutant in Xiangshan Bay. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 348
Ianni C, Magi E, Soggia F, et al. 2010. Heavy metal speciation in coastal and off-shore sediments from Ross Sea (Antarctica). Microchemical Journal, 96: 203–212
Kalloul S, Hamid W, Maanan M, et al. 2012. Source contributions to heavy metal fluxes into the Loukous estuary (Moroccan Atlantic Coast). Journal of Coastal Research, 28(1): 174–183
Liao Ziji. 1992. Environmental Chemistry and Biological Effect of Heavy Elements. Beijing: Environmental Science Press of China, 520
Liu Fangwen, Yan Wen, Wang Wenzhi, et al. 2002. Pollution of heavy metals in the Pearl River Estuary and its assessment of potential ecological risk. Marine Environment Science, 21(3): 34–39
Point D, Monperrus M, Tessier E, et al. 2007. Biological control of trace metal and organometal benthic fluxes in a eutrophic lagoon (Thau Lagoon, Mediterranean Sea, France). Estuarine, Coastal, and Shelf Science, 72: 457–471
Santos I R, Silva-Filho E V, Schaefer C E G R, et al. 2005. Heavy metal contamination in coastal sediments and soils near the Brazilian Antarctic Station, King george Island. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50: 185–194
Tessier A, Campbell P G C, Auclair J C, et al. 1984. Relationships between the partitining of trace metals in sediments their accumulation in the tissues of the freshwater mollusc Elliptio Complanata in a mining area. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 41: 1463–1472
Wasserman J C, Oliveira F B L, Bidarra M. 1998. Cu and Fe associated with humic acids in sediments of a tropical coastal lagoon. Organic Geochemistry, 28: 813–822
Zhou Yongqing. 2005. Geochemical Report of the Sediments in the Coastal of Zhejiang Province. Investigation Report. Hangzhou, China: Second Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province uner contract No. Y5110166.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, W., Yu, J., Xu, X. et al. Distribution and sources of heavy metals in the sediment of Xiangshan Bay. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 33, 101–107 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-014-0456-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-014-0456-z