Abstract
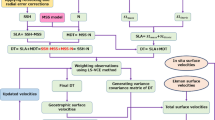
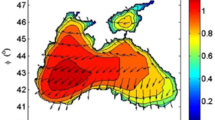
A 30-d current numerical simulation is running for the Yangshan Port, the Changjiang Estuary, the Hangzhou Bay and their adjacent seas using a finite volume coastal ocean model (FVCOM), with Changjiang River runoff and wind effect being considered. At the open boundary, this model is driven by the water level obtained from prediction including eight main partial tides. After the harmonic analysis, the cotidal chart and the iso-amplitude line as well as the current ellipse distribution map are displayed to illustrate the propagation property of a tidal wave. Horizontal velocity of both the U and V components coincides with the actual measurement, which shows that the model result is credible to describe the hydrodynamic pattern in this sea area. On this basis, real-time current data from high-frequency radar is assimilated with the implementation of quick ensemble Kalman filter, which takes the variation tendency of the state vector to compute the analysis field, instead of integrating the field for N (the number of ensemble) times as it used to in the standard EnKF, aiming at raising the efficiency of computation, reducing the error of prediction and at the same time, improving the forecast effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen C, Cowles G, Beardsly R C. 2004. An unstructured grid, Fnite-vdume coastal ocean model: FVCOM user manual, SMAST/UMASSD Technical Report-04, 601: 183
Chen C, Liu Hedong. 2003. An Unstructured grid, Finite-volume, three dimensional, Primitive equations ocean model: application to coastal ocean and estuaries. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 20: 159–186
Committee of Science and Technology, Marine Group Office of Marine Comprehensive Survey. 1963. Comprehensive Survey of the National Marine Atlas, Book III. 177–178
Evensen Geir. 1994. Inverse methods and data assimilation in nonlinear ocean models. Physica: D. Nonlinear Phenomena, 77: 108–129
Evensen Geir. 1994. Sequential data assimilation with a nonlinear quasi-geostrophic model using Monte Carlo methods to forecast error statistics. Journal of Geophysical Research, 99(C5): 10143–10162
Evensen Geir. 2003. The ensemble Kalman filter: theoretical formulation and practical implementation. Ocean Dynamics, 53: 343–367
Evensen Geir. 2004. sampling strategies and square root analysis schemes for the EnKF. Ocean Dynamics, 54: 539–560
Kalman R E. 1960. A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. Journal of Basic Engineering, 82D(1): 34–45
Ni Yongqiang, Geng Zhaoquan, Zhu Junzheng. 2003. Study on characteristic of hydrodynamics in Hangzhou Bay. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 18(4): 440–445
Liu Xincheng, Lu Yongjin, Pan Lihong, et al. 2006. Tidal current numerical simulating and water exchange research in The Changjiang Estuary and Hangzhou Bay. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 21(2): 171–180
Pawlowiczr R P, Beardsleyb B B, Lentzs S L. 2002. Classical tide harmonic analysis including estimates in MATLAB using T-TIDE. Computers and Geosciences, 28: 929–937
Wang Yonggang, Fang Guohong, Cao Deming, et al. 2004. Tides of Bohai, Yellow and East China Seas by assimilating gauging station data into a hydrodynamic model. Advances in Marine Science, 22(3): 253–274
Xu Jiangling. 2009. Assimilation of high frequency radar data into a shelf sea circulation model Cdissertation. Hamburg University of Hamburg
Yang Longhui, Zhu Jianrong, Zhu Shouxian. 2001. 3-D numerical simulation of tide and tidal current fields in the Changjiang Estuary, Hangzhou Bay and their adjacent sea. Journal of East China Normal University: Natural Science, (3): 74–84
Zhan Peng, Chen Xueen, Hu Xuejun, et al. 2010. Analysis of summertime current observations outside of the Changjiang Estuary in Donghai. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 40(8): 34–42
Zhu Dayong, Shao Hao, Li Yan, et al. 2007. Quality analyses of redial currents measured by a demonstration system of OSMAR HF radar in Fujian Province. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 26(1): 7–14
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The Hi-tech Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) under contract No. 2007AA09Z117; the Public Science and Technology Research Funds Projects of Ocean under contract Nos 200905001 and 201005019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Zhan, P., Chen, J. et al. Numerical study of current fields near the Changjiang Estuary and impact of Quick-EnKF assimilation. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 30, 33–44 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-011-0145-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-011-0145-0