Abstract
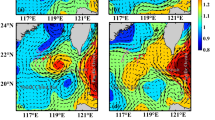
An algal bloom is defined as a relatively rapid increase in the biomass of phytoplankton in an aquatic system. During 30 March to 24 April 2007, a cruise was conducted in the central Southern Huanghai Sea to investigate the spring bloom processes. The spatial and temporal variations of phytoplankton are discussed based on the in-situ observations and simultaneous remote sensing data. The explosive algal blooming varied quickly in temporal and spatial scales, due to the highly patchy distribution. Data obtained at the 2 anchor stations (BM1 and BM2) were analyzed in the present study. Horizontal advection is speculated to be responsible for the abrupt decrease in the concentration of chlorophyll-a at stations BM1 and BM2. At station BM2, the intermediate high chlorophyll-a concentration, coinciding with the low temperature, was found to be advected from the inshore colder water mass located to the east of the site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham E R. 1998. The generation of plankton patchiness by turbulent stirring. Nature, 391(5): 577–580
Franks P J S. 1997. Spatial patterns in dense algal blooms. Limnology and Oceanography, 42(5, part 2): 1297–1305
Hillmer I, Imber J. 2007. Influence of advection on scales of ecological studies in a coastal equilibrium flow. Continental Shelf Research, 27: 134–153
Hu H G, Wan Z W, Yuan Y L. 2004. Simulation of seasonal variation of phytoplankton in the southern Huanghai (Yellow) Sea and analysis on its influential factors. Acta Oceanologica Sinica(in Chinese), 26(6): 74–88
Kudo I, Matsunaga K. 1999. Environmental factors affecting the occurrence and production of the spring phytoplankton bloom in Funka Bay, Japan. Journal of Oceanography, 55(4): 505–513
Lalli C M, Parsons T R. 1997. Biological oceanography: an introduction. Oxford: Butterworth Heinemann, 103
Lin C, Ning X, Su J, et al. 2005. Environmental changes and the responses of the ecosystems of the Yellow Sea during 1976–2000. Journal of Marine Systems, 55: 223–234
Meng F, Qiu J W, Wu B L. 1993. Zooplankton of the Yellow Sea large marine ecosystem. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai(in Chinese), 11(3): 30–37
Sun X P. 2006. Regional oceanography of China coastal waters(in Chinese). Beijing: Ocean Press, 98
Sverdrup HW. 1953. On conditions for the vernal blooming of phytoplankton. Journal du Conseil, 18: 287–295
Tang Q S, Su J L. 2000. The marine ecosystem dynamics research of China. I. The key science question and research development stratagem(in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 252
Tang Y X. Zou E M, Lie H J, et al. 1999. Analysis of hydrographic features and the circulation situation in the southern Huanghai Sea in early spring(in Chinese). Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 21(5): 1–11
Tian T, Wei H, Su J, et al. 2005. Simulations of annual cycle of phytoplankton production and the utilization of nitrogen in the Yellow Sea. Journal of Oceanography, 61: 343–357
Townsend D W, Cammen L M, Holligan P M, et al. 1994. Causes and consequences of variability in the timing of spring phytoplankton blooms. Deep Sea Research I, 41: 747–765
Wang B D, Wang G Y, Liu F. 1998. Distribution features of the chemical parameters in the Southern Yellow Sea in spring(in Chinese). Marine Enviromental Science, 17(3): 45–50
Wu Q M, Chen S Z, Yu Z G, et al. 2001. Dissolved inorganic nitrogen in the Southern Yellow Sea(in Chinese). Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 31(1): 129–135
Zhu M Y, Mao X H, Lu R H, et al. 1993. Chlorophyll a and primary productivity in the Yellow Sea(in Chinese). Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 11(3): 38–51
Zou E M, Guo B H, Tang Y X. 2000. The hydrographic features and water masses analyses of the southern Huanghai Sea in the spring of 1996 (in Chinese). Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 22(1): 17–26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The Major State Program of China for Basic Research under contract No. 2006CB400602; the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in the University of China under contract grant No. NCET-04-0641; the Numerical study on the support and regulate of hydrodynamics to biological productivity in the Huanghai Sea under contract grant No. NSFC-40830854.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, J., Wei, H., Zhao, L. et al. The effects of horizontal advection on the spring bloom of phytoplankton in the central Southern Huanghai Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 30, 24–31 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-011-0087-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-011-0087-6