Abstract
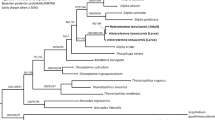
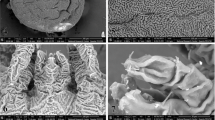
Trehala manna is the edible and trehalose-rich cocoons of a few Larinus species (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Lixinae: Lixini), and manufactured by the feeding activity of larvae on the Echinops plants. Knowledge on the morphological and molecular properties of immature stages of Larinus species, especially trehala-constructing ones, is still very limited. Herein, the mature larva and pupa of Larinus hedenborgi Boheman, 1845, are morphologically described for the first time, illustrated and compared with known immature stages of other Larinus species. Morphological identification keys prepared for all known immature stages of Larinus species. The DNA sequences of three mitochondrial (COI, Cytb, and 16S RNA) and four nuclear (enolase, histon 4, 18S rRNA, and 28S rRNA) markers were generated for L. hedenborgi and compared with the available sequences in the GenBank. Comparative morphology revealed the affinity of L. hedenborgi with the L. vulpes, L. inaequalicollis, and L. capsulatus based on five larval and two pupal characters. Molecular analysis based on 1859 bp of mtDNA and 1618 bp of nDNA sequences indicated a close association between the L. hedenborgi and other Lixinae namely Larinus species. Although both morphological and molecular descriptions supported the taxonomic status of L. hedenborgi within weevils, sufficient molecular data must be available to allow further comparisons. This pioneering study can be expanded to a large-scale zoogeographic study using morpho-molecular characters, simultaneously with population-level sampling of all trehala-constructing Larinus species.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmadabad, H. N., Firizi, M. N., & Behnamfar, M. (2016). Immunostimulatory effects of trehala manna ethanolic extract on splenocytes and peritoneal macrophages in vitro. Journal of Medicinal Plants and Natural Products, 1, 23–32.
Anderson, R. S. (1993). Weevils and plants: Phylogenetic versus ecological mediation of evolution of host plant associations in Curculioninae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). The Memoirs of the Entomological Society of Canada, 125(S165), 197–232.
Astrin, J. J., & Stüben, P. E. (2008). Phylogeny in cryptic weevils: Molecules, morphology and new genera of western palaearctic Cryptorhynchinae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Invertebrate Systematics, 22, 503–522.
Bodenheimer, F. S. (1951). Insects as human food: A chapter of thee ecology of man: Dr (p. 352). W. Junk.
Caner, S., Nguyen, N., Aguda, A., Zhang, R., Pan, Y. T., Withers, S. G., et al. (2013). The structure of the mycobacterium smegmatis trehalose synthase reveals an unusual active site configuration and acarbose-binding mode. Glycobiology, 23, 1075–1083.
Danforth, B. N., Lin, C. P., & Fang, J. (2005). How do insect nuclear ribosomal genes compare to protein-coding genes in phylogenetic utility and nucleotide substitution patterns? Systematic Entomology, 30, 549–562.
De Mandal, S., Chhakchhuak, L., Gurusubramanian, G., & Kumar, N. S. (2014). Mitochondrial markers for identification and phylogenetic studies in insects–a review. DNA Barcodes, 2, 1–9.
Donkin, R. (1980). Manna: An historical geography. Dr. W: Junk bv Publishers, The Hague. Edinburgh University Press.
Elbein, A. D., Pan, Y. T., Pastuszak, I., & Carroll, D. (2003). New insights on trehalose: A multifunctional molecule. Glycobiology, 13(4), 17R-27R.
Esseghir, S., Ready, P., Killick-Kendrick, R., & Ben-Ismail, R. (1997). Mitochondrial haplotypes and phylogeography of phlebotomus vectors of Leishmania major. Insect Molecular Biology, 6(3), 211–225.
Frati, F., Dell’Ampio, E., Casasanta, S., Carapelli, A., & Fanciulli, P. P. (2000). Large amounts of genetic divergence among italian species of the genus Orchesella (Insecta, Collembola) and the relationships of two new species. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 17, 456–461.
Gardner, J. (1934). Immature stages of indian Coleoptera (15) (Scolytidae). Indian Forest Records, 20(8), 1–17.
Gerber, A. S., Loggins, R., Kumar, S., & Dowling, T. E. (2001). Does nonneutral evolution shape observed patterns of DNA variation in animal mitochondrial genomes? Annual Review of Genetics, 35, 539–566.
Gosik, R., & Skuhrovec, J. (2011). Descriptions of mature larvae and pupae of the genus Larinus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae, Lixinae). Zootaxa, 3019, 1–25.
Gosik, R., Skuhrovec, J., Caldara, R., & Toševski, I. (2020). Immatures of Palearctic Mecinus species (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Curculioninae): Morphological characters diagnostic at genus and species levels. ZooKeys, 939(2), 87–165.
Gosik, R., Skuhrovec, J., Toševski, I., & Caldara, R. (2017). Morphological evidence from immature stages further suggests Lignyodina being close to Tychiina (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Curculioninae, Tychiini). Zootaxa, 4320, 426–446.
Gosik, R., Sprick, P., Skuhrovec, J., Deruś, M., & Hommes, M. (2016). Morphology and identification of the mature larvae of several species of the genus Otiorhynchus (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Entiminae) from Central Europe with an update of the life history traits. Zootaxa, 4108, 1–67.
Gosik, R., & Wanat, M. (2014). Descriptions of immature stages of the weevil Lixus punctiventris Boheman, 1835 (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Lixini). Zootaxa, 3754, 159–172.
Guibourt, M. (1858). Notice sur une matière pharmaceutique nommée le tréhala, produite par un insecte de la famille des charançons. Revue Et Magazin De Zoologie, 2, 276.
Gültekin, L. (2008). Taxonomic review of the stem-inhabiting trehala-constructing Larinus Dejean, 1821 (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): New species, systematics and ecology. Zootaxa, 1714, 1–18.
Gültekin, L., & Podlussany, A. (2012). Two new species of Larinus from Iran (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Lixinae). Acta Entomologica Musei Natioalis Pragae, 52, 245–258.
Gültekin, L., & Shahreyary-Nejad, S. (2015). A new trehala-constructing Larinus Dejean (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) from iran. Zoology in the Middle East, 61, 246–251.
Gunter, N. L., Oberprieler, R. G., & Cameron, S. L. (2016). Molecular phylogenetics of a ustralian weevils (Coleoptera: Curculionoidea): Exploring relationships in a hyperdiverse lineage through comparison of independent analyses. Austral Entomology, 55, 217–233.
Hall, T. A. (1999). BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series., 41, 95–98.
Hamedi, A., Farjadian, S., & Karami, M. R. (2015). Immunomodulatory properties of trehala manna decoction and its isolated carbohydrate macromolecules. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 162, 121–126.
Hickson, R. E., Simon, C., Cooper, A., Spicer, G. S., Sullivan, J., & Penny, D. (1996). Conserved sequence motifs, alignment, and secondary structure for the third domain of animal 12s rRNA. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 13, 150–169.
Hlaváč, P., Skuhrovec, J., & Pelikán, J. (2020). A new, peculiar genus of Cossoninae (Coleoptera, Curculionidae) from Oman with description of a new species, larva and notes on biology. Zootaxa, 4738(1), 129–142.
Hooper, D., McNair, J. B., & Field, H. (1937). Useful plants and drugs of Iran and Iraq. Field Museum of Natural History. Botanical Series, 9, 71–241.
Jiang, Ch., Caldara, R., Skuhrovec, J., & Zhang, R. (2020). Description of larva of Cionus olivieri Rosenschoeld, 1838 (Coleoptera, Curculionidae): A morphological comparison with other species of the genus and the tribe Cionini, and biological notes. ZooKeys, 976, 131–145.
Karimian, F., Oshaghi, M. A., Sedaghat, M. M., Waterhouse, R. M., Vatandoost, H., Hanafi-Bojd, A. A., et al. (2014). Phylogenetic analysis of the oriental-palearctic-afrotropical members of Anopheles (Culicidae: Diptera) based on nuclear rdna and mitochondrial DNA characteristics. Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases, 67, 361–367.
Lee, C. Y., & Morimoto, K. (1988). Larvae of the weevil family Curculionidae of Japan. Part 2. Hyperinae to Cioninae (Insecta: Coleoptera). Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University, 33, 131–152.
Legalov, A., Ghahari, H., & Arzanov, Y. G. (2010). Annotated catalogue of curculionid-beetles (Coleoptera: Anthribidae, Rhynchitidae, Attelabidae, Brentidae, Brachyceridae, Dryophthoridae and Curculionidae) of Iran. Amurian Zoological Journal, 2, 191–244.
Maleki-Ravasan, N., Bahrami, A., Vatandoost, H., Shayeghi, M., Koosha, M., & Oshaghi, M. A. (2017). Molecular characterization and phylogenetic congruence of Hydropsyche sciligra (Trichoptera: Hydropsychidae) using mitochondrial and nuclear markers. Journal of Arthropod-Borne Diseases, 11(1), 60–77.
Maleki-Ravasan, N., Shayeghi, M., Najibi, B., & Oshaghi, M. A. (2012). Infantile nosocomial myiasis in iran. Journal of Arthropod-Borne Diseases, 6(2), 156–163.
Marvaldi, A. E. (1998). Larvae of Entiminae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): Tribal diagnoses and phylogenetic key, with a proposal about natural groups within entimini. Entomologica Scandinavica, 29, 89–98.
Marvaldi, A. E. (1999). Morfología larval en Curculionidae (Insecta: Coleoptera). Acta Zoológica Lilloana, 45, 7–24.
May, B. M. (1977). Immature stages of curculionidae: Larvae of the soil-dwelling weevils of New Zealand. Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand, 7, 189–228.
May, B. M. (1993). Larvae of Curculionoidea (Insecta: Coleoptera): A systematic overview. Fauna of New Zealand, 28, 1-225.
May, B. M. (1994). An introduction to the immature stages of Australian Curculionoidea. Australian Weevils, 2, 365–728.
McKenna, D., Clarke, D., Anderson, R., Astrin, J., Brown, S., Chamorro, L., et al. (2018). Morphological and molecular perspectives on the phylogeny, evolution, and classification of weevils (Coleoptera: Curculionoidea): Proceedings from the 2016 international weevil meeting. Diversity, 10, 64.
Monaghan, M. T., Balke, M., Gregory, T. R., & Vogler, A. P. (2005). DNA-based species delineation in tropical beetles using mitochondrial and nuclear markers. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society b: Biological Sciences, 360, 1925–1933.
Mozaffarian, V. (2006). A taxonomic survey of Echinops l. Tribe Echinopeae (Asteraceae) in iran: 14 new species and diagnostic keys. The Iranian Journal of Botany, 11, 197–239.
Nasirzadeh, A., Javidtash, I., & Riasat, M. (2005). Identification of echinops species and study on some biological characteristics of Larinus vulpes ouv. As manna producer in fars province. Iranian Journal of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants, 21, 335–346.
Nikulina, O. (2007). New data on larvae of weevils of the genus Lixus (Coleoptera, Curculionidae) from central asia. Entomological Review, 87, 750–756.
Nikulina, O. N., & Gültekin, L. (2011). Larval morphology of Lixus cardui Olivier and Lixus filiformis (Fabricius) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): Biological control agents for scotch and musk thistles. Australian Journal of Entomology, 50, 253–257.
Nikulina, O., & Gültekin, L. (2014). New data on the larvae of the weevil genus Larinus Dejean, 1821 (Coleoptera, Curculionidae) from northeastern turkey. Entomological Review, 94, 1010–1018.
Nikulina, O. N., Gültekin, L., & Güçlü, Ş. (2004). Larval morphology of the capitulum weevil, Larinus latus (Herbst) (Coleoptera, Curculionidae). New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 31, 23–26.
Oberprieler, R. G., Marvaldi, A. E., & Anderson, R. S. (2007). Weevils, weevils, weevils everywhere. Zootaxa, 1668, 491–520.
Ohtake, S., & Wang, Y. J. (2011). Trehalose: Current use and future applications. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 100, 2020–2053.
Pineau, P., Henry, M., Suspène, R., Marchio, A., Dettai, A., Debruyne, R., et al. (2004). A universal primer set for pcr amplification of nuclear histone h4 genes from all animal species. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 22, 582–588.
Querino, R. B., & Z. R., Stouthamer R, . (2001). Molecular tool for identification of closely related species of Trichogramma (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae): T. Rojasi nagaraja & nagarkatti and t. Lasallei Pinto. Neotropical Entomology, 30, 575–578.
Richards, A., Krakowka, S., Dexter, L., Schmid, H., Wolterbeek, A., Waalkens-Berendsen, D., et al. (2002). Trehalose: A review of properties, history of use and human tolerance, and results of multiple safety studies. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 40, 871–898.
Riedel, A., Tänzler, R., Pons, J., Suhardjono, Y. R., & Balke, M. (2016). Large-scale molecular phylogeny of Cryptorhynchinae (Coleoptera, Curculionidae) from multiple genes suggests american origin and later australian radiation. Systematic Entomology, 41, 492–503.
Scheffer, S. J. (2000). Molecular evidence of cryptic species within the Liriomyza huidobrensis (Diptera: Agromyzidae). Journal of Economic Entomology, 93, 1146–1151.
Scherf, H. (1964). Die entwicklungsstadien der mitteleuropaischen curculioniden (morphologie: Bionomie, Ökologie). Abhandlungen Der Senckenbergischen Naturforschenden Gesellschaft, 506, 1–335.
Shull, V. L., Vogler, A. P., Baker, M. D., Maddison, D. R., & Hammond, P. M. (2001). Sequence alignment of 18s ribosomal rna and the basal relationships of adephagan beetles: Evidence for monophyly of aquatic families and the placement of trachypachidae. Systematic Biology, 50, 945–969.
Sievers, F., Wilm, A., Dineen, D., Gibson, T. J., Karplus, K., Li, W., et al. (2011). Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using clustal omega. Molecular Systems Biology, 7, 539.
Simon, C., Frati, F., Beckenbach, A., Crespi, B., Liu, H., & Flook, P. (1994). Evolution, weighting, and phylogenetic utility of mitochondrial gene sequences and a compilation of conserved polymerase chain reaction primers. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 87, 651–701.
Skuhrovec, J., & Bogusch, P. (2016). The morphology of the immature stages of Metadonus vuillefroyanus (Capiomont, 1868) (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Hyperini) and notes on its biology. ZooKeys, 589, 123–142.
Skuhrovec, J., Caldara, R., Gosik, R., Trnka, F., & Stejskal, R. (2021). On the Affinities and Systematic Position of Lachnaeus Schoenherr and Rhinocyllus Germar in the Tribe Lixini (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Lixinae) Based on the Morphological Characters of the Immature Stages. Insects, 12(6), 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12060489.
Skuhrovec, J., Gosik, R., & Caldara, R. (2014). Immatures of palaearctic species of the weevil genus Tychius (Coleoptera, Curculionidae): New descriptions and new bionomic data with an evaluation of their value in a phylogenetic reconstruction of the genus. Zootaxa, 3839, 1–84.
Skuhrovec, J., Gosik, R., Caldara, R., & Košťál, M. (2015). Immatures of palaearctic species of the weevil genus Sibinia (Coleoptera, Curculionidae): New descriptions and new bionomic data with suggestions on their potential value in a phylogenetic reconstruction of the genus. Zootaxa, 3955, 151–187.
Skuhrovec, J., Gosik, R., Caldara, R., Toševski, I., Łętowski, J., & Szwaj, E. (2018). Morphological characters of immature stages of Palaearctic species of Cleopomiarus and Miarus and their systematic value in Mecinini (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Curculioninae). ZooKeys, 808, 23-92.
Skuhrovec, J., & Volovnik, S. (2015). Biology and morphology of immature stages of Lixus canescens (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Lixinae). Zootaxa, 4033, 350–362.
Skuhrovec, J., Volovnik, S., & Gosik, R. (2017). Description of the immature stages of Larinus vulpes and notes on its biology (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Lixinae). ZooKeys, 679: 107-137.
Skuhrovec, J., Volovnik, S., Gosik, R., Stejskal, R., & Trnka, F. (2019). Cleonis pigra (Scopoli, 1763) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Lixinae): Morphological re-description of the immature stages, keys, tribal comparisons and biology. Insects, 10(10), 325.
Stejskal, R., Trnka, F., & Skuhrovec, J. (2014). Biology and morphology of immature stages of Coniocleonus nigrosuturatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Lixinae). Acta Entomologica Musei Nationalis Pragae, 54, 337–354.
Tahmasbi Afshar, S., Rezai Ahmad Abadi, A., & Bashari, H. (2008). Identification and investigation of mannas sources in Qom area. AGRIS, 1–30.
Talamelli, F. (2014). New faunistic data on selected Palearctic species of the tribe Lixini Schoenherr, 1823. Quaderno di Studi e Notizie di Storia Naturale della Romagna, 39, 161–174.
Teramoto, N., Sachinvala, N., & Shibata, M. (2008). Trehalose and trehalose-based polymers for environmentally benign, biocompatible and bioactive materials. Molecules, 13, 1773–1816.
Trnka, F., Stejskal, R., & Skuhrovec, J. (2015). Biology and morphology of immature stages of Adosomus roridus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Lixinae). Zootaxa, 4021, 433–446.
Trnka, F., Stejskal, R., & Skuhrovec, J. (2016). The morphology of the immature stages of two rare Lixus species (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Lixinae) and notes on their biology. ZooKeys, 604, 87-116.
Wild, A. L., & Maddison, D. R. (2008). Evaluating nuclear protein-coding genes for phylogenetic utility in beetles. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 48, 877–891.
Zardoya, R., & Meyer, A. (1996). Phylogenetic performance of mitochondrial protein-coding genes in resolving relationships among vertebrates. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 13, 933–942.
Zotov, A. (2009a). Morphology of the preimaginal stages of three species of weevil of the lixini (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Caucasian Entomological Bulletin, 5, 81–90.
Zotov, A. (2009b). Morphology of the preimaginal stages of weevil Lixus iridis Olivier, 1807 (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Caucasian Entomological Bulletin, 5, 249–252.
Zotov, A. (2010). Morphology of preimaginal stages of the genus Larinus Dejean, 1821 (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Part i. Caucasian Entomological Bulletin, 6, 171–178.
Zotov, A. (2011). Morphology of the preimaginal stages of weevils of the tribe Cleonini sensu lato (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Kavkazskiy Entomologicheskiy Byulleten-Caucasian Entomological Bulletin, 7, 153–162.
Funding
The study was supported by the collaborative linkage grants awarded to NMR and JS, by the Pasteur Institute of Iran and Czech Ministry of Agriculture (MZe ČR No RO0418), respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and international guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skuhrovec, J., Gosik, R., Maleki-Ravasan, N. et al. Morphological and molecular inference of immature stages of Larinus hedenborgi (Col: Curculionidae), a trehala-constructing weevil. Org Divers Evol 22, 161–176 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13127-021-00511-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13127-021-00511-1