Abstract
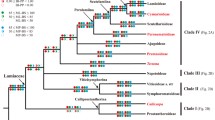
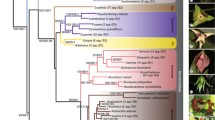
Cephaloziaceae represent a subcosmopolitan lineage of largely terrestrial leafy liverworts with three-keeled perianths, a reduced seta, capsules with bistratose walls, filamentous sporelings, large, thin-walled cells, and vegetative distribution by gemmae. Here we present the most comprehensively sampled phylogeny available to date based on the nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer region and the chloroplast markers trnL-trnF and rbcL of 184 accessions representing 41 of the 89 currently accepted species and four of the five currently accepted subfamilies. Alobielloideae are placed sister to the remainder of Cephaloziaceae. Odontoschismatoideae form a sister relationship with a clade consisting of Schiffnerioideae and Cephalozioideae. Cephalozioideae are subdivided in three genera, Fuscocephaloziopsis, Cephalozia, and Nowellia, the last two in a robust sister relationship. Most morphological species circumscriptions are supported by the molecular topologies but the Cephalozia bicuspidata complex and the Cephalozia hamatiloba complex require further study. A Neotropical clade of Odontoschisma originates from temperate ancestors. Odontoschisma yunnanense is described as new to science.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aranda, S. C., Gradstein, S. R., Patiño, J., Laenen, B., Désamoré, A., & Vanderpoorten, A. (2014). Phylogeny, classification and species delimitation in the liverwort genus Odontoschisma (Cephaloziaceae). Taxon, 63, 1008–1025.
Bakalin, V. A., & Vilnet, A. A. (2014). Two new species of the liverwort genus Hygrobiella Spruce (Marchantiophyta) described from the North Pacific based on integrative taxonomy. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 300, 2277–2291.
Bechteler, J., Lee, G. E., Schäfer-Verwimp, A., Pócs, T., Peralta, D. F., Renner, M. A. M., et al. (2016). Towards a monophyletic classification of Lejeuneaceae IV: reinstatement of Allorgella, transfer of Microlejeunea aphanella to Vitalianthus and refinements of the subtribal classification. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 302, 187–201.
Bednarek-Ochyra, H., Váňa, J., Ochyra, R., & Lewis Smith, R. I. (2000). The liverwort flora of Antarctica. Cracow: Polish Academy of Sciences.
Boisselier-Dubayle, M. E., Lambourdiere, J., & Bischler, H. (1998). Taxa delimitation in Reboulia investigated with morphological, cytological, and isozyme markers. The Bryologist, 101, 61–69.
Buczkowska, K., Odrzykoski, I. J., & Chudzińska, E. (2004). Delimitation of some European species of Calypogeia Raddi (Hepaticae, Jungermanniales) based on cytological characters of oil bodies and multienzyme phenotype. Nova Hedwigia, 78, 147–163.
Buczkowska, K., Sawicki, J., Szczecińska, M., Klama, H., & Baczkiewicz, A. (2012). Allopolyploid speciation of Calypogeia sphagnicola (Jungermanniopsida, Calypogeiaceae) based on isozyme and DNA markers. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 298, 549–560.
Buczkowska, K., Hornik, B., & Czolpińska, M. (2015). Two ploidy levels of genetically delimited groups of the Calypogeia fissa complex (Jungermanniopsida, Calypogeiaceae). Biodiversity Research and Conservation, 39, 1–6.
Crandall-Stotler, B., Stotler, R. E., & Long, D. G. (2009). Phylogeny and classification of the Marchantiophyta. Edinburgh Journal of Botany, 66, 155–198.
Damsholt, K. (2002). Illustrated flora of Nordic liverworts and hornworts. Lund: Nordic Bryological Society.
Darriba, D., Taboada, G. L., Doallo, R., & Posada, D. (2012). JModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nature Methods, 9, 772.
Dayrat, B. (2005). Towards integrative taxonomy. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 85, 407–415.
De Queiroz, K. (2007). Species concepts and species delimitation. Systematic Biology, 56, 879–886.
Dong, S., Schäfer-Verwimp, A., Meinecke, P., Feldberg, K., Bombosch, A., Pócs, T., et al. (2012). Tramps, narrow endemics and morphologically cryptic species in the epiphyllous liverwort Diplasiolejeunea. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 65, 582–594.
Engel, J. J. (1982). Hepaticopsida. In S. P. Parker (Ed.), Synopsis and classification of living organisms, Vol. 1 (pp. 271–304). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Engel, J. J., & Glenny, D. (2008). A flora of the liverworts and hornworts of New Zealand. Vol. 1. Monographs in Systematic Botany from the Missouri Botanical Garden, 110, 1–897.
Engel, J. J., He, X., & Glenny, D. (2010). Studies on Lophocoleaceae XXII. The systematic position of Amphilophocolea R.M. Schust. together with comments on the status of Tetracymbaliella Grolle and Lamellocolea R.M. Schust. Phytotaxa, 9, 41–52.
Feldberg, K., & Heinrichs, J. (2006). A taxonomic revision of Herbertus (Jungermanniidae: Herbertaceae) in the Neotropics based on nuclear and chloroplast DNA and morphology. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 151, 309–332.
Feldberg, K., Groth, H., Wilson, R., Schäfer-Verwimp, A., & Heinrichs, J. (2004). Cryptic speciation in Herbertus (Herbertaceae, Jungermanniopsida): range and morphology of Herbertus sendtneri inferred from nrITS sequences. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 249, 247–261.
Feldberg, K., Hentschel, J., Bombosch, A., Long, D. G., Váňa, J., & Heinrichs, J. (2009). Transfer of Gottschelia grollei, G. patoniae and Scaphophyllum speciosum to Solenostoma based on chloroplast DNA rbcL sequences. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 280, 243–250.
Feldberg, K., Váňa, J., Long, D. G., Shaw, A. J., Hentschel, J., & Heinrichs, J. (2010). A phylogeny of Adelanthaceae (Jungermanniales, Marchantiophyta) based on nuclear and chloroplast DNA markers, with comments on classification, cryptic speciation and biogeography. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 55, 293–304.
Feldberg, K., Heinrichs, J., Schmidt, A. R., Váňa, J., & Schneider, H. (2013). Exploring the impact of fossil constraints on the divergence time estimates of derived liverworts. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 299, 585–601.
Feldberg, K., Schneider, H., Stadler, T., Schäfer-Verwimp, A., Schmidt, A. R., & Heinrichs, J. (2014). Epiphytic leafy liverworts diversified in angiosperm-dominated forests. Scientific Reports, 4, 5974.
Felsenstein, J. (1985). Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution, 39, 783–791.
Forrest, L. L., Davis, E. C., Long, D. G., & Crandall-Stotler, B. J. (2006). Unraveling the evolutionary history of the liverworts (Marchantiophyta): multiple taxa, genomes and analyses. The Bryologist, 109, 303–334.
Fulford, M. H. (1968). Manual of the leafy Hepaticae—part III. Memoirs of the New York Botanical Garden, 11, 277–392.
Furuki, T., & Iwatsuki, Z. (1989). Mizutania riccardioides, gen. et spec. nov. (Mizutaniaceae, fam. nov.): a unique liverwort from tropical Asia. Journal of the Hattori Botanical Laboratory, 67, 291–296.
Fuselier, L., Davison, P. G., Clements, M., Shaw, B., Devos, N., Heinrichs, et al. (2009). Phylogeographic analyses reveal distinct lineages of Metzgeria furcata and M. conjugata (Metzgeriaceae) in Europe and North America. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 98, 745–756.
Fuselier, L., Shaw, B., Engel, J. J., von Konrat, M., Costa, D. P., Devos, N., et al. (2011). The status and phylogeography of the liverwort genus Apometzgeria Kuwah. (Metzgeriaceae). The Bryologist, 114, 92–101.
Gradstein, S. R., & Ilkiu-Borges, A. L. (2015). A taxonomic revision of the genus Odontoschisma (Marchantiophyta: Cephaloziaceae). Nova Hedwigia, 100, 15–100.
Gradstein, S. R., Churchill, S. P., & Salazar-Allen, N. (2001). Guide to the bryophytes of tropical America. Memoirs of the New York Botanical Garden, 86, 1–577.
Gradstein, S. R., Wilson, R., Ilkiu-Borges, A. L., & Heinrichs, J. (2006). Phylogenetic relationships and neotenic evolution of Metzgeriopsis (Lejeuneaceae) based on chloroplast DNA sequences and morphology. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 151, 293–308.
Gradstein, S. R., Aranda, S. C., & Vanderpoorten, A. (2014). Notes on early land plants today. 47. Transfer of Iwatsukia to Odontoschisma (Cephaloziaceae, Marchantiophyta). Phytotaxa, 162, 232–233.
Grolle, R., & Piippo, S. (1984). Bryophyte flora of the Huon Peninsula, Papua New Guinea. V. Lepidoziaceae subfam. Zoopsoideae and Cephaloziaceae subfam. Schiffnerioideae (Hepaticae). Annales Botanici Fennici, 21, 299–307.
Groth, H., Lindner, M., Wilson, R., Hartmann, F. A., Schmull, M., Gradstein, S. R., et al. (2003). Biogeography of Plagiochila (Hepaticae): natural species groups span several floristic kingdoms. Journal of Biogeography, 30, 965–978.
Guindon, S., & Gascuel, O. (2003). A simple, fast and accurate method to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Systematic Biology, 52, 696–704.
Hall, T. A. (1999). BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acid Symposia Series, 41, 95–98.
Hartmann, F. A., Wilson, R., Gradstein, S. R., Schneider, H., & Heinrichs, J. (2006). Testing hypotheses on species delimitations and disjunctions in the liverwort Bryopteris (Jungermanniopsida: Lejeuneaceae). International Journal of Plant Sciences, 167, 1205–1214.
He, X., & Glenny, D. (2010). Perssoniella and the genera of Schistochilaceae: a new classification based on molecular phylogenies. Australian Systematic Botany, 23, 229–238.
Hedenäs, L. (2008). Molecular variation and speciation in Antitrichia curtipendula s.l. (Leucodontaceae, Bryophyta). Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 156, 341–354.
Heinrichs, J., Gradstein, S. R., Wilson, R., & Schneider, H. (2005). Towards a natural classification of liverworts (Marchantiophyta) based on the chloroplast gene rbcL. Cryptogamie Bryologie, 26, 131–150.
Heinrichs, J., Hentschel, J., Feldberg, K., Bombosch, A., & Schneider, H. (2009). Phylogenetic biogeography and taxonomy of disjunctly distributed bryophytes. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 47, 497–508.
Heinrichs, J., Hentschel, J., Bombosch, A., Fiebig, A., Reise, J., Edelmann, M., et al. (2010). One species or at least eight? Delimitation and distribution of Frullania tamarisci (L.) Dumort. (Jungermanniopsida, Porellales) inferred from nuclear and chloroplast DNA markers. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 56, 1105–1114.
Heinrichs, J., Kreier, H.-P., Feldberg, K., Schmidt, A. R., Zhu, R. L., Shaw, B., et al. (2011). Formalizing morphologically cryptic biological entities: new insights from DNA taxonomy, hybridization, and biogeography in the leafy liverwort Porella platyphylla (Jungermanniopsida, Porellales). American Journal of Botany, 98, 1252–1262.
Heinrichs, J., Bombosch, A., Feldberg, K., Kreier, H.-P., Hentschel, J., Eckstein, J., et al. (2012a). A phylogeny of the northern temperate leafy liverwort genus Scapania (Scapaniaceae, Jungermanniales). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 62, 973–985.
Heinrichs, J., Dong, S., Yu, Y., Schäfer-Verwimp, A., Pócs, T., Feldberg, K., et al. (2012b). A 150-year old mystery solved: transfer of the rheophytic endemic liverwort Myriocolea irrorata to Colura. Phytotaxa, 66, 55–64.
Heinrichs, J., Dong, S., Schäfer-Verwimp, A., Pócs, T., Feldberg, K., Czumaj, A., et al. (2013). Molecular phylogeny of the leafy liverwort Lejeunea (Porellales). Evidence for a Neotropical origin, uneven distribution of sexual systems and insufficient taxonomy. PLoS ONE, 8, e82547.
Heinrichs, J., Feldberg, K., Bechteler, J., Scheben, A., Czumay, A., Pócs, T., et al. (2015). Integrative taxonomy of Lepidolejeunea (Porellales, Jungermanniopsida): ocelli allow the recognition of two neglected species. Taxon, 64, 216–228.
Hentschel, J., Wilson, R., Burghardt, M., Zündorf, H.-J., Schneider, H., & Heinrichs, J. (2006a). Reinstatement of Lophocoleaceae (Jungermanniopsida) based on chloroplast gene rbcL data: exploring the importance of female involucres for the systematics of Jungermanniales. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 258, 211–226.
Hentschel, J., Zündorf, H. J., Hellwig, F. H., Schäfer-Verwimp, A., & Heinrichs, J. (2006b). Taxonomic studies in Chiloscyphus Corda (Jungermanniales: Lophocoleaceae) based on nrITS sequences and morphology. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 262, 125–137.
He-Nygrén, X., Ahonen, I., Juslén, A., Glenny, D., & Piippo, S. (2004). Phylogeny of liverworts—beyond a leaf and a thallus. Monographs in Systematic Botany from the Missouri Botanical Garden, 98, 87–118.
He-Nygrén, X., Juslén, A., Ahonen, I., Glenny, D., & Piippo, S. (2006). Illuminating the evolutionary history of liverworts (Marchantiophyta)—towards a natural classification. Cladistics, 22, 1–31.
Hewitt, G. M. (1996). Some genetic consequences of ice ages, and their role in divergence and speciation. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 58, 247–276.
Hewitt, G. (2000). The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages. Nature, 405, 907–913.
Hillis, D. M., & Bull, J. J. (1993). An empirical test of bootstrapping as a method for assessing the confidence in phylogenetic analysis. Systematic Biology, 42, 182–192.
Hutsemekers, V., Vieira, C. C., Ros, R. M., Huttunen, S., & Vanderpoorten, A. (2012). Morphology informed by phylogeny reveals unexpected patterns of species differentiation in the aquatic moss Rhynchostegium riparioides s.l. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 62, 748–755.
Jablonski, D., Roy, K., & Valentine, J. W. (2006). Out of the tropics: evolutionary dynamics of the latitudinal diversity gradient. Science, 314, 102–106.
Kreier, H.-P., Feldberg, K., Mahr, F., Bombosch, A., Schmidt, A. R., Zhu, R.-L., et al. (2010). Phylogeny of the leafy liverwort Ptilidium: cryptic speciation and shared haplotypes between the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 57, 1260–1267.
Larget, B., & Simon, D. L. (1999). Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithms for the Bayesian analysis of phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 750–759.
Marshall, C. R. (2006). Fossil record reveals tropics as cradle and museum. Science, 313, 66–67.
Mason-Gamer, R. J., & Kellogg, E. A. (1996). Testing for phylogenetic conflict among molecular data sets in the tribe Triticeae (Gramineae). Systematic Biology, 45, 524–545.
Masuzaki, H., Shimamura, M., Furuki, T., Tsubota, H., Yamaguchi, T., Majid, H. M. A., et al. (2010). Systematic position of the enigmatic liverwort Mizutania (Mizutaniaceae, Marchantiophyta) inferred from molecular phylogenetic analyses. Taxon, 59, 448–458.
McKenna, D.D. & Farell, B.D. (2006). Tropical forests are both evolutionary cradles and museums of leaf beetle diversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science USA, 103, 10 947-10 951.
Miller, M.A., Pfeiffer, W., & Schwartz, T. (2010). Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), 14 Nov. 2010, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
Odrzykoski, I. J., Chudzińska, E., & Szweykowski, J. (1996). The hybrid origin of the polyploid liverwort Pellia borealis. Genetica, 98, 75–86.
Padial, J. M., Miralles, A., De la Riva, I., & Vences, M. (2010). The integrative future of taxonomy. Frontiers in Zoology, 2010, 7–16.
Paton, J. A. (1999). The liverwort flora of the British Isles. Colchester: Harley Books.
Patzak, S., Renner, M.A.M., Schäfer-Verwimp, A., Feldberg, K., Heslewood, M.M., Peralta, D. F., et al. (2016). A phylogeny of Lophocoleaceae-Plagiochilaceae-Brevianthaceae and a revised classification of Plagiochilaceae. Organisms Diversity and Evolution, doi 10.1007/s13127-015-0258-y.
Piippo, S. (1984). Bryophyte flora of the Huon Peninsula, Papua New Guinea. VI: Lepidoziaceae subfam. Lepidozioideae, Calypogeiaceae, Adelanthaceae, Cephaloziaceae subfam. Cephalozioideae and subfam. Odontoschismatoideae and Jubulaceae (Hepaticae). Annales Botanici Fennici, 21, 309–334.
Posada, D. (2008). jModelTest: phylogenetic model averaging. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 25, 1253–1256.
Potemkin, A. D., & Sofronova, E. A. (2013). Taxonomic study of Cephalozia in Russia and circumscription of the genus. Arctoa, 22, 173–206.
Ramaiya, M., Johnston, M. G., Shaw, B., Heinrichs, J., Hentschel, J., von Konrat, M., et al. (2010). Morphologically cryptic biological species within the liverwort Frullania asagrayana. American Journal of Botany, 97, 1707–1718.
Renner, M. A. M. (2014). Radula subg. Radula in Australasia and the Pacific (Jungermanniopsida). Telopea, 17, 107–167.
Renner, M. A. M., Devos, N., Brown, E. A., & von Konrat, M. J. (2013a). New records, replacements, reinstatements and four new species in the Radula parvitexta and R. ventricosa groups (Jungermanniopsida) in Australia: cases of mistaken identity. Australian Systematic Botany, 26, 298–345.
Renner, M. A. M., Devos, N., Patiño, J., Brown, E. A., Orme, A., Elgey, M., et al. (2013b). Integrative taxonomy resolves the cryptic and pseudo-cryptic Radula buccinifera complex (Porellales, Jungermanniopsida), including two reinstated and five new species. Phytokeys, 27, 1–113.
Rodríguez, F., Oliver, J. L., Martin, A., & Medina, J. R. (1990). The general stochastic model of nucleotide substitution. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 142, 485–501.
Ronquist, F., & Huelsenbeck, J. P. (2003). MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics, 19, 1572–1574.
Rycroft, D. S., Groth, H., & Heinrichs, J. (2004). Reinstatement of Plagiochila maderensis (Jungermanniopsida: Plagiochilaceae) based on chemical evidence and nrDNA ITS sequences. Journal of Bryology, 26, 37–45.
Schuster, R. M. (1974). The Hepaticae and Anthocerotae of North America east of the hundredth meridian (Vol. 3). New York and London: Columbia University Press.
Schuster, R. M. (2002). Austral Hepaticae Part II. Beihefte Nova Hedwigia, 119, 1–606.
Shaw, A. J. (2001). Biogeographic patterns and cryptic speciation in bryophytes. Journal of Biogeography, 28, 253–261.
Shaw, A. J., Boles, S., & Shaw, B. (2008). A phylogenetic delimitation of the “Sphagnum subsecundum complex” (Sphagnaceae, Bryophyta). American Journal of Botany, 95, 731–744.
Shaw, B., Crandall-Stotler, B., Váňa, J., Stotler, R. E., von Konrat, M., Engel, J. J., et al. (2015). Phylogenetic relationships and morphological evolution in a major clade of leafy liverworts (phylum Marchantiophyta, order Jungermanniales): suborder Jungermanniineae. Systematic Botany, 40, 27–45.
Silvestro, D., & Michalak, I. (2012). RaxmlGUI: a graphical front-end for RaxML. Organisms Diversity and Evolution, 12, 335–337.
Söderström, L., Hagborg, A., von Konrat, M., Bartholomew-Began, S., Bell, D., Briscoe, L., et al. (2016). World checklist of hornworts and liverworts. PhytoKeys, 59, 1–828.
Stamatakis, A. (2014). RaxML Version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics, doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/BTU033.
Taberlet, P., Gielly, L., Pautou, G., & Bouvet, J. (1991). Universal primers for amplification of three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Plant Molecular Biology, 17, 1105–1109.
Váňa, J. (1988). Cephalozia (Dum.) Dum. in Africa, with notes on the genus (Notes on some African Hepatic Genera 10). Beihefte Nova Hedwigia, 90, 179–198.
Váňa, J., & Long, D. G. (2011). Cephaloziaceae (Marchantiophyta) of the Sino-Himalayan region. Nova Hedwigia, 93, 153–164.
Váňa, J., Söderström, L., Hagborg, A., & von Konrat, M. (2013). Notes on Early Land Plants Today. 41. New combinations and synonyms in Cephaloziaceae (Marchantiophyta). Phytotaxa, 112, 7–15.
Vanderpoorten, A., Schäfer-Verwimp, A., Heinrichs, J., Devos, N., & Long, D. G. (2010). The taxonomy of the leafy liverwort genus Leptoscyphus (Lophocoleaceae) revisited. Taxon, 59, 176–186.
Villarreal, J. C., Crandall-Stotler, B. J., Hollingsworth, M. L., Long, D. G., & Forrest, L. L. (2016). Divergence times and the evolution of morphological complexity in an early land plant lineage (Marchantiopsida) with a slow molecular rate. New Phytologist, 209, 1734–1746.
Vilnet, A. A., Konstantinova, N. A., & Troitsky, A. V. (2010). Molecular insight on phylogeny and systematics of Lophoziaceae, Scapaniaceae, Gymnomitriaceae and Jungermanniaceae. Arctoa, 19, 31–50.
Vilnet, A. A., Konstantinova, N. A., & Troitsky, A. V. (2012). Molecular phylogeny and systematics of the suborder Cephaloziineae with special attention to the family Cephaloziaceae s.l. (Jungermanniales, Marchantiophyta). Arctoa, 21, 113–132.
Wang, J., Gradstein, S. R., Shi, X.-Q., & Zhu, R.-L. (2014). Phylogenetic position of Trocholejeunea and a new infrageneric classification of Acrolejeunea. Bryophyte Diversity and Evolution, 1, 31–44.
Wilson, R., Gradstein, S. R., Heinrichs, J., Groth, H., Ilkiu-Borges, A. L., & Hartmann, F. A. (2004). Phylogeny of Lejeuneaceae: a cladistic analysis of chloroplast gene rbcL sequences and morphology with preliminary comments on the mitochondrial nad4-2 spacer region. Monographs in Systematic Botany from the Missouri Botanical Garden, 98, 189–202.
Acknowledgments
We thank the directors and curators of the Göttingen University Herbarium (GOET), the Herbarium Haussknecht (JE), the Bavarian State collection for Botany (M), and the Herbarium of the Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh (E) for the loan of specimens and the permission for destructive sampling, and the staff members of the LMU Genomics Service unit for support. Parts of this study were supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG grant HE 3854 / 4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file 1: Table S1
Taxa used in the present study, including information about the origin of the studied material, voucher information, as well as GenBank accession numbers. Newly generated sequences in bold. (DOC 293 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feldberg, K., Váňa, J., Krusche, J. et al. A phylogeny of Cephaloziaceae (Jungermanniopsida) based on nuclear and chloroplast DNA markers. Org Divers Evol 16, 727–742 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13127-016-0284-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13127-016-0284-4