Abstract
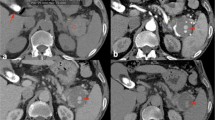
After the liver, the spleen is the second most commonly injured organ in blunt abdominal trauma. The past two decades have witnessed a trend towards non-surgical management of these injuries, and transarterial embolization (TAE) has greatly contributed to avoiding unnecessary laparotomies, especially in haemodynamically stable patients. We present the case of a 21-year-old male patient involved in a motor accident with subsequent injury of the left thorax and fracture of the left ulna. Abdominal computed tomography revealed the presence of a parenchymal haematoma and a pseudoaneurysm of the splenic artery. Since the patient was haemodynamically stable, he was admitted to the clinic and the pseudoaneurysm was treated with distal selective TAE. Six months later, he remains asymptomatic without signs of pathology on Doppler ultrasound at follow-up. The use of these modalities can contribute to better success rates of NOM and should be readily available at any hospital treating trauma patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith J, Caldwell E, D’Amours S, Jalaludin B, Sugrue M. Abdominal trauma: a disease in evolution. ANZ J Surg 2005;75:790–794
Gopal V, Bisno AL. Fulminant pneumococcal infections in “normal” asplenic hosts. Arch Int Med 1977;137:1526–1530
Holdsworth RJ, Irving AD, Cuschieri AL. Postsplenectomy sepsis and its mortality rate: actual versus perceived risks. Br J Surg 1991;78:1031–1038
Rozycki GS, Ochsner MG, Schmidt JA et al. A prospective study of surgeon-performed ultrasound as the primary adjuvant modality for injured patient assessment. J. Trauma 1995;39:492–498
Thompson BE, Munera F, Cohn SM, et al. Novel computed tomography scan scoring system predicts the need for intervention after splenic injury. J Trauma 2006;60:1083–1086.
Moore EE, Cogbill TH, Jurkovich GJ, et al. Organ injury scaling: spleen and liver (1994 revision). J Trauma 1995;38:323–324.
Sutyak JP, Chiu WC, D’Amelio LF, et al. Computed tomography is inaccurate in estimating the severity of adult splenic injury. J Trauma 1995;39:514–518.
Becker CD, Mentha G, Terrier F. Blunt abdominal trauma in adults: role of CT in the diagnosis and management of visceral injuries. Part 1: liver and spleen. Eur Radiol 1998;8:553–562.
Becker CD, Spring P, Glattli A, et al. Blunt splenic trauma in adults: Can CT findings be used to determine the need for surgery? AJR Am J Roentgenol 1994;162: 343–347.
Marmery H, Shanmuganathan K, Alexander MT, et al. Optimization of selection for nonoperative management of blunt splenic injury: comparison of MDCT grading systems. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2007;189:1421–1427.
Gavant ML, Schurr M, Flick PA, Croce MA, Fabian TC, Gold RE. Predicting clinical outcome of nonsurgical management of blunt splenic injury: using CT to revea abnormalities of splenic vasculature. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1997;168:207–212
Sclafani SJ, Shaftan GW, Scalea TM et al. Nonoperative salvage of computed tomography-diagnosed splenic injuries: utilization of angiography for triage and embolization for hemostasis. J Trauma 1995;39:818–825
Hagiwara A, Yukioka T, Ohta S, Nitatori T, Matsuda H, Shimazaki S. Nonsurgical management of patients with blunt splenic injury: efficacy of transcatheter arterial embolization. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1996;167:159–166
Davis KA, Fabian TC, Croce MA, et al. Improved success in nonoperative management of blunt splenic injuries: embolization of splenic artery pseudoaneurysms. J Trauma 1998;44:1008–1013; discussion 1013–1015.
Haan J, Ilahi ON, Kramer M, et al. Protocol-driven nonoperative management in patients with blunt splenic trauma and minimal associated injury decreases length of stay. J Trauma 2003;55:317–321; discussion 321–2.
Haan JM, Biffl W, Knudson MM, et al. Splenic embolization revisited: a multicenter review. J Trauma 2004;56:542–547.
Keramidas DC. The ligation of the splenic artery in the treatment of traumatic rupture of the spleen. Surgery 1979;85:530–533.
Bessoud B, Duchosal MA, Siegrist CA et al. Proximal splenic artery embolization for blunt splenic injury: clinical, immunologic, and ultrasound-Doppler follow-up. J Trauma 2007;62:1481–1486
Tominaga GT, Simon FJ Jr, Dandan IS et al. Immunologic function after splenic embolization, is there a difference? J Trauma 2009;67:289–295
Falimirski M, Syed A, Prybilla D. Immunocompetence of the severely injured spleen verified by differential interference contrast microscopy: the red blood cell pit test. J Trauma 2007;63(5):1087–1091
Webb CW, Crowell K, Cravens D. Clinical inquiries. Which vaccinations are indicated after splenectomy? J Fam Pract 2006;55:711–712.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dikaiakos, P., Paschalidis, N., Markakis, C. et al. Angiographic embolization of a post-traumatic splenic pseudoaneurysm. Hellenic J Surg 85, 207–211 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13126-013-0039-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13126-013-0039-z