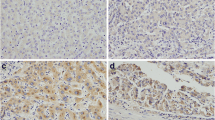
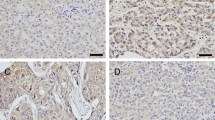
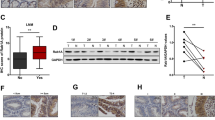
Abstract
Recent studies suggest that Rab11-family interacting proteins (Rab11-FIPs) play an important role in tumorigenesis and progression. Among the Rab11-FIPs, Rab11-FIP4 has been reported to be significantly upregulated in various cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the possible effect on HCC stemness and the underlying mechanism has never been characterized. Here, we found that Rab11-FIP4 was dramatically increased in HCC cell lines and tissues, and had a positive correlation with cancer stemness. Functional studies revealed that elevated expression of Rab11-FIP4 in HCC cells significantly promoted sphere formation, and enhanced the mRNA and protein levels of stemness-associated markers, ALDH1A1, CD133, NANOG, and OCT4. Conversely, the knockdown of Rab11-FIP4 suppressed the cancer stem cell (CSC)-like characteristics of HCC cells. Moreover, silencing of Rab11-FIP4 obviously increased the sensitivity of HCC cells to sorafenib. Mechanistically, Rab11-FIP4 was shown to interact with ADP-ribosylation factor 5 (ARF5) to influence cell cycle-related proteins, CDK1/cyclin B, thereby promoting HCC stemness. Taken together, our results uncovered an essential role for Rab11-FIP4 in regulating CSC-like features of HCC cells and identified Rab11-FIP4 as a potential target for HCC therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Abbreviations
- NANOG:
-
Nanog homeobox
- SOX2:
-
SRY-Box transcription factor 2
- KLF4:
-
KLF transcription factor 4
- OCT4:
-
POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1
- ERK1:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3
- ERK2:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1
- AKT:
-
AKT serine/threonine kinase
- PRAS40:
-
AKT1 substrate 1
- CDK1:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium
- MEM:
-
Minimum essential medium
- RPMI-1640:
-
Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- RT-qPCR:
-
Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- RIPA:
-
Radio immunoprecipitation assay
- CCK-8:
-
Cell counting kit-8
- DMEM/F12:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle media: nutrient mixture F-12
- IgG:
-
Immunoglobulin G
- RT:
-
Room temperature
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- CD133:
-
Prominin 1
- ALDH1A1:
-
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family member A1
- DYTN:
-
Dystrotelin
- EXOC7:
-
Exocyst Complex Component 7
- MYO1D:
-
Myosin ID
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- CDK1:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1
- CCNB1:
-
Cyclin B1
- CCNB1:
-
Cyclin B2
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Chen LT, Martinelli E, Cheng AL, Pentheroudakis G, Qin S, Bhattacharyya GS, Ikeda M, Lim HY, Ho GF, Choo SP, Ren Z, Malhotra H, Ueno M, Ryoo BY, Kiang TC, Tai D, Vogel A, Cervantes A, Lu SN et al (2020) Pan-Asian adapted ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with intermediate and advanced/relapsed hepatocellular carcinoma: a TOS-ESMO initiative endorsed by CSCO, ISMPO, JSMO, KSMO, MOS and SSO. Ann Oncol 31(3):334–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2019.12.001
Chiba T, Iwama A, Yokosuka O (2016) Cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma: therapeutic implications based on stem cell biology. Hepatol Res 46(1):50–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/hepr.12548
Chiba T, Kamiya A, Yokosuka O, Iwama A (2009) Cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma: recent progress and perspective. Cancer Lett 286(2):145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2009.04.027
D'Souza RS, Lim JY, Turgut A, Servage K, Zhang J, Orth K, Sosale NG, Lazzara MJ, Allegood J, Casanova JE (2020) Calcium-stimulated disassembly of focal adhesions mediated by an ORP3/IQSec1 complex. Elife 9:e54113. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.54113
D'Souza-Schorey C, Chavrier P (2006) ARF proteins: roles in membrane traffic and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7(5):347–358. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1910
Dean M, Fojo T, Bates S (2005) Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer 5(4):275–284. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1590
Fielding AB, Schonteich E, Matheson J, Wilson G, Yu X, Hickson GR, Srivastava S, Baldwin SA, Prekeris R, Gould GW (2005) Rab11-FIP3 and FIP4 interact with Arf6 and the exocyst to control membrane traffic in cytokinesis. EMBO J 24(19):3389–3399. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600803
Gordan JD, Kennedy EB, Abou-Alfa GK, Beg MS, Brower ST, Gade TP, Goff L, Gupta S, Guy J, Harris WP, Iyer R, Jaiyesimi I, Jhawer M, Karippot A, Kaseb AO, Kelley RK, Knox JJ, Kortmansky J, Leaf A et al (2020) Systemic therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: ASCO guideline. J Clin Oncol 38(36):4317–4345. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.20.02672
Gupta PB, Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA (2009) Cancer stem cells: mirage or reality? Nat Med 15(9):1010–1012. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0909-1010
He Y, Ye M, Zhou L, Shan Y, Lu G, Zhou Y, Zhong J, Zheng J, Xue Z, Cai Z (2017) High Rab11-FIP4 expression predicts poor prognosis and exhibits tumor promotion in pancreatic cancer. Int J Oncol 50(2):396–404. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2016.3828
Hu F, Deng X, Yang X, Jin H, Gu D, Lv X, Wang C, Zhang Y, Huo X, Shen Q, Luo Q, Zhao F, Ge T, Zhao F, Chu W, Shu H, Yao M, Fan J, Qin W (2015) Hypoxia upregulates Rab11-family interacting protein 4 through HIF-1alpha to promote the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 34(49):6007–6017. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.49
Jeng KS, Chang CF, Sheen IS, Jeng CJ, Wang CH (2023) Cellular and molecular biology of cancer stem cells of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 24(2):1417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021417
Kim HJ, Jeong J, Park S, Jin YW, Lee SS, Lee SB, Choi D (2017) Establishment of hepatocellular cancer induced pluripotent stem cells using a reprogramming technique. Gut Liver 11(2):261–269. https://doi.org/10.5009/gnl15389
Krzyzaniak MA, Mach M, Britt WJ (2009) HCMV-encoded glycoprotein M (UL100) interacts with Rab11 effector protein FIP4. Traffic 10(10):1439–1457. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00967.x
Kulasekaran G, Chaineau M, Piscopo VEC, Verginelli F, Fotouhi M, Girard M, Tang Y, Dali R, Lo R, Stifani S, McPherson PS (2021) An Arf/Rab cascade controls the growth and invasiveness of glioblastoma. J Cell Biol 220(2):e202004229. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.202004229
Lee TK, Guan XY, Ma S (2022) Cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma - from origin to clinical implications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 19(1):26–44. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-021-00508-3
Li XY, Shen Y, Zhang L, Guo X, Wu J (2022) Understanding initiation and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through single cell sequencing. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1877(3):188720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2022.188720
Man KF, Ma S (2022) Mechanisms of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in liver cancer stem cells and potential therapeutic approaches. Essays Biochem 66(4):371–386. https://doi.org/10.1042/EBC20220001
Meyers JM, Prekeris R (2002) Formation of mutually exclusive Rab11 complexes with members of the family of Rab11-interacting proteins regulates Rab11 endocytic targeting and function. J Biol Chem 277(50):49003–49010. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M205728200
Michowski W, Chick JM, Chu C, Kolodziejczyk A, Wang Y, Suski JM, Abraham B, Anders L, Day D, Dunkl LM, Li Cheong Man M, Zhang T, Laphanuwat P, Bacon NA, Liu L, Fassl A, Sharma S, Otto T, Jecrois E et al (2020) Cdk1 controls global epigenetic landscape in embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell 78(3):459–476 e413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2020.03.010
Moravec R, Conger KK, D’Souza R, Allison AB, Casanova JE (2012) BRAG2/GEP100/IQSec1 interacts with clathrin and regulates alpha5beta1 integrin endocytosis through activation of ADP ribosylation factor 5 (Arf5). J Biol Chem 287(37):31138–31147. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.383117
Muto A, Aoki Y, Watanabe S (2007) Mouse Rab11-FIP4 regulates proliferation and differentiation of retinal progenitors in a Rab11-independent manner. Dev Dyn 236(1):214–225. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.21009
Muto A, Arai K, Watanabe S (2006) Rab11-FIP4 is predominantly expressed in neural tissues and involved in proliferation as well as in differentiation during zebrafish retinal development. Dev Biol 292(1):90–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.12.050
Ravindran Menon D, Luo Y, Arcaroli JJ, Liu S, KrishnanKutty LN, Osborne DG, Li Y, Samson JM, Bagby S, Tan AC, Robinson WA, Messersmith WA, Fujita M (2018) CDK1 interacts with Sox2 and promotes tumor initiation in human melanoma. Cancer Res 78(23):6561–6574. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0330
Song F, Zhang Y, Pan Z, Hu X, Yi Y, Zheng X, Wei H, Huang P (2021) Identification of novel key genes associated with the metastasis of prostate cancer based on bioinformatics prediction and validation. Cancer Cell Int 21(1):559. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-02258-3
Song F, Zhang Y, Pan Z, Hu X, Zhang Q, Huang F, Ye X, Huang P (2021) The role of alcohol dehydrogenase 1C in regulating inflammatory responses in ulcerative colitis. Biochem Pharmacol 192:114691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114691
Tsui YM, Chan LK, Ng IO (2020) Cancer stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma: mechanisms and translational potential. Br J Cancer 122(10):1428–1440. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-020-0823-9
Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ (2008) Cancer stem cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved questions. Nat Rev Cancer 8(10):755–768. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2499
Wang H, Lu Z, Zhao X (2019) Tumorigenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic potential of exosomes in liver cancer. J Hematol Oncol 12(1):133. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0806-6
Wang JZ, Yang SX, Ye F, Xia XP, Shao XX, Xia SL, Zheng B, Xu CL (2018) Hypoxia-induced Rab11-family interacting protein 4 expression promotes migration and invasion of colon cancer and correlates with poor prognosis. Mol Med Rep 17(3):3797–3806. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.8283
Welz T, Wellbourne-Wood J, Kerkhoff E (2014) Orchestration of cell surface proteins by Rab11. Trends Cell Biol 24(7):407–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2014.02.004
Wu CX, Wang XQ, Chok SH, Man K, Tsang SHY, Chan ACY, Ma KW, Xia W, Cheung TT (2018) Blocking CDK1/PDK1/beta-Catenin signaling by CDK1 inhibitor RO3306 increased the efficacy of sorafenib treatment by targeting cancer stem cells in a preclinical model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics 8(14):3737–3750. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.25487
Xiao Y, Li Y, Shi D, Wang X, Dai S, Yang M, Kong L, Chen B, Huang X, Lin C, Liao W, Xu B, Chen X, Wang L, Chen X, Ouyang Y, Liu G, Li H, Song L (2022) MEX3C-mediated decay of SOCS3 mRNA promotes JAK2/STAT3 signaling to facilitate metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 82(22):4191–4205. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-1203
Yan Q, Fang X, Li C, Lan P, Guan X (2022) Oncofetal proteins and cancer stem cells. Essays Biochem 66(4):423–433. https://doi.org/10.1042/EBC20220025
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82003853), Zhejiang Province Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LQ20H310005 and No. LYY21H310009), Medical and Health Research Program of Zhejiang (No. 2021KY046 and No. 2022KY047), and Leading Talent of “Ten Thousand Plan”—National High-Level Talents Special Support Plan and the Science Technology Plan Project of Zhejiang Province (No. 2020R52029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P. H. and F. S. designed the study. P. H. and Y. Z. supervised the study. F. S., Q. Z., X. L., and T. X. jointly performed the experiments. Q. H., X. H., and W. F. analyzed the data. F. S. wrote the manuscript. P. H. and Y. Z. revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital (approved code NO. KT2022041).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key points
• RAB11-FIP4 promotes stemness and increases sorafenib resistance in HCC.
• Rab11-FIP4 interacts with ARF5 to promote stemness in HCC.
• Rab11-FIP4 promotes HCC stemness via influencing the CDK1/cyclin B complex.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 738 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, F., Zhang, Q., Lu, X. et al. Rab11-FIP4 interacts with ARF5 to promote cancer stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Physiol Biochem 79, 757–770 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-023-00972-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-023-00972-2