Abstract
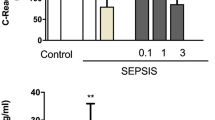
Accumulating evidence suggest that ghrelin plays a role as an antiseptic peptide. The present study aimed to clarify whether the brain may be implicated ghrelin’s antiseptic action. We examined the effect of brain ghrelin on survival in a novel endotoxemic model achieved by treating rats with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and colchicine. The observation of survival stopped three days after chemicals’ injection or at death. Intracisternal ghrelin dose-dependently reduced lethality in the endotoxemic model; meanwhile, neither intraperitoneal injection of ghrelin nor intracisternal des-acyl-ghrelin injection affected the mortality rate. The brain ghrelin-induced lethality reduction was significantly blocked by surgical vagotomy. Moreover, intracisternal injection of a ghrelin receptor antagonist blocked the improved survival achieved by intracisternal ghrelin injection or intravenous 2-deoxy-d-glucose administration. Intracisternal injection of an adenosine A2B receptor agonist reduced the lethality and the ghrelin-induced improvement of survival was blocked by adenosine A2B receptor antagonist. I addition, intracisternal ghrelin significantly blocked the colonic hyperpermeability produced by LPS and colchicine. These results suggest that ghrelin acts centrally to reduce endotoxemic lethality. Accordingly, activation of the vagal pathway and adenosine A2B receptors in the brain may be implicated in the ghrelin-induced increased survival. Since the efferent vagus nerve mediates anti-inflammatory mechanisms, we speculate that the vagal cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway is implicated in the decreased septic lethality caused by brain ghrelin.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Some data may not be made available because of privacy or ethical restrictions.
References
Angus DC, van der Poll T (2013) Severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med 369(9):840–851. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1208623
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H, Botchkina GI, Watkins LR et al (2000) Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature. 405(6785):458–462. https://doi.org/10.1038/35013070
Camici M, Garcia-Gil M, Tozzi MG (2018) The Inside Story of Adenosine. Int J Mol Sci 19(3):784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030784
Cecconi M, Evans L, Levy M, Rhodes A (2018) Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet 392(10141):75–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)30696-2
Cowley MA, Smith RG, Diano S, Tschöp M, Pronchuk N, Grove KL et al (2003) The distribution and mechanism of action of ghrelin in the CNS demonstrates a novel hypothalamic circuit regulating energy homeostasis. Neuron. 37(4):649–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00063-1
Dai C, Guandalini S, Zhao DH, Jiang M (2012) Antinociceptive effect of VSL#3 on visceral hypersensitivity in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome: a possible action through nitric oxide pathway and enhance barrier function. Mol Cell Biochem 362(1-2):43–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1126-5
De-Souza DA, Greene LJ (2005) Intestinal permeability and systemic infections in critically ill patients: effect of glutamine. Crit Care Med 33(5):1125–1135. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ccm.0000162680.52397.97
Dixit VD, Schaffer EM, Pyle RS, Collins GD, Sakthivel SK, Palaniappan R et al (2004) Ghrelin inhibits leptin- and activation-induced proinflammatory cytokine expression by human monocytes and T cells. J Clin Invest 114(1):57–66. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci21134
Elenkov IJ, Wilder RL, Chrousos GP, Vizi ES (2000) The sympathetic nerve--an integrative interface between two supersystems: the brain and the immune system. Pharmacol Rev 52(4):595–638
Gilg S, Lutz TA (2006) The orexigenic effect of peripheral ghrelin differs between rats of different age and with different baseline food intake, and it may in part be mediated by the area postrema. Physiol Behav 87(2):353–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2005.10.015
Goyal RK, Guo Y, Mashimo H (2019) Advances in the physiology of gastric emptying. Neurogastroenterol Motil 31(4):e13546. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13546
Hosoda H, Kojima M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K (2000) Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin: two major forms of rat ghrelin peptide in gastrointestinal tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 279(3):909–913. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2000.4039
Igarashi S, Nozu T, Ishioh M, Kumei S, Saito T, Toki Y et al (2020) Centrally administered orexin prevents lipopolysaccharide and colchicine induced lethality via the vagal cholinergic pathway in a sepsis model in rats. Biochem Pharmacol 182:114262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114262
Ishioh M, Nozu T, Igarashi S, Tanabe H, Kumei S, Ohhira M et al (2020) Ghrelin acts in the brain to block colonic hyperpermeability in response to lipopolysaccharide through the vagus nerve. Neuropharmacology. 173:108116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108116
Ishioh M, Nozu T, Igarashi S, Tanabe H, Kumei S, Ohhira M et al (2021) Activation of central adenosine A2B receptors mediate brain ghrelin-induced improvement of intestinal barrier function through the vagus nerve in rats. Exp Neurol 341:113708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113708
Kanda Y (2013) Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software 'EZR' for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant 48(3):452–458. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.244
Kitajima S, Takuma S, Morimoto M (1999) Changes in colonic mucosal permeability in mouse colitis induced with dextran sulfate sodium. Exp Anim 48(3):137–143. https://doi.org/10.1538/expanim.48.137
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K (1999) Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 402(6762):656–660. https://doi.org/10.1038/45230
Korbonits M, Goldstone AP, Gueorguiev M, Grossman AB (2004) Ghrelin--a hormone with multiple functions. Front Neuroendocrinol 25(1):27–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2004.03.002
Lange S, Delbro DS, Jennische E (1994) Evans blue permeation of intestinal mucosa in the rat. Scand J Gastroenterol 29(1):38–46. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365529409090435
Li Y, Wu X, Zhao Y, Chen S, Owyang C (2006) Ghrelin acts on the dorsal vagal complex to stimulate pancreatic protein secretion. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290(6):G1350–G1358. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00493.2005
Mathur N, Mehdi SF, Anipindi M, Aziz M, Khan SA, Kondakindi H et al (2020) Ghrelin as an Anti-Sepsis Peptide: Review. Front Immunol 11:610363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.610363
Nikitopoulou I, Kampisiouli E, Jahaj E, Vassiliou AG, Dimopoulou I, Mastora Z et al (2020) Ghrelin alterations during experimental and human sepsis. Cytokine. 127:154937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154937
Nozu T, Miyagishi S, Kumei S, Nozu R, Takakusaki K, Okumura T (2018a) Glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, liraglutide, improves visceral sensation and gut permeability in rats. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 33(1):232–239. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.13808
Nozu T, Miyagishi S, Kumei S, Nozu R, Takakusaki K, Okumura T (2018c) Lovastatin inhibits visceral allodynia and increased colonic permeability induced by lipopolysaccharide or repeated water avoidance stress in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 818:228–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.10.056
Nozu T, Miyagishi S, Nozu R, Takakusaki K, Okumura T (2018b) Altered colonic sensory and barrier functions by CRF: roles of TLR4 and IL-1. J Endocrinol 239(2):241–252. https://doi.org/10.1530/joe-18-0441
Ogawa Y, Irukayama-Tomobe Y, Murakoshi N, Kiyama M, Ishikawa Y, Hosokawa N et al (2016) Peripherally administered orexin improves survival of mice with endotoxin shock. Elife. 5:e21055. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21055
Okumura T, Fukagawa K, Tso P, Taylor IL, Pappas TN (1994) Intracisternal injection of apolipoprotein A-IV inhibits gastric secretion in pylorus-ligated conscious rats. Gastroenterology. 107(6):1861–1864. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(94)90833-8
Okumura T, Namiki M (1990) Vagal motor neurons innervating the stomach are site-specifically organized in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve in rats. J Auton Nerv Syst 29(2):157–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1838(90)90181-h
Okumura T, Nozu T, Ishioh M, Igarashi S, Kumei S, Ohhira M (2020) Brain orexin improves intestinal barrier function via the vagal cholinergic pathway. Neurosci Lett 714:134592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134592
Pavlov VA, Tracey KJ (2004) Neural regulators of innate immune responses and inflammation. Cell Mol Life Sci 61(18):2322–2331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4102-3
Pavlov VA, Wang H, Czura CJ, Friedman SG, Tracey KJ (2003) The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: a missing link in neuroimmunomodulation. Mol Med 9(5-8):125–134
Sato N, Kanai S, Takano S, Kurosawa M, Funakoshi A, Miyasaka K (2003) Central administration of ghrelin stimulates pancreatic exocrine secretion via the vagus in conscious rats. Jpn J Physiol 53(6):443–449. https://doi.org/10.2170/jjphysiol.53.443
Smart D, Sabido-David C, Brough SJ, Jewitt F, Johns A, Porter RA et al (2001) SB-334867-A: the first selective orexin-1 receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol 132(6):1179–1182. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0703953
Swartz EM, Browning KN, Travagli RA, Holmes GM (2014) Ghrelin increases vagally mediated gastric activity by central sites of action. Neurogastroenterol Motil 26(2):272–282. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12261
Takahashi N, Okumura T, Yamada H, Kohgo Y (1999) Stimulation of gastric acid secretion by centrally administered orexin-A in conscious rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 254(3):623–627. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1998.9994
Toshinai K, Yamaguchi H, Sun Y, Smith RG, Yamanaka A, Sakurai T et al (2006) Des-acyl ghrelin induces food intake by a mechanism independent of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Endocrinology. 147(5):2306–2314. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2005-1357
Tracey KJ (2002) The inflammatory reflex. Nature. 420(6917):853–859. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01321
Tracey KJ (2007) Physiology and immunology of the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway. J Clin Invest 117(2):289–296. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI30555
Traebert M, Riediger T, Whitebread S, Scharrer E, Schmid HA (2002) Ghrelin acts on leptin-responsive neurones in the rat arcuate nucleus. J Neuroendocrinol 14(7):580–586. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2826.2002.00810.x
Ukena SN, Singh A, Dringenberg U, Engelhardt R, Seidler U, Hansen W et al (2007) Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 inhibits leaky gut by enhancing mucosal integrity. PloS One 2(12):e1308. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001308
Wang W, Bansal S, Falk S, Ljubanovic D, Schrier R (2009) Ghrelin protects mice against endotoxemia-induced acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297(4):F1032–F1037. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00044.2009
Ziegler TR, Smith RJ, O'Dwyer ST, Demling RH, Wilmore DW (1988) Increased intestinal permeability associated with infection in burn patients. Arch Surg 123(11):1313–1319. https://doi.org/10.1001/archsurg.1988.01400350027003
Zigman JM, Jones JE, Lee CE, Saper CB, Elmquist JK (2006) Expression of ghrelin receptor mRNA in the rat and the mouse brain. J Comp Neurol 494(3):528–548. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.20823
Funding
This work was supported in part by grants-in-aid from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan [19K08410 (TO) and 18K07896 (TN)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SI: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing-original draft, TN: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing-original draft, MI: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, TF: Formal analysis, Investigation, CS: Formal analysis, Investigation, TS: Formal analysis, Investigation, MH: Formal analysis, Investigation, YT: Formal analysis, Investigation, MY: Formal analysis, Investigation, MS: Formal analysis, Investigation, HT: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, TO: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing-original draft. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Ethical considerations
Approval was obtained from the Research and Development and Animal Care committees at Asahikawa Medical University (No. 13030) for all of the experiments conducted in this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key Points
• Ghrelin acts centrally to improve survival in a rat endotoxemic lethality model.
• Improvement of survival by ghrelin was not observed in vagotomized rats.
• Ghrelin-induced improvement was blocked by adenosine A2B receptor antagonist.
• Ghrelin improves survival via the vagal pathway and adenosine signal in sepsis.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Igarashi, S., Nozu, T., Ishioh, M. et al. Ghrelin prevents lethality in a rat endotoxemic model through central effects on the vagal pathway and adenosine A2B signaling. J Physiol Biochem 79, 625–634 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-023-00962-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-023-00962-4