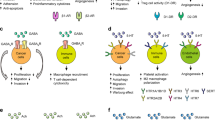
Abstract
Tachykinins (TKs) include an evolutionarily conserved group of small bio-active peptides which possess a common carboxyl-terminal sequence, Phe-X-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2. TKs also have been shown to have implications in different steps of carcinogenesis, such as angiogenesis, mitogenesis, metastasis, and other growth-related events. The biological actions of substance P (SP), as the most important member of the TK family, are mainly mediated through a G protein-coupled receptor named neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R). More recently, it has become clear that SP/NK1R system is involved in the initiation and activation of signaling pathways involved in cancer development and progression. Therefore, SP may contribute to triggering a variety of effector mechanisms including protein synthesis and a number of transcription factors that modulate the expression of genes involved in these processes. The overwhelming insights into the blockage of NK1R using specific antagonists could suggest a therapeutic approach in cancer therapy. In this review, we focus on evidence supporting an association between the signaling pathways of the SP/NK1R system and cancer cell proliferation and development.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham AG, O’Neill E (2014) PI3K/Akt-mediated regulation of p53 in cancer. Portland Press Limited, London
Akazawa T, Kwatra SG, Goldsmith LE, Richardson MD, Cox EA, Sampson JH, Kwatra MM (2009) A constitutively active form of neurokinin 1 receptor and neurokinin 1 receptor-mediated apoptosis in glioblastomas. J Neurochem 109:1079–1086
Bayati S, Bashash D, Ahmadian S, Safaroghli-Azar A, Alimoghaddam K, Ghavamzadeh A, Ghaffari SH (2016) Inhibition of tachykinin NK 1 receptor using aprepitant induces apoptotic cell death and G1 arrest through Akt/p53 axis in pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Eur J Pharmacol 791:274–283
Bigioni M, Benzo A, Irrissuto C, Maggi CA, Goso C (2005) Role of NK-1 and NK-2 tachykinin receptor antagonism on the growth of human breast carcinoma cell line MDA-MB-231. Anti-Cancer Drugs 16:1083–1089
Catasus L, Gallardo A, Cuatrecasas M, Prat J (2009) Concomitant PI3K–AKT and p53 alterations in endometrial carcinomas are associated with poor prognosis. Mod Pathol 22:522–529
Chan S (2004) Targeting the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR): a new approach to treating cancer. Br J Cancer 91:1420–1424
Cremins JD, Michel J, Farah JM, Krause JE (1992) Characterization of substance P-like immunoreactivity and tachykinin-encoding mRNAs in rat medullary thyroid carcinoma cell lines. J Neurochem 58:817–825
Davoodian M, Boroumand N, Mehrabi Bahar M, Jafarian AH, Asadi M, Hashemy SI (2019) Evaluation of serum level of substance P and tissue distribution of NK-1 receptor in breast cancer. Mol Biol Rep 46:1285–1293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-04599-9
Debeljuk L (2006) Tachykinins and ovarian function in mammals. Peptides 27:736–742
Farooq A, Zhou M-M (2004) Structure and regulation of MAPK phosphatases. Cell Signal 16:769–779
Fidler IJ (2003) The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer 3:453–458
Fiebich BL, Schleicher S, Butcher RD, Craig A, Lieb K (2000) The neuropeptide substance P activates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase resulting in IL-6 expression independently from NF-kappa B. J Immunol (Baltimore, MD : 1950) 165:5606–5611
Fukuhara S, Shimizu M, Matsushima H, Mukai H, Munekata E (1998) Signaling pathways via NK1 receptors and their desensitization in an AR42J cell line. Peptides 19:1349–1357
Garnier A, Vykoukal J, Hubertus J, Alt E, von Schweinitz D, Kappler R, Berger M, Ilmer M (2015) Targeting the neurokinin-1 receptor inhibits growth of human colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol 47:151–160. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2015.3016
Gharaee N, Pourali L, Jafarian AH, Hashemy SI (2018) Evaluation of serum level of substance P and tissue distribution of NK-1 receptor in endometrial cancer. Mol Biol Rep:1–6
Gurevich VV, Gurevich EV (2006) The structural basis of arrestin-mediated regulation of G-protein-coupled receptors. Pharmacol Ther 110:465–502
Hahn WC, Weinberg RA (2002) Rules for making human tumor cells. N Engl J Med 347:1593–1603
Hassanian SM, Dinarvand P, Smith SA, Rezaie AR (2015) Inorganic polyphosphate elicits pro-inflammatory responses through activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin complexes 1 and 2 in vascular endothelial cells. J Thromb Haemost 13:860–871
Hausmann G, Bänziger C, Basler K (2007) Helping wingless take flight: how WNT proteins are secreted. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:331–336
Henssen AG, Odersky A, Szymansky A, Seiler M, Althoff K, Beckers A, Speleman F, Schäfers S, De Preter K, Astrahanseff K (2017) Targeting tachykinin receptors in neuroblastoma. Oncotarget 8:430
Ilmer M, Garnier A, Vykoukal J, Alt E, von Schweinitz D, Kappler R, Berger M (2015) Targeting the neurokinin-1 receptor compromises canonical Wnt signaling in hepatoblastoma. Mol Cancer Ther 14:2712–2721. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-15-0206
Iwamura M, Egawa S, Uchida T, Koshiba K, Cockett AT, Gershagen S (1998) Suppression of the growth and invasiveness of human prostate cancer cells in vitro by neuropeptide antagonist substance P analogues. In: Urologic oncology: seminars and original investigations, vol 1. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 24–28
Javid H, Soltani A, Mohammadi F, Hashemy SI (2019) Emerging roles of microRNAs in regulating the mTOR signaling pathway during tumorigenesis. J Cell Biochem 120:10874–10883. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28401
Laplante M, Sabatini DM (2012) mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 149:274–293
Li J, Zeng Q, Zhang Y, Li X, Hu H, Miao X, Yang W, Zhang W, Song X, Mou L, Wang R (2016) Neurokinin-1 receptor mediated breast cancer cell migration by increased expression of MMP-2 and MMP-14. Eur J Cell Biol 95:368–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcb.2016.07.005
Logan CY, Nusse R (2004) The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20:781–810
Luo J, Manning BD, Cantley LC (2003) Targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway in human cancer. Cancer Cell 4:257–262
Ma J, Yuan S, Cheng J, Kang S, Zhao W, Zhang J (2016) Substance P promotes the progression of endometrial adenocarcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer 26:845–850. https://doi.org/10.1097/igc.0000000000000683
Mao J, Wang J, Liu B, Pan W, Farr GH III, Flynn C, Yuan H, Takada S, Kimelman D, Li L (2001) Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-5 binds to Axin and regulates the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Mol Cell 7:801–809
Martini M, De Santis MC, Braccini L, Gulluni F, Hirsch E (2014) PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: an updated review. Ann Med 46:372–383
Mayordomo C, García-Recio S, Ametller E, Fernández-Nogueira P, Pastor-Arroyo EM, Vinyals L, Casas I, Gascón P, Almendro V (2012) Targeting of substance P induces cancer cell death and decreases the steady state of EGFR and Her2. J Cell Physiol 227:1358–1366
Molinos-Quintana A, Trujillo-Hacha P, Piruat J, Bejarano-García J, García-Guerrero E, Pérez-Simón J, Muñoz M (2018) Human acute myeloid leukemia cells express Neurokinin-1 receptor, which is involved in the antileukemic effect of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists. Investig New Drugs 1–10
Moraes M, Neto J, Menck C (2012) DNA repair mechanisms protect our genome from carcinogenesis. Front Biosci 17:1362–1388
Mou L, Xing Y, Kong Z, Zhou Y, Chen Z, Wang R (2011) The N-terminal domain of human hemokinin-1 influences functional selectivity property for tachykinin receptor neurokinin-1. Biochem Pharmacol 81:661–668
Munoz M, Covenas R (2018) Glioma and neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists: a new therapeutic approach. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem
Munoz M, Rosso M, Covenas R (2011) The NK-1 receptor: a new target in cancer therapy. Curr Drug Targets 12:909–921
Munoz M, Covenas R, Esteban F, Redondo M (2015) The substance P/NK-1 receptor system: NK-1 receptor antagonists as anti-cancer drugs. J Biosci 40:441–463
Murthy RG, Reddy BY, Ruggiero JE, Rameshwar P (2007) Tachykinins and hematopoietic stem cell functions: implications in clinical disorders and tissue regeneration. Front Biosci 12:4779–4787
Newton S, Walker A, Page N (2009) Stimulation of PKC [beta] II-dependent ERK1/2 signalling by endokinin B and substance P may cause gene transcription via the tachykinin NK1 receptor in astrocytoma cells
Niu X-L, Hou J-F, Li J-X (2018) The NK1 receptor antagonist NKP608 inhibits proliferation of human colorectal cancer cells via Wnt signaling pathway. Biol Res 51:14
Nojima H, Tokunaga C, Eguchi S, Oshiro N, Hidayat S, Yoshino K-I, Hara K, Tanaka N, Avruch J, Yonezawa K (2003) The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) partner, raptor, binds the mTOR substrates p70 S6 kinase and 4E-BP1 through their TOR signaling (TOS) motif. J Biol Chem 278:15461–15464
Oakley RH, Laporte SA, Holt JA, Caron MG, Barak LS (2000) Differential affinities of visual arrestin, βarrestin1, and βarrestin2 for G protein-coupled receptors delineate two major classes of receptors. J Biol Chem 275:17201–17210
Öztürk Ö, Aki-Yalcin E, Ertan-Bolelli T, Bolelli K, Nur-Hidayat A, Bingol-Ozakpinar O, Ozdemir F, Yalcin I (2017) Possible mechanism of action of neurokinin-1 receptors (NK1R) antagonists. J Pharm Pharmacol 5:787–797
Palma C (2006) Tachykinins and their receptors in human malignancies. Curr Drug Targets 7:1043–1052
Patacchini R, Maggi CA (2001) Peripheral tachykinin receptors as targets for new drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 429:13–21
Pennefather JN, Lecci A, Candenas ML, Patak E, Pinto FM, Maggi CA (2004) Tachykinins and tachykinin receptors: a growing family. Life Sci 74:1445–1463
Rahmani F, Avan A, Hashemy SI, Hassanian SM (2018) Role of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling regulatory microRNAs in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. J Cell Physiol 233:811–817. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25897
Raman M, Chen W, Cobb M (2007) Differential regulation and properties of MAPKs. Oncogene 26:3100–3112
Reya T, Clevers H (2005) Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature 434:843–850. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03319
Rosso M, Munoz M, Berger M (2012) The role of neurokinin-1 receptor in the microenvironment of inflammation and cancer. Sci World J 2012
Roux PP, Blenis J (2004) ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: a family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:320–344
Schieven GL (2005) The biology of p38 kinase: a central role in inflammation. Curr Top Med Chem 5:921–928
Severini C, Improta G, Falconieri-Erspamer G, Salvadori S, Erspamer V (2002) The tachykinin peptide family. Pharmacol Rev 54:285–322
Sharif M (1998) Mitogenic signaling by substance P and bombesin-like neuropeptide receptors in astrocytic/glial brain tumor-derived cell lines. Int J Oncol 12:273–286
Sharif M, Sharif T, Dilling M, Hosoi H, Lawrence J, Houghton P (1997) Rapamycin inhibits substance P-induced protein synthesis and phosphorylation of PHAS-I (4E-BP1) and p70 S6 kinase (p70 (S6K)) in human astrocytoma cells. Int J Oncol 11:797–805
Shaw RJ, Cantley LC (2006) Ras, PI(3) K and mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth. Nature 441:424–430. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04869
Singh D, Joshi DD, Hameed M, Qian J, Gascón P, Maloof PB, Mosenthal A, Rameshwar P (2000) Increased expression of preprotachykinin-I and neurokinin receptors in human breast cancer cells: implications for bone marrow metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97:388–393
Smolich BD, McMahon JA, McMahon AP, Papkoff J (1993) Wnt family proteins are secreted and associated with the cell surface. Mol Biol Cell 4:1267–1275
Song H, Yin W, Zeng Q, Jia H, Lin L, Liu X, Mu L, Wang R (2012) Hemokinins modulate endothelium function and promote angiogenesis through neurokinin-1 receptor. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:1410–1421
Weinberg R (2007) Moving out: invasion and metastasis. Biol Cancer 1:587–654
Yamaguchi K, Kugimiya T, Miyazaki T (2005) Substance P receptor in U373 MG human astrocytoma cells activates mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK1/2 through Src. Brain Tumor Pathol 22:1–8
Yamaguchi K, Richardson MD, Bigner DD, Kwatra MM (2005) Signal transduction through substance P receptor in human glioblastoma cells: roles for Src and PKCdelta. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 56:585–593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-005-1030-3
Yamaguchi K, Kumakura S, Murakami T, Someya A, Inada E, Nagaoka I (2017) Ketamine suppresses the substance P-induced production of IL-6 and IL-8 by human U373MG glioblastoma/astrocytoma cells. Int J Mol Med 39:687–692. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2017.2875
Zhan T, Rindtorff N, Boutros M (2017) Wnt signaling in cancer. Oncogene 36:1461–1473
Zhang Y-X, Li X-F, Yuan G-Q, Hu H, Song X-Y, Li J-Y, Miao X-K, Zhou T-X, Yang W-L, Zhang X-W (2017) β-Arrestin 1 has an essential role in neurokinin-1 receptor-mediated glioblastoma cell proliferation and G2/M phase transition. J Biol Chem M116:770420
Zhang YX, Li XF, Yuan GQ, Hu H, Song XY, Li JY, Miao XK, Zhou TX, Yang WL, Zhang XW, Mou LY, Wang R (2017) Beta-arrestin 1 has an essential role in neurokinin-1 receptor-mediated glioblastoma cell proliferation and G2/M phase transition. J Biol Chem 292:8933–8947. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.770420
Zhou J, Ling J, Song H, Lv B, Wang L, Shang J, Wang Y, Chang C, Ping F, Qian J (2016) Neurokinin-1 receptor is a novel positive regulator of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in melanogenesis. Oncotarget 7:81268
Zhuo H, Helke C (1993) Neurokinin B peptide-2 neurons project from the hypothalamus to the thoracolumbar spinal cord of the rat. Neuroscience 52:1019–1028
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the gathering of data and writing the manuscript; HJ was responsible to coordinate with the authors, and SIH finalized and submitted the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key points
• Tachykinins have implications in different steps of carcinogenesis.
• SP/NK1R system activates signaling pathways involved in tumorigenesis.
• The blockage of NK1R could suggest a therapeutic approach in cancer therapy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Javid, H., Mohammadi, F., Zahiri, E. et al. The emerging role of substance P/neurokinin-1 receptor signaling pathways in growth and development of tumor cells. J Physiol Biochem 75, 415–421 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-019-00697-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-019-00697-1