Abstract
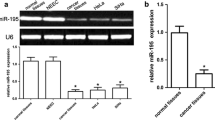
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous, non-coding, small RNAs, which play a critical role in regulating varieties of the biological and pathologic processes. miR-181a has been reported to participate in tumorigenic progression. However, the roles of miR-181a in cervical cancer (CC) are still unknown. The aim of this research was to explore the effects and molecular mechanism of miR-181a in CC cells. In this paper, the levels of miR-181a in CC cell lines were determined by real-time PCR. We found that the levels of miR-181a were evidently enhanced in CC cell lines compared with normal cervical epithelium cells. Then, the miR-181a inhibitor was transiently transfected into HeLa and CaSKi cells using Lipofectamine 2000 reagent. Subsequently, the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and BrdU-ELISA results showed that down-regulation of miR-181a inhibited the cell viability and proliferation. Our data also demonstrated that miR-181a inhibitor arrested cell cycle progression of HeLa and CaSKi cells by up-regulation of p21 and p27 expressions. In addition, inhibition of miR-181a promoted apoptosis of HeLa and CaSKi cells due to increasing Bax expression and decreasing Bcl-2 expression. Ultimately, the effect of miR-181a inhibitor on the PTEN/Akt/FOXO1 signaling pathway was investigated by Western blot. From our results, down-regulation of miR-181a increased the expression of PTEN and decreased phosphorylation of Akt and FOXO1. Altogether, miR-181a might be an oncogene in CC cells. The potential mechanism was that inhibition of miR-181a might suppress proliferation and invasion and promote apoptosis of HeLa and CaSKi cells by modulating the PTEN/Akt/FOXO1 signaling pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cantley LC, Neel BG (1999) New insights into tumor suppression: PTEN suppresses tumor formation by restraining the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(8):4240–4245
Castellsague X, Diaz M, de Sanjose S, Munoz N, Herrero R, Franceschi S, et al. (2006) Worldwide human papillomavirus etiology of cervical adenocarcinoma and its cofactors: implications for screening and prevention. J Natl Cancer Inst 98(5):303–315
Chen Y, Ke G, Han D, Liang S, Yang G, Wu X (2014) MicroRNA-181a enhances the chemoresistance of human cervical squamous cell carcinoma to cisplatin by targeting PRKCD. Exp Cell Res 320(1):12–20
Ciafre SA, Galardi S, Mangiola A, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Sabatino G, et al. (2005) Extensive modulation of a set of microRNAs in primary glioblastoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334(4):1351–1358
Colombo N, Carinelli S, Colombo A, Marini C, Rollo D, Sessa C (2012) Cervical cancer: esmo clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 23(Suppl 7):i27–i32
Di Cristofano A, Pandolfi PP (2000) The multiple roles of PTEN in tumor suppression. Cell 100(4):387–390
Franke TF, Kaplan DR, Cantley LC, Toker A (1997) Direct regulation of the Akt proto-oncogene product by phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate. Science 275(5300):665–668
Gao W, Yu Y, Cao H, Shen H, Li X, Pan S, et al. (2010) Deregulated expression of miR-21, miR-143 and miR-181a in non small cell lung cancer is related to clinicopathologic characteristics or patient prognosis. Biomed Pharmacother 64(6):399–408
Greer EL, Brunet A (2005) FOXO transcription factors at the interface between longevity and tumor suppression. Oncogene 24(50):7410–7425
Haie-Meder C, Morice P, Castiglione M (2010) Cervical cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 21(Suppl 5):v37–v40
Huang H, Tindall DJ (2007) Dynamic FoxO transcription factors. J Cell Sci 120(Pt 15):2479–2487
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61(2):69–90
Jianwei Z, Fan L, Xiancheng L, Enzhong B, Shuai L, Can L (2013) MicroRNA 181a improves proliferation and invasion, suppresses apoptosis of osteosarcoma cell. Tumour Biol 34(6):3331–3337
Ke G, Liang L, Yang JM, Huang X, Han D, Huang S, Zhao Y, Zha R, He X, Wu X (2013) MiR-181a confers resistance of cervical cancer to radiation therapy through targeting the pro-apoptotic PRKCD gene. Oncogene 32(25):3019–3027
Li ZC, Zhang LM, Wang HB, Ma JX, Sun JZ (2014) Curcumin inhibits lung cancer progression and metastasis through induction of FOXO1. Tumour Biol 35(1):111–116
Lin S, Pan L, Guo S, Wu J, Jin L, Wang JC, et al. (2013) Prognostic role of microRNA-181a/b in hematological malignancies: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 8(3):e59532
Lu D, Qian J, Yin X, Xiao Q, Wang C, Zeng Y (2012) Expression of PTEN and survivin in cervical cancer: promising biological markers for early diagnosis and prognostic evaluation. Br J Biomed Sci 69(4):143–146
Mayor-Lynn K, Toloubeydokhti T, Cruz AC, Chegini N (2011) Expression profile of microRNAs and mRNAs in human placentas from pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia and preterm labor. Reprod Sci 18(1):46–56
Miller TE, Ghoshal K, Ramaswamy B, Roy S, Datta J, Shapiro CL, et al. (2008) MicroRNA-221/222 confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer by targeting p27Kip1. J Biol Chem 283(44):29897–29903
Min R, Tong J, Wenjun Y, Wenhu D, Xiaojian Z, Jiacai H, et al. (2008) Growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in human oral squamous cell carcinoma Tca-8113 cell lines by Shikonin was partly through the inactivation of NF-kappaB pathway. Phytother Res 22(3):407–415
Narla G, Friedman SL, Martignetti JA (2003) Kruppel cripples prostate cancer: KLF6 progress and prospects. Am J Pathol 162(4):1047–1052
Neel JC, Lebrun JJ (2013) Activin and TGF-beta regulate expression of the microRNA-181 family to promote cell migration and invasion in breast cancer cells. Cell Signal 25(7):1556–1566
Nian W, Ao X, Wu Y, Huang Y, Shao J, Wang Y, et al. (2013) MiR-223 functions as a potent tumor suppressor of the Lewis lung carcinoma cell line by targeting insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Oncol Lett 6(2):359–366
Nishimura J, Handa R, Yamamoto H, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Mimori K, et al. (2012) MicroRNA-181a is associated with poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 28(6):2221–2226
Parikh A, Lee C, Joseph P, Marchini S, Baccarini A, Kolev V, et al. (2014) MicroRNA-181a has a critical role in ovarian cancer progression through the regulation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Commun 5:2977
Shen L, Chen XD, Zhang YH (2014) MicroRNA-128 promotes proliferation in osteosarcoma cells by downregulating PTEN. Tumour Biol 35(3):2069–2074
Shin KH, Bae SD, Hong HS, Kim RH, Kang MK, Park NH (2011) MiR-181a shows tumor suppressive effect against oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by downregulating K-ras. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 404(4):896–902
Sun Y, Zhang B, Cheng J, Wu Y, Xing F, Wang Y, et al. (2014) MicroRNA-222 promotes the proliferation and migration of cervical cancer cells. Clin Invest Med 37(3):E131
Valeri N, Braconi C, Gasparini P, Murgia C, Lampis A, et al. (2014) MicroRNA-135b promotes cancer progression by acting as a downstream effector of oncogenic pathways in colon cancer. Cancer Cell 25(4):469–483
Wang B, Hsu SH, Majumder S, Kutay H, Huang W, Jacob ST, et al. (2010) TGFbeta-mediated upregulation of hepatic miR-181b promotes hepatocarcinogenesis by targeting TIMP3. Oncogene 29(12):1787–1797
Wang Z, Cai H, Lin L, Tang M, Cai H (2014) Upregulated expression of microRNA-214 is linked to tumor progression and adverse prognosis in pediatric osteosarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 61(2):206–210
Wu J, Chen C, Zhao KN (2013) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling as a therapeutic target for cervical cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 13(2):143–156
Xu WT, Yang Z, Lu NH (2014) Roles of PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog) in gastric cancer development and progression. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15(1):17–24
Zhang X, Nie Y, Du Y, Cao J, Shen B, Li Y (2012) MicroRNA-181a promotes gastric cancer by negatively regulating tumor suppressor KLF6. Tumour Biol 33(5):1589–1597
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by The Training Program of Jilin University Outstanding Young Teacher Project (No. 419080500357).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Zhu, J., Hu, C. et al. Inhibition of microRNA-181a may suppress proliferation and invasion and promote apoptosis of cervical cancer cells through the PTEN/Akt/FOXO1 pathway. J Physiol Biochem 72, 721–732 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-016-0511-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-016-0511-7