Abstract
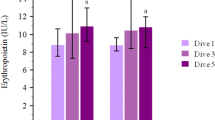
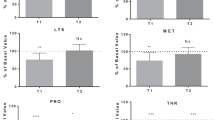
The aim was evaluating the effects of hypoxia/reoxygenation repetitive episodes during 5 days of apnea diving (3-day training/2-day competition) on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) antioxidant defenses, oxidative damage, and plasma xanthine oxidase activity. Blood samples, from seven professional apnea divers, were taken under basal conditions the previous morning to the first training session (pre-diving basal), 4 h after ending the competition (4 h post-diving) and the following morning (15 h after last dive) in basal conditions (post-diving basal). Glucose levels significantly decreased whereas triglycerides increased at 4 h post-diving, both returning to basal values at post-diving basal. Glutathione reductase and catalase activity significantly increased after 4 h post-diving remaining elevated at post-diving basal. Glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase activities and catalase protein levels progressively increased after diving with significant differences respect to initial values at post-diving basal. No significant differences were observed in circulating PBMCs and oxidative damage markers. Plasma xanthine oxidase activity and nitrite levels, but not the inducible nitric oxide synthetase, significantly increased 4 h post-diving, returning to the basal values after 15 h. In conclusion, chronic and repetitive episodes of diving apnea during five consecutive days increased plasma xanthine oxidase activity and nitric oxide production which could enhance the signalling role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species for PBMCs antioxidant adaptation against hypoxia/reoxygenation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi HE (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Bescos R, Rodriguez FA, Iglesias X, Ferrer MD, Iborra E, Pons A (2011) Acute administration of inorganic nitrate reduces VO(2peak) in endurance athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43:1979–1986
Bulmer AC, Coombes JS, Sharman JE, Stewart IB (2008) Effects of maximal static apnea on antioxidant defenses in trained free divers. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40:1307–1313
Cantu-Medellin N, Kelley EE (2013) Xanthine oxidoreductase-catalyzed reactive species generation: a process in critical need of reevaluation. Redox Biol 1:353–358
Datta B, Tufnell-Barrett T, Bleasdale RA, Jones CJ, Beeton I, Paul V, Frenneaux M, James P (2004) Red blood cell nitric oxide as an endocrine vasoregulator: a potential role in congestive heart failure. Circulation 109:1339–1342
Dejam A, Hunter CJ, Pelletier MM, Hsu LL, Machado RF, Shiva S, Power GG, Kelm M, Gladwin MT, Schechter AN (2005) Erythrocytes are the major intravascular storage sites of nitrite in human blood. Blood 106:734–739
DeLeve LD, Kaplowitz N (1991) Glutathione metabolism and its role in hepatotoxicity. Pharmacol Ther 52:287–305
Dhaliwal H, Kirshenbaum LA, Randhawa AK, Singal PK (1991) Correlation between antioxidant changes during hypoxia and recovery on reoxygenation. Am J Physiol 261:H632–H638
Dujic Z, Palada I, Valic Z, Duplancic D, Obad A, Wisloff U, Brubakk AO (2006) Exogenous nitric oxide and bubble formation in divers. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38:1432–1435
Flohe L, Gunzler WA (1984) Assays for glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105:114–121
Flohe L, Otting F (1984) Superoxide dismutase assays. Methods Enzymol 105:93–104
Gladwin MT, Crawford JH, Patel RP (2004) The biochemistry of nitric oxide, nitrite, and hemoglobin: role in blood flow regulation. Free Radic Biol Med 36:707–717
Gomes EC, Silva AN, de Oliveira MR (2012) Oxidants, antioxidants, and the beneficial roles of exercise-induced production of reactive species. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2012:756132
Gomez-Cabrera MC, Martinez A, Santangelo G, Pallardo FV, Sastre J, Vina J (2006) Oxidative stress in marathon runners: interest of antioxidant supplementation. Br J Nutr 96(Suppl 1):S31–S33
Gomez-Cabrera MC, Pallardo FV, Sastre J, Vina J, Garcia-del-Moral L (2003) Allopurinol and markers of muscle damage among participants in the Tour de France. JAMA 289:2503–2504
Joulia F, Steinberg JG, Faucher M, Jamin T, Ulmer C, Kipson N, Jammes Y (2003) Breath-hold training of humans reduces oxidative stress and blood acidosis after static and dynamic apnea. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 137:19–27
Joulia F, Steinberg JG, Wolff F, Gavarry O, Jammes Y (2002) Reduced oxidative stress and blood lactic acidosis in trained breath-hold human divers. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 133:121–130
Kelm M, Schrader J (1990) Control of coronary vascular tone by nitric oxide. Circ Res 66:1561–1575
Keller T, Pleskova M, McDonald MC, Thiemermann C, Pfeilschifter J, Beck KF (2003) Identification of manganese superoxide dismutase as a NO-regulated gene in rat glomerular mesangial cells by 2D gel electrophoresis. Nitric Oxide 9:183–193
Kesarwani P, Murali AK, Al-Khami AA, Mehrotra S (2013) Redox regulation of T-cell function: from molecular mechanisms to significance in human health and disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 18:1497–1534
Khassaf M, McArdle A, Esanu C, Vasilaki A, McArdle F, Griffiths RD, Brodie DA, Jackson MJ (2003) Effect of vitamin C supplements on antioxidant defence and stress proteins in human lymphocytes and skeletal muscle. J Physiol 549:645–652
Levine RL, Williams JA, Stadtman ER, Shacter E (1994) Carbonyl assays for determination of oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol 233:346–357
Li C, Jackson RM (2002) Reactive species mechanisms of cellular hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 282:C227–C241
Marin DP, Bolin AP, Campoio TR, Guerra BA, Otton R (2013) Oxidative stress and antioxidant status response of handball athletes: implications for sport training monitoring. Int Immunopharmacol 17:462–470
McCord JM (1985) Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med 312:159–163
Powers SK, Nelson WB, Hudson MB (2011) Exercise-induced oxidative stress in humans: cause and consequences. Free Radic Biol Med 51:942–950
Richardson MX, Engan HK, Lodin-Sundstrom A, Schagatay E (2012) Effect of hypercapnia on spleen-related haemoglobin increase during apnea. Diving Hyperb Med 42:4–9
Rousseau AS, Richer C, Richard MJ, Favier A, Margaritis I (2006) Plasma glutathione peroxidase activity as a potential indicator of hypoxic stress in breath-hold diving. Aviat Space Environ Med 77:551–555
Steensberg A, Keller C, Hillig T, Frosig C, Wojtaszewski JF, Pedersen BK, Pilegaard H, Sander M (2007) Nitric oxide production is a proximal signaling event controlling exercise-induced mRNA expression in human skeletal muscle. Faseb J 21:2683–2694
Su SH, Jen CJ, Chen HI (2011) NO signaling in exercise training-induced anti-apoptotic effects in human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 405:58–63
Sureda A, Batle JM, Capo X, Martorell M, Cordova A, Tur JA, Pons A (2014) Scuba diving induces nitric oxide synthesis and the expression of inflammatory and regulatory genes of the immune response in neutrophils. Physiol Genomics 46:647–654
Sureda A, Batle JM, Tauler P, Ferrer MD, Tur JA, Pons A (2006) Vitamin C supplementation influences the antioxidant response and nitric oxide handling of erythrocytes and lymphocytes to diving apnea. Eur J Clin Nutr 60:838–846
Sureda A, Ferrer MD, Tauler P, Romaguera D, Drobnic F, Pujol P, Tur JA, Pons A (2009) Effects of exercise intensity on lymphocyte H2O2 production and antioxidant defences in soccer players. Br J Sports Med 43:186–190
Sureda A, Ferrer MD, Tauler P, Tur JA, Pons A (2008) Lymphocyte antioxidant response and H2O2 production after a swimming session: gender differences. Free Radic Res 42:312–319
Sureda A, Tauler P, Aguilo A, Fuentespina E, Cordova A, Tur JA, Pons A (2006) Blood cell NO synthesis in response to exercise. Nitric Oxide 15:5–12
Tauler P, Aguilo A, Gimeno I, Noguera A, Agusti A, Tur JA, Pons A (2003) Differential response of lymphocytes and neutrophils to high intensity physical activity and to vitamin C diet supplementation. Free Radic Res 37:931–938
Tauler P, Sureda A, Cases N, Aguilo A, Rodriguez-Marroyo JA, Villa G, Tur JA, Pons A (2006) Increased lymphocyte antioxidant defences in response to exhaustive exercise do not prevent oxidative damage. J Nutr Biochem 17:665–671
Theunissen S, Sponsiello N, Rozloznik M, Germonpre P, Guerrero F, Cialoni D, Balestra C (2013) Oxidative stress in breath-hold divers after repetitive dives. Diving Hyperb Med 43:63–66
Umbrello M, Dyson A, Feelisch M, Singer M (2013) The key role of nitric oxide in hypoxia: hypoxic vasodilation and energy supply–demand matching. Antioxid Redox Signal 19:1690–1710
Vina J, Gomez-Cabrera MC, Lloret A, Marquez R, Minana JB, Pallardo FV, Sastre J (2000) Free radicals in exhaustive physical exercise: mechanism of production, and protection by antioxidants. IUBMB Life 50:271–277
Wisloff U, Richardson RS, Brubakk AO (2004) Exercise and nitric oxide prevent bubble formation: a novel approach to the prevention of decompression sickness? J Physiol 555:825–829
Funding
This work is funded by Acción Estratégica en Salud del Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación DPS2008-07033-C03-03, Program of Promotion of Biomedical Research and Health Sciences, Projects 11/01791, Red Predimed-RETIC RD06/0045/1004, CIBEROBN CB12/03/30038 and Balearic Island Government (35/2011 and 23/2012), and FEDER funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sureda, A., Batle, J.M., Tur, J.A. et al. Competitive apnea diving sessions induces an adaptative antioxidant response in mononucleated blood cells. J Physiol Biochem 71, 373–380 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-015-0417-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-015-0417-9