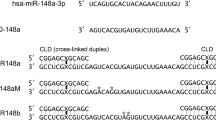Abstract
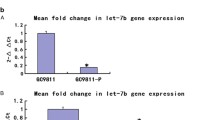
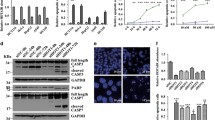
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a class of small, single-stranded endogenous RNAs, act as post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression. The ability of one single miRNA regulating multiple functionally related mRNAs makes it a new potential candidate for cancer gene therapy. Let-7s miRNAs have been demonstrated as tumor-suppressor genes in various types of cancers, providing one choice of gene therapy by replenishing this miRNA. In the present studies, we demonstrate that the chemically synthesized, double-stranded Let-7 mimics can inhibit the growth and migration and induce the cell cycle arrest of lung cancer cell lines in vitro. Let-7 mimics silence gene expression by binding to the 3′ UTR of targeting mRNAs. Mutation of seed sequence significantly depresses the gene silencing activity of Let-7 mimics. Our results also demonstrate that it is possible to increase the activity of Let-7s through mutating the sequence within the 3′end of the antisense strand. Directly, co-transfection Let-7 mimics with active siRNAs impairs the anti-cancer activities of Let-7 mimics. However, a 3-h interval between the introduction of Let-7 mimics and a kind of siRNA avoids the competition and enhances the anti-cancer activities of Let-7 mimics. Taken together, these results have revealed that Let-7s mimics are potential candidates for cancer gene therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akao Y, Nakagawa Y, Naoe T (2006) Let-7 microRNA functions as a potential growth suppressor in human colon cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull 29:903–906
Baek D, Villén J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi SP, Bartel DP (2008) The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 455:64–71
Boudreau RL, Martins I, Davidson BL (2008) Artificial microRNAs as siRNA shuttles: improved safety as compared to shRNAs in vitro and in vivo. Mol Ther 17:169–175
Castanotto D, Rossi JJ (2009) The promises and pitfalls of RNA-interference-based therapeutics. Nature 457:426–433
Castanotto D, Sakurai K, Lingeman R et al (2007) Combinatorial delivery of small interfering RNAs reduces RNAi efficacy by selective incorporation into RISC. Nucleic Acids Res 35:5154–5164
Ding L, Getz G, Wheeler DA et al (2008) Somatic mutations affect key pathways in lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 455:1069–1075
Doench JG, Petersen CP, Sharp PA (2003) siRNAs can function as miRNAs. Genes Dev 17:438–442
Esmerina T, Jean-Jacques M, Varsha G, William P, Deepa S, Adrian CG (2007) MiRNAs and their potential for use against cancer and other diseases, miRNA-based gene therapy. Future Oncol 3:521–537
Esquela-Kerscher A, Trang P, Wiggins JF et al (2008) The let-7 microRNA reduces tumor growth in mouse models of lung cancer. Cell Cycle 7:759–764
Filipowicz W, Jaskiewicz L, Kolb FA, Pillai RS (2005) Post-transcriptional gene silencing by siRNAs and miRNAs. Curr Opin Struct Biol 15:331–341
Garzon R, Liu S, Fabbri M et al (2009) MicroRNA-29b induces global DNA hypomethylation and tumor suppressor gene reexpression in acute myeloid leukemia by targeting directly DNMT3A and 3B and indirectly DNMT1. Blood 113:6411–6418
Gregory RI, Chendrimada TP, Cooch N, Shiekhattar R (2005) Human RISC couples microRNA biogenesis and posttranscriptional gene silencing. Cell 123:631–640
Hüser D, Gogol-Döring A, Lutter T et al (2010) Integration preferences of wildtype AAV-2 for consensus rep-binding sites at numerous loci in the human genome. PLoS Pathog 6:e1000985
Inamura K, Togashi Y, Nomura K et al (2007) Let-7 microRNA expression is reduced in bronchioloalveolar carcinoma, a non-invasive carcinoma, and is not correlated with prognosis. Lung Cancer 58:392–396
Ivanovska I, Ball AS, Diaz RL et al (2008) MicroRNAs in the miR-106b family regulate p21/CDKN1A and promote cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol 28:2167–2174
Jackson A, Linsley PS (2010) The therapeutic potential of microRNA modulation. Discov Med 9:311–318
Johnson CD, Esquela-Kerscher A, Stefani G et al (2007) The let-7 microRNA represses cell proliferation pathways in human cells. Cancer Res 67:7713–7722
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J et al (2005) RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 120:635–647
Jones S, Zhang X, Parsons DW et al (2008) Core signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancers revealed by global genomic analyses. Science 321:1801–1806
Kaiser PK, Symons RC, Shah SM et al (2010) RNAi-based treatment for neovascular age-related macular degeneration by Sirna-027. Am J Ophthalmol 150:33–39.e2
Khvorova A, Reynolds A, Jayasena SD (2003) Functional siRNAs and miRNAs exhibit strand bias. Cell 115:209–216
Koller E, Propp S, Murray H et al (2006) Competition for RISC binding predicts in vitro potency of siRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 34:4467–4476
Kota J, Chivukula RR, O’Donnell KA et al (2009) Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell 137:1005–1017
Kumar MS, Erkeland SJ, Pester RE, Chen CY, Ebert MS, Sharp PA, Jacks T (2008) Suppression of non-small cell lung tumor development by the let-7 microRNA family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:3903–3908
Lee I, Ajay SS, Yook JI et al (2009) New class of microRNA targets containing simultaneous 5′-UTR and 3′-UTR interaction sites. Genome Res 19:1175–1183
Lee ST, Chu K, Oh HJ et al (2010) Let-7 microRNA inhibits the proliferation of human glioblastoma cells. J Neurooncol (in press)
Lee YS, Dutta A (2007) The tumor suppressor microRNA let-7 represses the HMGA2 oncogene. Gene Dev 21:1025–1030
Lin T, Dong W, Huang J, Pan Q, Fan X, Zhang C, Huang L (2009) MicroRNA-143 as a tumor suppressor for bladder cancer. J Urol 181:1372–1380
Lu J, Qian J, Chen F et al (2005) Differential expression of components of the microRNA machinery during mouse organogenesis. Biochem Biophy Res Co 334:319–323
Luo J, Solinini NL, Elledge SJ (2009) Principles of cancer therapy: oncogene and non-oncogene addiction. Cell 136:823–837
Maniataki E, Mourelatos Z (2005) A human, ATP-independent, RISC assembly machine fueled by pre-miRNA. Genes Dev 19:2979–2990
Manno CS, Pierce GF, Arruda VR et al (2006) Successful transduction of liver in hemophilia by AAV-factor IX and limitations imposed by the host immune response. Nat Med 12:342–347
Matsubara H, Takeuchi T, Nishikawa E et al (2007) Apoptosis induction by antisense oligonucleotides against miR-17-5p and miR-20a in lung cancers overexpressing miR-17-92. Oncogene 26:6099–6105
Metias SM, Lianidou E, Yousef GM (2009) MicroRNAs in clinical oncology: at the crossroads between promises and problems. J Clin Pathol 62:771–776
Oberdoerffer P, Kanellopoulou C, Heissmeyer V et al (2005) Efficiency of RNA interference in the mouse hematopoietic system varies between cell types and developmental stages. Mol Cell Biol 25:3896–3905
Parsons DW, Jones S, Zhang X et al (2008) An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma multiforme. Science 321:1807–1812
Peng Y, Laser J, Shi G, Mittal K, Melamed J, Lee P, Wei JJ (2008) Antiproliferative effects by Let-7 repression of high-mobility group A2 in uterine leiomyoma. Mol Cancer Res 6:663–673
Petri A, Lindow M, Kauppinen S (2009) MicroRNA silencing in primates: towards development of novel therapeutics. Cancer Res 69:393–395
Sampson VB, Rong NH, Han J et al (2007) MicroRNA let-7a down-regulates MYC and reverts MYC-induced growth in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Cancer Res 67:9762–9770
Sasaki T, Shiohama A, Minoshima S, Shimizu N (2003) Identification of eight members of the Argonaute family in the human genome small star, filled. Genomics 82:323–330
Schwarz DS, Hutvágner G, Du T, Xu Z, Aronin N, Zamore PD (2003) Asymmetry in the assembly of the RNAi enzyme complex. Cell 115:199–208
Selbach M, Schwanhäusser B, Thierfelder N, Fang Z, Khanin R, Rajewsky N (2008) Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature 455:58–63
Sharma SV, Settleman J (2007) Oncogene addiction: setting the stage for molecularly targeted cancer therapy. Genes Dev 21:3214–3231
Shell S, Park SM, Radjabi AR (2007) Let-7 expression defines two differentiation stages of cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:11400–11405
Solimini NL, Luo J, Elledge SJ (2007) Non-oncogene addiction and the stress phenotype of cancer cells. Cell 130:986–988
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K et al (2004) Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res 64:3753–3756
Tavazoie SF, Alarcón C, Oskarsson T et al (2008) Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature 451:147–152
Torrisani J, Bournet B, du Rieu MC et al (2009) Let-7 microRNA transfer in pancreatic cancer-derived cells inhibits in vitro cell proliferation but fails to alter tumor progression. Hum Gene Ther 20:831–844
Tsuda N, Kawano K, Efferson CL, Ioannides CG (2005) Synthetic microRNA and double-stranded RNA targeting the 3′-untranslated region of HER-2/neu mRNA inhibit HER-2 protein expression in ovarian cancer cells. Int J Oncol 27:1299–1306
van Rooij E, Marshall WS, Olson EN (2008) Toward microRNA based therapeutics for heart disease: the sense in antisense. Circ Res 103:919–928
Vickers TA, Lima WF, Nichols JG (2007) Reduced levels of Ago2 expression result in increased siRNA competition in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res 35:6598–6610
Wang Q, Diao Y, Lv Y, Li Z, XU R (2009) Mutant K-ras-specific siRNA inhibits proliferation, migration and induces apoptosis of lung cancer A549 cells. Chin J Cancer Biother 16:564–569
Wang Q, Lv Y, Diao Y, Xu R (2008) The design of vectors for RNAi delivery system. Curr Pharma Design 14:1327–1340
Wang Q, Xu W, Habib N, Xu R (2009) Potential uses of miRNA in lung cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 9:572–594
Weidhaas JB, Babar I, Nallur SM et al (2007) MicroRNAs as potential agents to alter resistance to cytotoxic anticancer therapy. Cancer Res 67:11111–11116
Weinstein IB, Joe A (2008) Oncogene addiction. Cancer Res 68:3077–3080
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E et al (2006) Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 9:189–198
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P et al (2007) Let-7 regulates self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell 131:1109–1123
Zeng Y, Yi R, Cullen BR (2003) MicroRNAs and small interfering RNAs can inhibit mRNA expression by similar mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9779–9784
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 30900822), the Key grant Project of Chinese Ministry of Education (No: 210252), the Key Project of Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology (No.2010Y0036), and Huaqiao University program (09BS517).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Qz., Lv, Yh., Gong, Yh. et al. Double-stranded Let-7 mimics, potential candidates for cancer gene therapy. J Physiol Biochem 68, 107–119 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-011-0124-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-011-0124-0