Abstract
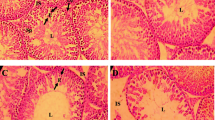
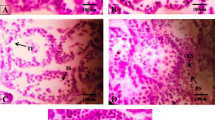
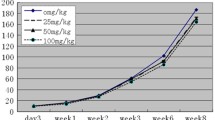
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of bisphenol A (BPA) on the neuroendocrine mechanism of control of the reproductive axis in adult male rats exposed to it during pre- and early postnatal periods. Wistar mated rats were treated with either 0.1% ethanol or BPA in their drinking water until their offspring were weaned at the age of 21 days. The estimated average dose of exposure to dams was approximately 2.5 mg/kg body weight per day of BPA. After 21 days, the pups were separated from the mother and sacrificed on 70 day of life. Gn-RH and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) release from hypothalamic fragments was measured. LH, FSH, and testosterone concentrations were determined, and histological and morphometrical studies of testis were performed. Gn-RH release decreased significantly, while GABA serum levels were markedly increased by treatment. LH serum levels showed no changes, and FSH and testosterone levels decreased significantly. Histological studies showed abnormalities in the tubular organization of the germinal epithelium. The cytoarchitecture of germinal cells was apparently normal, and a reduction of the nuclear area of Leydig cells but not their number was observed. Taken all together, these results provide evidence of the effect caused by BPA on the adult male reproductive axis when exposed during pre- and postnatal period. Moreover, our findings suggest a probable GABA involvement in its effect at the hypothalamic level.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi T, Yasuda K, Mori C, Yoshinaga M, Aoki N, Tsujimoto G et al (2005) Promoting insulin secretion in pancreatic islets by means bisphenol A and nonylphenol via intracellular estrogen receptors. Food Chem Toxicol 43(5):713–719
Akingbemi B, Sottas C, Koulova A, Klinefelter G, Hardy M (2004) Inhibition of testicular steroidogenesis by the xenoestrogen Bisphenol A is associated with reduced pituitary luteinizing hormone secretion and decreased steroidogenic enzyme gene expression in rat Leydig cells. Endocrinology 145:592–603
Alonso-Magdalena P, Morimoto S, Ripoll C, Fuentes E, Nadal A (2006) The estrogenic effect of bisphenol A disrupts pancreatic beta-cell function in vivo and induces insulin resistance. Environ Health Perspect 114(1):106–112
Brann DW, Mahesh VB (1992) Excitatory amino acid regulation of gonadotrophin secretion: modulation by steroid hormone. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 41:847–850
Brotons JA, Olea Serrano MF, Villalobos M, Olea N (1995) Xenoestrogens released from laquer coating in food cans. Environ Health Perspect 103:608–612
Cagen SZ, Waechter JM Jr, Dimond SS, Breslin WJ, Butala JH, Jekat FW et al (1999) Normal reproductive organ development in Wistar rats exposed to bisphenol A in the drinking water. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 30:130–139
Ebling FJP, Brooks N, Cronin AS et al (2000) Estrogenic induction of spermatogenesis in the hypogonadal mouse. Endocrinology 141:2861–2869
Farach-Carson MC, Davis PJ (2003) Steroid hormone interactions with target cells: cross talk between membrane and nuclear pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307(3):839–845
Flugge G, Oertel WH, Wuttke W (1986) Evidence for estrogen-receptive GABAergic neurons in the preoptic/anterior hypothalamic area of the rat brain. Neuroendocrinology 43:1–5
Francis RC, Soma K, Fernald RD (1993) Social regulation of the brain-pituitary-gonadal axis. Proc Natl Acad SCi USA 90(16):7748–7749
Funabashi T, Kawaguchi M, Furuta M, Fukushima A, Kimura F (2004) Exposure to Bisphenol A during gestation and lactation causes loss of sex difference in corticotropin-releasing hormone immunoreactive neurons in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis of rats. Psyconeuroendocrinology 29:475–485
Gore AC, Heindel JJ, Zoeller RT (2006) Endocrine disruption for endocrinologist (and others). Endocrinology 147(6 Suppl):S1–S3
Gould JC, Leonard LS, Maness SC, Wagner BL, Conner K, Zacharewski T et al (1998) Bisphenol A interacts with the estrogen receptor alpha in distinct manner from estradiol. Mol Cell Endocrinol 142(1/2):203–214
Herbison AE (1998) Multimodal influence of estrogen upon gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons. Endocr Rev 19:302–330
Hrabovszky E, Steinhauser AM, Barabás K, Shughrue J, Petersen S, Merchenthaler I et al (2000) Estrogen receptor β immunoreactivity in luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone neurons of the rat brain. Endocrinology 142(7):3261–3264
Jarry H, Hirsch B, Leonhardt S, Wuttke W (1992) Amino acid neurotransmitter release in the preoptic area of rats during the positive feedback actions of estradiol on LH release. Neuroendocrinology 56:133–140
Kawai K, Murakami S, Semba E, Yamanaka T, Fuyiwara Y, arimura C et al (2007) Changes in estrogen receptors α and β expression in the brain of mice exposed prenatally to Bisphenol A. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 47:166–170
Leranth C, Shanabrough M, Naftolin F (1991) Estrogen induces ultrastructural changes in progesterone receptor-containing GABA neurons of the primate hypothalamus. Neuroendocrinology 54:571–579
Maffini M, Rubin B, Sonnenschein C, Soto A (2006) Endocrine disruptors and reproductive health: the case of bisphenol A. Mol Cell Endocrinol 254–225:179–186
Maffucci JA, Gore AC (2009) Hypothalamic neural systems controlling the female reproductive life cycle: gonadotropin-releasing hormone, glutamate, and GABA. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 274:69–127
Mitsushima D, Hei DL, Terasawa E (1994) Aminobutyric acid is an inhibitory neurotransmitter restricting the release of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone before the onset of puberty. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:395–399
Mitsushima D, Kimura F (1997) The maturation of GABA A receptor-mediated control of luteinizing hormone secretion in immature male rats. Brain Res 748:258–262
Moguilevsky JA, Wuttke W (2001) Changes in the control of gonadotropin secretion by neurotransmitters during sexual development in rats. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 109:188–195
Nagel SC, vom Saal FS, Thayer KA, Dhar MG, Boechler M, Welshons WV (1997) Relative binding affinity-serum modified access assay predicts the relative in vivo bioactivity of xenoestrogens bisphenol A and octylphenol. Environ Health Perspect 105:70–76
Nakamura D, Yanagiba Y, Duan Z, Ito Y, Okamura A, Asaeda N, Tagawa Y, Li C, Taya K, Zhang SY, Naito H, Ramdhan DH, Kamijima M, Nakajima T (2010) Bisphenol A may cause testosterone reduction by adversely affecting both testis and pituitary systems similar to estradiol. Toxicol Lett 15;194(1–2):16–25.
Olea N, Pulgar R, Perez P, Olea-Serrano F, Rivas A, Novillo-Fertrell A et al (1996) Estrogenicity of resin-based composites and sealants used in dentistry. Environ Health Perspect 104:298–305
Pedram A, Razandi M, Levin ER (2006) Nature of functional estrogen receptors at the plasma membrane. Mol Endocrinol 20(9):196–209
Petersen SL, Ottem EN, Carpenter CD (2003) Direct and indirect regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons by estradiol. Biol Reprod 69(6):1771–1778
Ramos J, Varayoud J, Kass L, Rodriguez H, Costabel L, Muñoz del Toro M, Luque E (2003) Bisphenol A induces both transient and permanent histofunctional alterations of the hypothalamic pituitary gonadal axis in prenatally exposed male rats. Endocrinology 114:3206–3215
Rey D, Angelini N, Belsham D (1999) Estrogen directly represses gonadotropin-releasing hormone (Gn-RH) gene expression in estrogen receptor alpha (ER alpha) and ER-beta expressing GTI-7 Gn-RH neurons. Endocrinology 140:5045–5053
Richter CA, Birnbaum LS, Farabollini F, Newbold RR, Rubin BS, Talsness CE, Vandenbergh JG, Walser-Kuntz DR, vom Saal FS (2007) In vivo effects of bisphenol A in laboratory rodent studies. Reprod Toxicol 24:199–224
Rochira V, Zirilli L, Genazzani AD, Balestrieri A, Aranda C, Fabre B et al (2006) Hypothalamic pituitary-gonadal axis in two men with aromatase deficiency: evidence that circulating estrogens are required at the hypothalamic level for the integrity of gonadotropin negative feedback. Eur J Endocrinol 155:513–522
Rubin B, Murray M, Damassa D, King J, Soto AM (2001) Perinatal exposure to low doses of Bisphenol A affects body weight, patterns of estrous cyclicity and plasma LH levels. Environ Health Perspect 109:675–680
Sakaue M, Ohsako S, Ishimura R, Kurosawa S, Kurohmaru M, Hayashi Y, Aoki Y, Yomemoto J, Tohyama C (2001) Bisphenol A affects spermatogenesis in the adult rat even at low dose. J Occup Health 43:185–190
Sharpe RM, Atanasova N, McKinnell C, Parte P, Turner KJ, Fisher JS, Kerr JB, Groome NP, Macpherson S, Millar MR, Saunders PTK (1998) Abnormalities in functional development of the Sertoli cells in rats treated neonatally with diethylstilbestrol: a possible role of estrogens in Sertoli cell development. Biol Reprod 59:1084–1094
Skynner MJ, Sim JA, Herbison AE (1999) Detection of estrogen receptor alfa and beta messenger ribonucleic acids in adult gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons. Endocrinology 140:5195–5201
Stillman RJ (1982) In utero exposure to diethylstilbestrol: adverse effects on the reproductive tract and reproductive performance in male and female offspring. Am J Obstet Gynecol 142:905–921
Sullivan SD, DeFazio RA, Moenter SM (2003) Metabolic regulation of fertility through presynaptic and postsynaptic signaling to gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons. J Neurosci 23:8578–8585
Terasawa E, Fernandez DL (2001) Neurobiological mechanisms of the onset of puberty in primates. Endocr Rev 22(1):111–151
Tohei A, Suda S, Taya K, Hashimoto T, Kogo H (2001) Bisphenol A inhibits testicular functions and increases luteinizing hormone secretion in adult male rats. Exp Biol Med 226(3):216–221
vom Saal FS, Cooke PS, Buchanan DL, Palanza P, Thayer KA, Nagel SC, Parmigiani S, Welshons WV (1998) A physiologically based approach to the study of Bisphenol A and other estrogenic chemicals on the size of reproductive organs, daily sperm production and behavior. Toxicol Ind Health 14:239–260
Wetherill Y, Akingbemi B, Kanno J, McLachlan J, Nadal A, Sonnennschein C, Watson C, Zoeller T, Belcher S (2007) In vitro molecular mechanisms of Bisphenol A action. Reprod Toxicol 24:178–198
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the University of Buenos Aires (UBACYT M434- M006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cardoso, N., Pandolfi, M., Lavalle, J. et al. Probable gamma-aminobutyric acid involvement in bisphenol A effect at the hypothalamic level in adult male rats. J Physiol Biochem 67, 559–567 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-011-0102-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-011-0102-6