Abstract
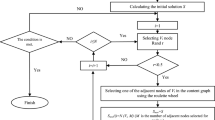
Network anomaly detection (NAD) is a crucial Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based security solution for protecting computer networks. However, analyzing high-dimensional data is a significant impediment for NAD systems. The process of Feature Selection (FS) addresses this challenge by reducing or eliminating irrelevant or redundant features. Conventional FS algorithms face the drawbacks of diminished accuracy, elevated computational costs, and the inclusion of irrelevant and redundant features. This paper presents a novel three-fold Hybrid Filter-Clustering-Coevolutionary Wrapper (HFCCW) based FS approach to overcome these issues. The proposed method integrates filter and clustering techniques in the initial phases to prevent irrelevant and redundant features from being included. The first phase involves removing irrelevant features by employing the Fisher score filter method, followed by the application of clustering based on the Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) in the second phase. The second phase aims to eliminate redundant features and effectively narrow down the search space of the coevolutionary algorithm in the third phase. The method employed in the third phase adeptly integrates the strengths of particle swarm optimization (PSO) and binary grey wolf optimization (BGWO) techniques, effectively harmonizing the exploration and exploitation trade-off in the optimization process. The incorporation of the Levy Flight (LF) concept in the final iterations of BGWOPSO enhances the search steps of GWO during the third phase. It addresses the issue of GWO being confined to local optima. This improvement is achieved by applying BLFGWOPSO in the final phase of the proposed HFCCW approach. Empirical findings on the CICIDS2017 dataset substantiate the efficacy of the proposed method in enhancing classification accuracy, selecting optimal feature subsets with fewer features, reducing computing costs and improving convergence rates. Furthermore, the proposed method achieves a favorable trade-off between accuracy and computing time when contrasted with state-of-the-art methods such as filter, metaheuristic-based wrapper, and hybrid FS approaches.






























Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The research has been conducted only with openly available datasets and will be publicly available in https://www.unb.ca/cic/datasets/ids-2017.html
References
Sharma N, Arora B (2021) Review of machine learning techniques for network traffic classification. SSRN Electron J. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3747605
Shrivas AK, Dewangan AK (2014) An ensemble model for classification of attacks with feature selection based on KDD99 and NSL-KDD data set. Int J Comput Appl 99(15):8–13. https://doi.org/10.5120/17447-5392
Panda M, Abraham A, Patra MR (2015) Hybrid intelligent systems for detecting network intrusions. Secur Commun Networks 8(16):2741–2749. https://doi.org/10.1002/SEC.592
Bostani H, Sheikhan M (2017) Hybrid of binary gravitational search algorithm and mutual information for feature selection in intrusion detection systems. Soft Comput 21(9):2307–2324. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00500-015-1942-8/TABLES/9
Sharma N, Arora B (2021) Data mining and machine learning techniques for malware detection. Adv Intell Syst Comput 1187:557–567. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6014-9_66
Liu D et al.. Opprentice: Towards practical and automatic anomaly detection through machine learning. Proc. ACM SIGCOMM Internet Meas. Conf. IMC, vol. 2015-October, pp. 211–224, Oct. 2015, doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/2815675.2815679.
Hoque N, Bhattacharyya DK, Kalita JK (2014) MIFS-ND: A mutual information-based feature selection method. Expert Syst Appl 41(14):6371–6385. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ESWA.2014.04.019
Yang XS, Deb S, Mishra SK (2018) Multi-species cuckoo search algorithm for global optimization. Cognit Comput 10(6):1085–1095. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12559-018-9579-4/TABLES/7
Kim S, Xing EP (2009) Tree-guided group lasso for multi-response regression with structured sparsity, with an application to eQTL mapping. Ann Appl Stat 6(3):1095–1117. https://doi.org/10.1214/12-AOAS549
Li B, Wang Q, Hu J (2011) Feature subset selection: a correlation-based SVM filter approach. IEEJ Trans Electr Electron Eng 6(2):173–179. https://doi.org/10.1002/TEE.20641
Vergara JR, Estévez PA (2014) A review of feature selection methods based on mutual information. Neural Comput Appl 24(1):175–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00521-013-1368-0/TABLES/4
Shen S, Sun Y, Gao X, Qiu J, Tian Z (2019) A correlation-change based feature selection method for IoT equipment anomaly detection. Appl Sci 9(3):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030437
Yap BW, Ibrahim N, Hamid HA, Rahman SA, Fong S (2018) Feature selection methods: Case of filter and wrapper approaches for maximising classification accuracy, pertanika J. Sci. Technol..
Molina D, LaTorre A, Herrera F (2018) An insight into bio-inspired and evolutionary algorithms for global optimization: review, analysis, and lessons learnt over a decade of competitions. Cognit Comput 10(4):517–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12559-018-9554-0/FIGURES/4
Al-Thanoon NA, Algamal ZY, Qasim OS (2021) Feature selection based on a crow search algorithm for big data classification. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 212:104288. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOLAB.2021.104288
Kahya MA, Altamir SA, Algamal ZY, Kahya MA, Altamir SA, Algamal ZY (2020) Improving whale optimization algorithm for feature selection with a time-varying transfer function. Numer Algebr Control Optim 11(1):87–98. https://doi.org/10.3934/NACO.2020017
J. Mani Tripathi, S. Kumar Mallik -, O. Saber Qasim, and Z. Yahya Algamal, “Variable selection in Gamma regression model using binary gray Wolf optimization algorithm Protection coordination of DOCRs for different modes of microgrid operation Variable selection in Gamma regression model using binary gray Wolf optimization algorithm 1) Niam Abdulmunim Al-Thanoon, 2),” J. Phys. Conf. Ser., vol. 1591, p. 12036, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1591/1/012036.
Deb K (1999) An introduction to genetic algorithms. Sadhana 24(4–5):293–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823145
R. Eberhart and J. Kennedy. New optimizer using particle swarm theory, Proc. Int. Symp. Micro Mach. Hum. Sci., pp. 39–43, 1995, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/MHS.1995.494215.
M. Dorigo and G. Di Caro. Ant colony optimization: A new meta-heuristic. Proc. 1999 Congr. Evol. Comput. CEC 1999, vol. 2, pp. 1470–1477, 1999, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.1999.782657.
Storn R, Price K (1997) Differential evolution - a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J Glob Optim 11(4):341–359. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008202821328/METRICS
Yang XS, Deb S (2010) Engineering optimisation by cuckoo search. Int J Math Model Numer Optim 1(4):330–343. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMMNO.2010.035430
X. S. Yang. Firefly algorithms for multimodal optimization, Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. (including Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinformatics), vol. 5792 LNCS, pp. 169–178, 2009, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04944-6_14/COVER.
Yang XS (2011) Bat algorithm for multi-objective optimisation. Int J Bio-Inspired Comput 3(5):267–274. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBIC.2011.042259
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A (2014) Grey wolf optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ADVENGSOFT.2013.12.007
Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2016) The whale optimization algorithm. Adv Eng Softw 95:51–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ADVENGSOFT.2016.01.008
Mirjalili S, Gandomi AH, Mirjalili SZ, Saremi S, Faris H, Mirjalili SM (2017) Salp swarm algorithm: a bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv Eng Softw 114:163–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ADVENGSOFT.2017.07.002
Heidari AA, Mirjalili S, Faris H, Aljarah I, Mafarja M, Chen H (2019) Harris hawks optimization: algorithm and applications. Futur Gener Comput Syst 97:849–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FUTURE.2019.02.028
Purushothaman R, Rajagopalan SP, Dhandapani G (2020) Hybridizing gray wolf optimization (GWO) with grasshopper optimization algorithm (GOA) for text feature selection and clustering. Appl Soft Comput 96:106651. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ASOC.2020.106651
Song XF, Zhang Y, Guo YN, Sun XY, Wang YL (2020) Variable-Size cooperative coevolutionary particle swarm optimization for feature selection on high-dimensional data. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 24(5):882–895. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2020.2968743
Ansari G, Ahmad T, Doja MN (2019) Hybrid filter-wrapper feature selection method for sentiment classification. Arab J Sci Eng 44(11):9191–9208. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13369-019-04064-6/TABLES/2
Kamarudin MH, Maple C, Watson T (2019) Hybrid feature selection technique for intrusion detection system. Int J High Perform Comput Netw 13(2):232. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJHPCN.2019.097503
Chaudhuri A, Sahu TP (2021) A hybrid feature selection method based on Binary Jaya algorithm for micro-array data classification. Comput Electr Eng 90:106963. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPELECENG.2020.106963
Sadeghian Z, Akbari E, Nematzadeh H (2021) A hybrid feature selection method based on information theory and binary butterfly optimization algorithm. Eng Appl Artif Intell 97:104079. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENGAPPAI.2020.104079
Kundu R, Mallipeddi R (2022) HFMOEA: a hybrid framework for multi-objective feature selection. J Comput Des Eng 9(3):949–965. https://doi.org/10.1093/JCDE/QWAC040
S. A. B. P, C. S. R. Annavarapu, and S. Dara, “Clustering-based hybrid feature selection approach for high dimensional microarray data,” Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst., vol. 213, p. 104305, Jun. 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOLAB.2021.104305.
Song XF, Zhang Y, Gong DW, Gao XZ (2022) A Fast Hybrid feature selection based on correlation-guided clustering and particle swarm optimization for high-dimensional data. IEEE Trans Cybern 52(9):9573–9586. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2021.3061152
S. Yoshida et al.. Multi-filter clustering fusion for feature selection in rotating machinery fault classification. Sensors 2022, Vol. 22, Page 2192, vol. 22, no. 6, p. 2192, Mar. 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/S22062192.
Al-Tashi Q, Abdul Kadir SJ, Rais HM, Mirjalili S, Alhussian H (2019) Binary optimization using hybrid grey wolf optimization for feature selection. IEEE Access 7, 39496–39508. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2906757
Mohammadzadeh H, Gharehchopogh FS (2021) A novel hybrid whale optimization algorithm with flower pollination algorithm for feature selection: case study Email spam detection. Comput Intell 37(1):176–209. https://doi.org/10.1111/COIN.12397
Kareem SS, Mostafa RR, Hashim FA, El-Bakry HM (2022) An effective feature selection model using hybrid metaheuristic algorithms for IoT intrusion detection. Sensors 22(4):1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041396
Abdelhamid AA et al (2023) Innovative feature selection method based on hybrid sine cosine and dipper throated optimization algorithms. IEEE Access 11:79750–79776. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3298955
Pirgazi J, Alimoradi M, Abharian TE, Olyaee MH (2019) An efficient hybrid filter-wrapper metaheuristic-based gene selection method for high dimensional datasets. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54987-1
Mundra PA, Rajapakse JC (2010) SVM-RFE with MRMR filter for gene selection. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 9(1):31–37. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNB.2009.2035284
Hancer E, Xue B, Zhang M (2018) Differential evolution for filter feature selection based on information theory and feature ranking. Knowledge-Based Syst 140:103–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.KNOSYS.2017.10.028
Djellali H, Zine NG, Azizi N (2016) Two stages feature selection based on filter ranking methods and SVMRFE on medical applications. Lect Notes Networks Syst 1:281–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-33410-3_20/COVER
Yin Y et al (2023) IGRF-RFE: a hybrid feature selection method for MLP-based network intrusion detection on UNSW-NB15 dataset. J Big Data 10(1):1–26. https://doi.org/10.1186/S40537-023-00694-8/TABLES/9
Dey AK, Gupta GP, Sahu SP (2023) Hybrid meta-heuristic based feature selection mechanism for cyber-attack detection in IoT-enabled Networks. Procedia Comput Sci 218:318–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROCS.2023.01.014
Xue Y, Zhu H, Neri F (2023) A feature selection approach based on NSGA-II with ReliefF. Appl Soft Comput 134:109987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2023.109987
Guyon I, Elisseeff A (2003) An introduction to variable and feature selection. J Mach Learn Res 3:1157–1182. https://doi.org/10.5555/944919.944968
Li M, Wang H, Yang L, Liang Y, Shang Z, Wan H (2020) Fast hybrid dimensionality reduction method for classification based on feature selection and grouped feature extraction. Expert Syst Appl 150:113277. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ESWA.2020.113277
Rajab M, Wang D (2020) Practical challenges and recommendations of filter methods for feature selection. J. Inf. Knowl.. Manag., 19(1), 2040019. doi:https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219649220400195.
Singh B, Sankhwar JS, Vyas OP (2015) Optimization of feature selection method for high dimensional data using fisher score and minimum spanning tree. 11th IEEE India Conf. Emerg. Trends Innov. Technol. INDICON 2014. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/INDICON.2014.7030450.
Xu Z, Xuan J, Liu J, Cui X (2016) MICHAC: Defect prediction via feature selection based on Maximal Information Coefficient with Hierarchical Agglomerative Clustering. 2016 IEEE 23rd Int. Conf. Softw. Anal. Evol. Reengineering, SANER 2016, vol. 2016-January, pp. 370–381. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/SANER.2016.34.
Arun Kumar R, Vijay Franklin J, Koppula N (2022) A comprehensive survey on metaheuristic algorithm for feature selection techniques. Mater Today: Proc 64:435–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.04.803
Singh N, Singh SB (2017) A novel hybrid GWO-SCA approach for optimization problems. Eng Sci Technol Int J 20(6):1586–1601. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JESTCH.2017.11.001
Kitonyi PM, Segera DR (2021) Hybrid gradient descent grey wolf optimizer for optimal feature selection. Biomed Res. Int., , 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/2555622.
Otair M, Ibrahim OT, Abualigah L, Altalhi M, Sumari P (2022) An enhanced grey wolf optimizer based particle swarm optimizer for intrusion detection system in wireless sensor networks. Wirel Networks 28(2):721–744. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11276-021-02866-X/METRICS
Robnik-Šikonja M, Kononenko I (2003) Theoretical and empirical analysis of ReliefF and RReliefF. Mach Learn 53(1–2):23–69. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025667309714/METRICS
Alalga A, Benabdeslem K, Taleb N (2016) Soft-constrained Laplacian score for semi-supervised multi-label feature selection. Knowl Inf Syst 47(1):75–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10115-015-0841-8/METRICS
Kumar A, Yin B, Shaikh AM, Ali M, Wei W (2022) CorrNet: pearson correlation based pruning for efficient convolutional neural networks. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 13(12):3773–3783. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13042-022-01624-5/FIGURES/7
Sumaiya Thaseen I, Aswani Kumar C (2017) Intrusion detection model using fusion of chi-square feature selection and multi class SVM. J. King Saud Univ. - Comput. Inf. Sci. 29(4), 462–472. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JKSUCI.2015.12.004.
Nie F, Xiang S, Jia Y, Zhang C, Yan S (2008) Trace ratio criterion for feature selection. In ‘Proceedings of the Twenty-Third AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. AAAI 2008, Chicago, Illinois, USA, July 13-17, 2008
Li J, et al., Feature selection: A data perspective. ACM Comput. Surv., 50(6), 2017, doi:https://doi.org/10.1145/3136625
Al-Ani A, Deriche M (2002) Feature selection using a mutual information based measure. Proc - Int Conf Pattern Recognit 16(4):82–85. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR.2002.1047405
M. K. Publishers. Programs for Machine Learning, 2004.
Jiang B-N, Ding X-Q, Ma L-T, He Y, Wang T, Xie W-W. A hybrid feature selection algorithm: combination of symmetrical uncertainty and genetic algorithms. 2008.
I. Kononenko, “Estimating attributes: Analysis and extensions of RELIEF,” Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. (including Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinformatics), vol. 784 LNCS, pp. 171–182, 1994, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-57868-4_57/COVER.
Heidari AA, Pahlavani P (2017) An efficient modified grey wolf optimizer with Lévy flight for optimization tasks. Appl Soft Comput 60:115–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ASOC.2017.06.044
Faris H, Aljarah I, Al-Betar MA, Mirjalili S (2018) Grey wolf optimizer: a review of recent variants and applications. Neural Comput Appl 30(2):413–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00521-017-3272-5/FIGURES/9
Kennedy J, Eberhart R. Particle swarm optimization. Proc. ICNN’95 - Int. Conf. Neural Networks, vol. 4, pp. 1942–1948. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968.
Arun Prabha K, Karthikeyani Visalakshi N (2014). Improved particle swarm optimization based K-Means clustering. Proc. - 2014 Int. Conf. Intell. Comput. Appl. ICICA 2014, pp. 59–63. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICA.2014.21
Singh N, Singh SB (2017). Hybrid algorithm of particle swarm optimization and grey wolf optimizer for improving convergence performance. J. Appl. Math., 2017. doi:https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2030489.
Talbi E-G (2009) Metaheuristics: from desing to implementation. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p. 624, 2009, Accessed: Mar. 31, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Metaheuristics%3A+From+Design+to+Implementation+-p-9780470278581.
Talbi EG (2002) A taxonomy of hybrid metaheuristics. J Heuristics 8(5):541–564. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016540724870/METRICS
“IDS 2017 | Datasets | Research | Canadian Institute for Cybersecurity | UNB.” https://www.unb.ca/cic/datasets/ids-2017.html (accessed May 25, 2022).
Sharafaldin I, Lashkari AH, Ghorbani AA (2018) Toward generating a new intrusion detection dataset and intrusion traffic characterization. ICISSP 2018 - Proc. 4th Int. Conf. Inf. Syst. Secur. Priv., vol. 2018-January, pp. 108–116. doi:https://doi.org/10.5220/0006639801080116.
Dash T (2017) A study on intrusion detection using neural networks trained with evolutionary algorithms. Soft Comput 21(10):2687–2700. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00500-015-1967-Z/TABLES/11
Khammassi C, Krichen S (2020) A NSGA2-LR wrapper approach for feature selection in network intrusion detection. Comput Networks 172:107183. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMNET.2020.107183
“(1) (PDF) Evaluating the Impact of Feature Selection Methods on the Performance of the Machine Learning Models in Detecting DDoS Attacks.” https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343850781_Evaluating_the_Impact_of_Feature_Selection_Methods_on_the_Performance_of_the_Machine_Learning_Models_in_Detecting_DDoS_Attacks (accessed Mar. 28, 2023).
Ghatasheh N, Faris H, Aljarah I, Al-Sayyed RMH (2019) Optimizing Software Effort Estimation Models Using Firefly Algorithm. J Softw Eng Appl 08(03):133–142. https://doi.org/10.4236/jsea.2015.83014
Chen H, Jiao S, Heidari AA, Wang M, Chen X, Zhao X (2019) An opposition-based sine cosine approach with local search for parameter estimation of photovoltaic models. Energy Convers Manag 195:927–942. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENCONMAN.2019.05.057
Hu P, Pan JS, Chu SC (2020) Improved binary grey wolf optimizer and its application for feature selection. Knowledge-Based Syst 195:105746. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.KNOSYS.2020.105746
Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2013) S-shaped versus V-shaped transfer functions for binary particle swarm optimization. Swarm Evol Comput 9:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SWEVO.2012.09.002
Chechkin AV, Metzler R, Klafter J, Gonchar VY (2008) Introduction to the Theory of Lévy Flights. Anomalous Transp. Found. Appl., 129–162. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527622979.CH5.
Yang XS, Deb S (2013) Multiobjective cuckoo search for design optimization. Comput Oper Res 40(6):1616–1624. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COR.2011.09.026
Emary E, Zawbaa HM, Hassanien AE (2016) Binary grey wolf optimization approaches for feature selection. Neurocomputing 172:371–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NEUCOM.2015.06.083
X. Yin and J. Han, “CPAR: Classification based on Predictive Association Rules *.
Mafarja M, Qasem A, Heidari AA, Aljarah I, Faris H, Mirjalili S (2020) Efficient hybrid nature-inspired binary optimizers for feature selection. Cognit Comput 12(1):150–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12559-019-09668-6/FIGURES/12
Kumar GH, Sreenubabu C (2015) A clustering-based feature subset selection algorithm for high dimensional data.
Meidani K, Hemmasian AP, Mirjalili S, Barati Farimani A (2022). Adaptive grey wolf optimizer, Neural Comput. Appl. 34(10), 7711–7731. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/S00521-021-06885-9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, N., Arora, B. HFCCW: A Novel Hybrid Filter-Clustering-Coevolutionary Wrapper Feature Selection Approach for Network Anomaly Detection. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-024-02187-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-024-02187-3