Abstract
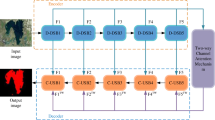
The automatic lake water extraction method based on semantic segmentation is a research hotspot in the field of remote sensing image processing. In remote sensing images, the presence of complex noise information at the lake boundary hinders the normal expression of boundary information, which leads to methods cannot extract a coherent lake boundary. Moreover, partial small-scale lakes’ texture features are weak and easily masked by the background information. To address the above issues, an end-to-end semantic segmentation network is designed. The network uses a symmetric encoder-decoder architecture to extract lake water in remote sensing images. On the one hand, a directional noise reduction filtering algorithm is proposed to reduce the impact of noise information on the network segmentation process. The algorithm utilizes a preset directional guide map to guide the nonlinear propagation of boundary noise and suppress low-contrast halo artifacts in the image, thereby better preserving the boundary sharpness of the lake. On the other hand, for the problem of missing small-scale lakes, an attention gate compression module is embedded in the skip connection. This module can adaptively integrate the correlation features between different ground objects, and selectively assign more attention to small-scale lakes, thereby improving the network’s ability to recognize such lakes. In the experimental results, our method can produce more accurate lake water extraction results than the current mainstream methods. Besides it has an excellent performance in accurately identifying lake boundaries and small-scale lakes.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Lian Guofei et al (2022) Towards unified on-road object detection and depth estimation from a single image. Int J Mach Learn Cybernet. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-021-01444-z
Shamki ZAM, Rabee F (2022) Image mining technique using Hadoop map reduce over distributed multi-node computers connections. Al-Salam J Eng Technol 1(2):18–24. https://doi.org/10.55145/ajest.2022.01.02.004
Qadir MS, Bilgin G (2023) Active learning with Bayesian CNN using the BALD method for hyperspectral image classification. Mesopotamian J Big Data https://doi.org/10.58496/MJBD/2023/008
Li S, Liu J, Song Z (2022) Brain tumor segmentation based on region of interest-aided localization and segmentation U-Net. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 13(9):2435–2445
Mohanad Ghazi Yaseen, Mohammad Aljanabi, Ahmed Hussein Ali, Saad Abbas Abd (2022) Current cutting-edge research in computer science. Mesopotamian J Comput Sci https://doi.org/10.58496/MJCSC/2022/001
Miao Z, Fu K, Sun H, Sun X, Yan M (2018) Automatic water-body segmentation from high-resolution satellite images via deep networks. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 15(4):602–606. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2018.2794545
Wang R et al (2019) Remote sensing semantic segregation for water information extraction: optimization of samples via training error performance. IEEE Access 7:13383–13395. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2894099
Duan L, Hu X (2019) Multiscale refinement network for water-body segmentation in high-resolution satellite imagery. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 17(4):686–690. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2019.2926412
Wang Y, Li Z, Zeng C, Xia G, Shen H (2020) An urban water extraction method combining deep learning and Google Earth engine. IEEE J Select Topics Appl Earth Observ Remote Sens 13:769–782. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2971783
Liu Y, Key J, Mahoney R (2016) Sea and freshwater ice concentration from VIIRS on Suomi NPP and the future JPSS satellites. Remote Sens 8(6):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060523
Rashid T, Bin Hamzah M, Rasheed M, Jaber A, Sarhan M, Aldaraji M, Saidani T (2023) Image segmentation for animals in the wild using scilab software. Al-Salam J Eng Technol 2(2):72–77. https://doi.org/10.55145/ajest.2023.02.02.009
Zheng Y, Zhang X, Hou B, Liu G (2013) Using combined difference image and k -means clustering for SAR image change detection. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 11(3):691–695. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2013.2275738
Singh B, Sihag P, Singh K (2017) Modelling of impact of water quality on infiltration rate of soil by random forest regression. Modeling Earth Syst Environ 3:999–1004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0347-3
McFeeters SK (1996) The use of the normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int J Remote Sens 17(7):1425–1432. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431169608948714
Wang C, Jia M, Chen N, Wang W (2018) Long-term surface water dynamics analysis based on Landsat imagery and the Google Earth Engine platform: a case study in the middle Yangtze River Basin. Remote Sens 10(10):1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101635
Zhang J et al (2020) Water body detection in high-resolution SAR images with cascaded fully-convolutional network and variable focal loss. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 59(1):316–332. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2020.2999405
Li L et al (2019) Water body extraction from very high spatial resolution remote sensing data based on fully convolutional networks. Remote Sens 11(10):1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101162
Li M et al (2021) A deep learning method of water body extraction from high resolution remote sensing images with multisensors. IEEE J Select Topics Appl Earth Observ Remote Sens 14:3120–3132. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3060769
Al-Khaldi MM et al (2021) Inland water body mapping using CYGNSS coherence detection. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 59(9):7385–7394. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2020.3047075
Liang X, Zhang Y, Zhang J (2021) Water retrieval embedded attention network with multiscale receptive fields for hyperspectral image refined classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2021.3091985
Lu M, Fang L, Li M, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Ghamisi P (2022) NFANet: a novel method for weakly supervised water extraction from high-resolution remote-sensing imagery. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2022.3140323
Feng W, Sui H, Huang W, Xu C, An K (2018) Water body extraction from very high-resolution remote sensing imagery using deep U-Net and a superpixel-based conditional random field model. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 16(4):618–622. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2018.2879492
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. Int Confer Med image Comput Comput Asssist Intervent. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Wang Z, Gao X, Zhang Y (2021) HA-Net: a lake water body extraction network based on hybrid-scale attention and transfer learning. Remote Sens 13(20):4121. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13204121
Weng L et al (2020) Water areas segmentation from remote sensing images using a separable residual segnet network. ISPRS Int J Geo Inf 9(4):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9040256
Li Z, Wang R, Zhang W, Hu FM, Meng LK (2019) Multiscale features supported DeepLabV3+ optimization scheme for accurate water semantic segmentation. IEEE Access 7:155787–155804. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2949635
Chen L et al (2017) Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(4):834–848. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184
Zhong HF, Sun HM, Han DN, Li ZH, Jia RS (2022) Lake water body extraction of optical remote sensing images based on semantic segmentation. Appl Intell 52:17974–17989. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03345-2
Guo H et al (2020) A multi-scale water extraction convolutional neural network (MWEN) method for GaoFen-1 remote sensing images. ISPRS Int J Geo Inf 9(4):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9040189
Zhang X, Li J, Hua Z (2022) MRSE-Net: multiscale residuals and SE-attention network for water body segmentation from satellite images. IEEE J Select Topics Appl Earth Observ Remote Sens 15:5049–5064. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3185245
Lyu X, Fang Y, Tong B, Li X, Zeng T (2022) Multiscale normalization attention network for water body extraction from remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens 14(19):4983. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194983
Ding L, Tang H, Bruzzone L (2020) LANet: Local attention embedding to improve the semantic segmentation of remote sensing images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 59(1):426–435. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2020.2994150
Zhu Q et al (2020) MAP-Net: multiple attending path neural network for building footprint extraction from remote sensed imagery. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 59(7):6169–6181. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2020.3026051
Li R et al (2021) Multiattention network for semantic segmentation of fine-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2021.3093977
Zhang X et al (2020) ICENET: A semantic segmentation deep network for river ice by fusing positional and channel-wise attentive features. Remote Sens 12(2):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020221
Zhang Z et al (2021) Rich CNN Features for water-body segmentation from very high resolution aerial and satellite imagery. Remote Sens 13(10):1912. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13101912
Hu K, Li M, Xia M, Lin H (2022) Multi-scale feature aggregation network for water area segmentation. Remote Sens 14(1):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010206
Dosovitskiy A et al (2020) An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929
Vaswani A et al (2017) Attention is all you need. Adv Neural Inform Process Syst 30
Chen J et al (2021) Transunet: transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.04306
Cao H et al (2022) Swin-unet: Unet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation. European conference on computer vision. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland pp: 205–218
Chen B et al (2021) Transattunet: multi-level attention-guided u-net with transformer for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.05274
Xie E et al (2021) SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 34:12077–12090
Cai H, Li J, Hu M, Gan C, Han S (2022) EfficientViT: lightweight multi-scale attention for on-device semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.14756
Gao L et al (2021) STransFuse: Fusing swin transformer and convolutional neural network for remote sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE J Select Topics Appl Earth Observ Remote Sens 14:10990–11003. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3119654
Song P et al (2022) CTMFNet: CNN and transformer multi-scale fusion network of remote sensing urban scene imagery. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 61:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2022.3232143
Li Y et al (2023) RCCT-ASPPNet: dual-encoder remote image segmentation based on transformer and ASPP. Remote Sens 15(2):379. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020379
Zhong HF, Sun Q, Sun HM, Jia RS (2022) NT-net: a semantic segmentation network for extracting lake water bodies from optical remote sensing images based on transformer. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2022.3197402
Li S, Zou Y, Wang G, Lin C (2023) Infrared and visible image fusion method based on a principal component analysis network and image pyramid. Remote Sens 15(3):685. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030685
He K, Sun J, Tang X (2012) Guided image filtering. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(6):1397–1409. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.213
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G (2018) Squeeze-and-excitation networks. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
He K et al (2015) Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. pp: 1026–1034
Schmidt-Hieber J (2020) Nonparametric regression using deep neural networks with ReLU activation function. 48(4):1875–1897. https://doi.org/10.1214/19-AOS1875
Liu Z et al (2021) Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. pp: 10012–10022
He X et al (2022) Swin transformer embedding UNet for remote sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2022.3144165
Zhang J et al (2020) A contextual bidirectional enhancement method for remote sensing image object detection. IEEE J Select Topics Appl Earth Observ Remote Sens 13:4518–4531. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3015049
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980
Wang Yu, Li J (2016) Credible intervals for precision and recall based on a K-fold cross-validated beta distribution. Neural Comput 28(8):1694–1722. https://doi.org/10.1162/NECO_a_00857
Wong T-T, Yeh P-Y (2019) Reliable accuracy estimates from k-fold cross validation. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 32(8):1586–1594. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2019.2912815
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for collaborative funding support from the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, PR. China (ZR2022ME091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, RR., Sun, HM., Wang, RX. et al. A novel semantic feature enhancement network for extracting lake water from remote sensing images. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-024-02133-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-024-02133-3