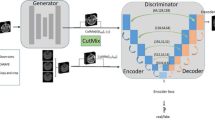
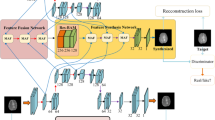
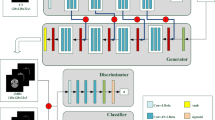
Abstract
Magnetic resonance (MR) and computer tomography (CT) imaging are valuable tools for diagnosing diseases and planning treatment. However, limitations such as radiation exposure and cost can restrict access to certain imaging modalities. To address this issue, medical image synthesis can generate one modality from another, but many existing models struggle with high-quality image synthesis when multiple slices are present in the dataset. This study proposes an attention-based dual contrast generative model, called ADC-cycleGAN, which can synthesize medical images from unpaired data with multiple slices. The model integrates a dual contrast loss term with the CycleGAN loss to ensure that the synthesized images are distinguishable from the source domain. Additionally, an attention mechanism is incorporated into the generators to extract informative features from both channel and spatial domains. To improve performance when dealing with multiple slices, the K-means algorithm is used to cluster the dataset into K groups, and each group is used to train a separate ADC-cycleGAN. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed ADC-cycleGAN model produces comparable samples to other state-of-the-art generative models, achieving the highest PSNR and SSIM values of 19.04385 and 0.68551, respectively. We publish the code at https://github.com/JiayuanWang-JW/ADC-cycleGAN.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
We have put our Github link for the code in the abstract. For the dataset, we introduce in our 4.2 subsections and provide a source link: https://github.com/ChengBinJin/MRI-to-CT-DCNN-TensorFlow.
References
Xu L, Zeng X, Zhang H, Li W, Lei J, Huang Z (2020) Bpgan: Bidirectional ct-to-mri prediction using multi-generative multi-adversarial nets with spectral normalization and localization. Neural Netw 128:82–96
Yang H, Lu X, Wang S-H, Lu Z, Yao J, Jiang Y, Qian P (2021) Synthesizing multi-contrast mr images via novel 3d conditional variational auto-encoding gan. Mobile Netw Appl 26(1):415–424
Chen X, Lian C, Wang L, Deng H, Fung SH, Nie D, Thung K-H, Yap P-T, Gateno J, Xia JJ et al (2019) One-shot generative adversarial learning for mri segmentation of craniomaxillofacial bony structures. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(3):787–796
Lee JH, Han IH, Kim DH, Yu S, Lee IS, Song YS, Joo S, Jin C-B, Kim H (2020) Spine computed tomography to magnetic resonance image synthesis using generative adversarial networks: a preliminary study. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 63(3):386–396
Tomar D, Lortkipanidze M, Vray G, Bozorgtabar B, Thiran J-P (2021) Self-attentive spatial adaptive normalization for cross-modality domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 40(10):2926–2938
Mérida I, Costes N, Heckemann RA, Drzezga A, Förster S, Hammers A (2015) Evaluation of several multi-atlas methods for pseudo-ct generation in brain mri-pet attenuation correction. In: 2015 IEEE 12th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp. 1431–1434. IEEE
Lian C, Li X, Kong L, Wang J, Zhang W, Huang X, Wang L (2022) Cocyclereg: collaborative cycle-consistency method for multi-modal medical image registration. Neurocomputing
Li X, Jia M, Islam MT, Yu L, Xing L (2020) Self-supervised feature learning via exploiting multi-modal data for retinal disease diagnosis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(12):4023–4033
Jiao J, Namburete AI, Papageorghiou AT, Noble JA (2020) Self-supervised ultrasound to mri fetal brain image synthesis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(12):4413–4424
Berker Y, Franke J, Salomon A, Palmowski M, Donker HC, Temur Y, Mottaghy FM, Kuhl C, Izquierdo-Garcia D, Fayad ZA et al (2012) Mri-based attenuation correction for hybrid pet/mri systems: a 4-class tissue segmentation technique using a combined ultrashort-echo-time/dixon mri sequence. J Nucl Med 53(5):796–804
Sjölund J, Forsberg D, Andersson M, Knutsson H (2015) Generating patient specific pseudo-ct of the head from mr using atlas-based regression. Phys Med Biol 60(2):825
Bhosale YH, Patnaik KS (2022) Application of deep learning techniques in diagnosis of covid-19 (coronavirus): a systematic review. Neural Process Lett: 1–53
Bhosale YH, Patnaik KS (2023) Puldi-covid: chronic obstructive pulmonary (lung) diseases with covid-19 classification using ensemble deep convolutional neural network from chest x-ray images to minimize severity and mortality rates. Biomed Signal Process Control 81:104445
Li R, Zhang W, Suk H-I, Wang L, Li J, Shen D, Ji S (2014) Deep learning based imaging data completion for improved brain disease diagnosis. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention, pp. 305–312. Springer
Huang Y, Shao L, Frangi AF (2017) Simultaneous super-resolution and cross-modality synthesis of 3d medical images using weakly-supervised joint convolutional sparse coding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6070–6079
Zhao Y, Liao S, Guo Y, Zhao L, Yan Z, Hong S, Hermosillo G, Liu T, Zhou XS, Zhan Y (2018) Towards mr-only radiotherapy treatment planning: synthetic ct generation using multi-view deep convolutional neural networks. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 286–294
Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, Courville A, Bengio Y (2014) Generative adversarial nets. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2672–2680
Nie D, Trullo R, Lian J, Wang L, Petitjean C, Ruan S, Wang Q, Shen D (2018) Medical image synthesis with deep convolutional adversarial networks. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 65(12):2720–2730
Dalmaz O, Yurt M, Çukur T (2022) Resvit: residual vision transformers for multi-modal medical image synthesis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging
Zhu J-Y, Park T, Isola P, Efros AA (2017) Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2223–2232
Liu S, Zhang B, Liu Y, Han A, Shi H, Guan T, He Y (2021) Unpaired stain transfer using pathology-consistent constrained generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 40(8):1977–1989
Huo Y, Xu Z, Moon H, Bao S, Assad A, Moyo TK, Savona MR, Abramson RG, Landman BA (2018) Synseg-net: synthetic segmentation without target modality ground truth. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(4):1016–1025
Liu Y, Lei Y, Wang T, Fu Y, Tang X, Curran WJ, Liu T, Patel P, Yang X (2020) Cbct-based synthetic ct generation using deep-attention cyclegan for pancreatic adaptive radiotherapy. Med Phys 47(6):2472–2483
Huang Z, Chen Z, Zhang Q, Quan G, Ji M, Zhang C, Yang Y, Liu X, Liang D, Zheng H et al (2020) Cagan: a cycle-consistent generative adversarial network with attention for low-dose ct imaging. IEEE Trans Comput Imaging 6:1203–1218
Xu Z, Qi C, Xu G (2019) Semi-supervised attention-guided cyclegan for data augmentation on medical images. In: IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), pp. 563–568
Nie D, Shen D (2020) Adversarial confidence learning for medical image segmentation and synthesis. Int J Comput Vis 128(10):2494–2513
Yang H, Sun J, Carass A, Zhao C, Lee J, Prince JL, Xu Z (2020) Unsupervised mr-to-ct synthesis using structure-constrained cyclegan. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(12):4249–4261
Wang J, Wu Q, Pourpanah F (2022) Dc-cyclegan: bidirectional ct-to-mr synthesis from unpaired data. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.01293
Han X (2017) Mr-based synthetic ct generation using a deep convolutional neural network method. Med Phys 44(4):1408–1419
Abu-Srhan A, Almallahi I, Abushariah MA, Mahafza W, Al-Kadi OS (2021) Paired-unpaired unsupervised attention guided gan with transfer learning for bidirectional brain mr-ct synthesis. Comput Biol Med 136:104763
Woo S, Park J, Lee J-Y, Kweon IS (2018) CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 3–19
Wang T, Lei Y, Fu Y, Wynne JF, Curran WJ, Liu T, Yang X (2021) A review on medical imaging synthesis using deep learning and its clinical applications. J Appl Clin Med Phys 22(1):11–36
Hofmann M, Steinke F, Scheel V, Charpiat G, Farquhar J, Aschoff P, Brady M, Schölkopf B, Pichler BJ (2008) Mri-based attenuation correction for pet/mri: a novel approach combining pattern recognition and atlas registration. J Nucl Med 49(11):1875–1883
Chen M, Jog A, Carass A, Prince JL (2015) Using image synthesis for multi-channel registration of different image modalities. In: Medical Imaging 2015: Image Processing, vol. 9413, pp. 462–468. SPIE
Dowling JA, Lambert J, Parker J, Salvado O, Fripp J, Capp A, Wratten C, Denham JW, Greer PB (2012) An atlas-based electron density mapping method for magnetic resonance imaging (mri)-alone treatment planning and adaptive mri-based prostate radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83(1):5–11
Izquierdo-Garcia D, Hansen AE, Förster S, Benoit D, Schachoff S, Fürst S, Chen KT, Chonde DB, Catana C (2014) An spm8-based approach for attenuation correction combining segmentation and nonrigid template formation: application to simultaneous pet/mr brain imaging. J Nucl Med 55(11):1825–1830
Delpon G, Escande A, Ruef T, Darréon J, Fontaine J, Noblet C, Supiot S, Lacornerie T, Pasquier D (2016) Comparison of automated atlas-based segmentation software for postoperative prostate cancer radiotherapy. Front Oncology 6:178
Hsu S-H, Cao Y, Huang K, Feng M, Balter JM (2013) Investigation of a method for generating synthetic ct models from mri scans of the head and neck for radiation therapy. Physics Med Biol 58(23):8419
Burgos N, Cardoso MJ, Thielemans K, Modat M, Pedemonte S, Dickson J, Barnes A, Ahmed R, Mahoney CJ, Schott JM et al (2014) Attenuation correction synthesis for hybrid pet-mr scanners: application to brain studies. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 33(12):2332–2341
Sevetlidis V, Giuffrida MV, Tsaftaris SA (2016) Whole image synthesis using a deep encoder-decoder network. In: International Workshop on Simulation and Synthesis in Medical Imaging, pp. 127–137. Springer
Zhou T, Fu H, Chen G, Shen J, Shao L (2020) Hi-net: hybrid-fusion network for multi-modal mr image synthesis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(9):2772–2781
Cao B, Zhang H, Wang N, Gao X, Shen D (2020) Auto-gan: self-supervised collaborative learning for medical image synthesis. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 10486–10493
Zhang T, Fu H, Zhao Y, Cheng J, Guo M, Gu Z, Yang B, Xiao Y, Gao S, Liu J (2019) Skrgan: sketching-rendering unconditional generative adversarial networks for medical image synthesis. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 777–785. Springer
Hu S, Yuan J, Wang S (2019) Cross-modality synthesis from mri to pet using adversarial u-net with different normalization. In: 2019 International Conference on Medical Imaging Physics and Engineering (ICMIPE), pp. 1–5. IEEE
Wu H, Jiang X, Jia F (2019) Uc-gan for mr to ct image synthesis. In: Workshop on Artificial Intelligence in Radiation Therapy, pp. 146–153. Springer
Yang H, Sun J, Carass A, Zhao C, Lee J, Prince JL, Xu Z (2020) Unsupervised mr-to-ct synthesis using structure-constrained cyclegan. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(12):4249–4261
Chen R, Huang W, Huang B, Sun F, Fang B (2020) Reusing discriminators for encoding: Towards unsupervised image-to-image translation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8168–8177
Lee J, Gu J, Ye JC (2021) Unsupervised ct metal artifact learning using attention-guided \(\beta\)-cyclegan. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 40(12):3932–3944
Kong L, Lian C, Huang D, Hu Y, Zhou Q et al (2021) Breaking the dilemma of medical image-to-image translation. Adv Neural Inform Process Syst 34
Kim J, Kim M, Kang H, Lee KH U-gat-it: Unsupervised generative attentional networks with adaptive layer-instance normalization for image-to-image translation. In: International Conference on Learning Representations
Larochelle H, Hinton GE (2010) Learning to combine foveal glimpses with a third-order boltzmann machine. Adv Neural Inform Process Syst 23
Fukui H, Hirakawa T, Yamashita T, Fujiyoshi H (2019) Attention branch network: Learning of attention mechanism for visual explanation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10705–10714
Fu J, Liu J, Tian H, Li Y, Bao Y, Fang Z, Lu H (2019) Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3146–3154
Liu G, Guo J (2019) Bidirectional lstm with attention mechanism and convolutional layer for text classification. Neurocomputing 337:325–338
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser Ł, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. Adv Neural Inform Process Syst:30
Chen C-FR, Fan Q, Panda R (2021) Crossvit: cross-attention multi-scale vision transformer for image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 357–366
Guo M-H, Xu T-X, Liu J-J, Liu Z-N, Jiang P-T, Mu T-J, Zhang S-H, Martin RR, Cheng M-M, Hu S-M (2022) Attention mechanisms in computer vision: a survey. Comput Vis Med:1–38
Misra D, Nalamada T, Arasanipalai AU, Hou Q (2021) Rotate to attend: convolutional triplet attention module. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 3139–3148
Wang S-H, Fernandes SL, Zhu Z, Zhang Y-D (2021) Avnc: attention-based vgg-style network for covid-19 diagnosis by cbam. IEEE Sens J 22(18):17431–17438
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778
Snell J, Ridgeway K, Liao R, Roads BD, Mozer MC, Zemel RS (2017) Learning to generate images with perceptual similarity metrics. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 4277–4281. IEEE
Zhou Y, Wang X, Zhang M, Zhu J, Zheng R, Wu Q (2019) Mpce: a maximum probability based cross entropy loss function for neural network classification. IEEE Access 7:146331–146341
Zhong Y, Liu L, Zhao D, Li H (2020) A generative adversarial network for image denoising. Multimed Tools Appl 79(23):16517–16529
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The dataset analyzed during the current study are available in the Github repository, https://github.com/ChengBinJin/MRI-to-CT-DCNN-TensorFlow.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Wu, Q.M.J. & Pourpanah, F. An attentive-based generative model for medical image synthesis. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 14, 3897–3910 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-023-01871-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-023-01871-0