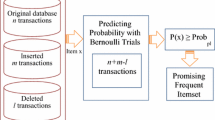
Abstract
Finding an efficient approach to incrementally update and maintain frequent itemsets is an important aspect of data mining. Earlier incremental algorithms focused on reducing the number of scans of the original database while it is updated. However, they still required the database to be rescanned in some situations. Here we propose a three-way decision update pattern approach (TDUP) along with a synchronization mechanism for this issue. With two support-based measures, all possible itemsets are divided into positive, boundary, and negative regions. TDUP efficiently updates frequent itemsets online, while the synchronization mechanism is periodically triggered to recompute the itemsets offline. The operation of the mechanism based on appropriate settings of two support-based measures is examined through experiments. Results from three real-world data sets show that the proposed approach is efficient and reliable.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal R, Srikant R (1994) Fast algorithms for mining association rules. In: Proceedings of the 20th VLDB conference, pp 487–499
Vo B, Le T, Coenen F, Hong TP (2014) Mining frequent itemsets using the n-list and subsume concepts. Int J Mach Learn Cybern, pp 1–13
Duan L, Street WN (2014) Speeding up maximal fully-correlated itemsets search in large databases. Int J Mach Learn Cybern, pp 1–11
Li Y, Zhang ZH, Chen WB, Min F (2014) Mining high utility itemsets with discount strategies. Inf Comput Sci 11:6297–6307
Kopa M, D’Ecclesia RL, Tichy T (2012) Financial modeling
Higgins RC, Reimers M (2007) Analysis for financial management. McGraw-Hill, Irwin
Ahmed KM, El-Makky NM, Taha Y (2000) A note on beyond market baskets: generalizing association rules to correlations. ACM SIGKDD Explor Newsl 1(2):46–48
Berry MJ, Linoff GS (2004) Data mining techniques: for marketing, sales, and customer relationship management. Wiley
Min F, Zhu W (2012) Granular association rule mining through parametric rough sets. In: brain informatics. Springer, pp 320–331
Min F, Hu QH, Zhu W (2014) Feature selection with test cost constraint. Int J Approax Reason 55(1)
Yang XB, Qi YS, Song XN, Yang JY (2013) Test cost sensitive multigranulation rough set: model and minimal cost selection. Inf Sci 250:184–199
Wikipedia: big data. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Big\_data#cite\_note-15
Chang CC, Li YC, Lee JS (2005) An efficient algorithm for incremental mining of association rules. In: IEEE research issues in data engineering: stream data mining and applications, pp 3–10
Cheung DW, Han J, Ng VT, Wong CY (1996) Maintenance of discovered association rules in large databases: an incremental updating approach. In: Proceedings of the twelfth international conference, data engineering, pp 106–114
Agrawal R, Srikant R (1994) Fast algorithms for mining association rules in large databases. In: Proceedings of the 20th international conference on very large data bases, pp 487–499
Yao YY (2012) An outline of a theory of three-way decisions. Comput Sci 7413:1–17
Jia XY, Shang L, Zhou XZ, Liang JY, Miao DQ, Wang GY, Li TR, Zhang YP (eds) (2012) Theory of three-way decisions and application (in chinese). Nanjing University Press
Liu D, Li TR, Miao DQ, Wang GY, Liang JY (eds) (2013) Three-way decisions and granular computing (in chinese). Science Press
Yu H, Liu ZG, Wang GY (2014) An automatic method to determine the number of clusters using decision-theoretic rough set. Int J Approx Reason 55(1):101–115
Mohamed MH, Darwieesh MM (2013) Efficient mining frequent itemsets algorithms. Int J Mach Learn Cybern, pp 1–11
Pei J, Han JW, Lakshmanan LV (2001) Mining frequent itemsets with convertible constraints. In: Proceedings of 17th international conference, data engineering, pp 433–442
Agarwal RC, Aggarwal CC, Prasad V (2001) A tree projection algorithm for generation of frequent itemsets. J Parallel Distrib Comput 61:350–371
Cheung W, Zaiane OR (2003) Incremental mining of frequent patterns without candidate generation or support constraint. In: IEEE Proceedings of seventh international symposium applications database engineering, pp 111–116
Shan S, Wang X, Sui M (2010) Mining association rules: a continuous incremental updating technique. In: International conference web information systems and mining (WISM), 1:62–66
Yao YY (2009) Three-way decision: an interpretation of rules in rough set theory. Comput Sci 5589:642–649
Li HX, Zhou XZ (2011) Risk decision making based on decision-theoretic rough set: a three-way view decision model. Int J Comput Intell Syst 4(1):1–11
Jia XY, Tang ZM, Liao WH, Shang L (2014) On an optimization representation of decision-theoretic rough set models. Int J Approx Reason 55:156–166
Yao YY (2010) Three-way decisions with probabilistic rough sets. Inf Sci 180:341–353
Goethals B, Le Page W, Mampaey M (2010) Mining interesting sets and rules in relational databases. In: Proceedings of the ACM symposium on applied computing, ACM, pp 997–1001
Han JW, Pei J, Yin YW (2000) Mining frequent patterns without candidate generation. In: ACM SIGMOD record, ACM, 29:1–12
Cheung D, Lee S, Kao B (1997) A general incremental technique for maintaining discovered association rules. In: Proceedings of 5th international conference on database systems for advanced applications, pp 185–194
Thomas S, Bodagala S, Alsabti K, Ranka S (1997) An efficient algorithm for the incremental updation of association rules in large databases. In: Proceedings of 3rd international conference on data mining and knowledge discovery, pp 263–266
Veloso AA, Jr Meira W, de Carvalho MB, Pôssas B, Parthasarathy S, Zaki MJ (2002) Mining frequent itemsets in evolving databases. In: Proceedings of 2nd SIAM international conference on data mining
Ayan N, Tansel A, Arkun E (1999) An efficient algorithm to update large itemsets with early pruning. In: Proceeding KDD proceedings of the fifth ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 287–291
Lee CH, Lin CR, Chen MS (2001) Sliding-window filtering: an efficient algorithm for incremental mining. In: Proceeding CIKM proceedings of the tenth international conference on information and knowledge management, pp 263–270
Chang C, Li Y, Lee J (2005) An efficient algorithm for incremental mining of association rules. In: 15th international workshop on research issues in data engineering: stream data mining and applications. RIDE-SDMA, pp 3–10
Yu H, Wang Y, Jiao P (2014) A three-way decisions approach to density-based overlapping clustering. In: Transactions on rough sets XVIII, pp 92–109
Liang DC, Liu D (2014) Systematic studies on three-way decisions with interval-valued decision-theoretic rough sets. Inf Sci 276:186–203
UCI: mushroom data set. http://www.cs.sfu.ca/wangk/ucidata/dataset/mushroom
UCI: nursery and kdd\_internet\_usage data set. http://repository.seasr.org/Datasets/UCI/arff/
Olave M, Rajkovic V, Bohanec M (1989) An application for admission in public school systems. Expert Syst Public Adm, pp 145–160
Zupan B, Bohanec M, Bratko I, Demsar J (1997) Machine learning by function decomposition. In: ICML, pp 421–429
Duch W, Adamczak R, Grabczewski K et al (1997) Extraction of crisp logical rules using constrained backpropagation networks
Liu HW, Liu L, Zhang HJ (2008) Feature selection using mutual information: an experimental study. In: PRICAI: trends in artificial intelligence. Springer, pp 235–246
Ceglar A, Roddick JF, Powers DM (2007) Curio: a fast outlier and outlier cluster detection algorithm for large datasets. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international workshop on Integrating artificial intelligence and data mining, vol 84. Australian Computer Society, Inc., pp 39–47
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61379089 and 61379049 and by the Seedling Project of Sichuan Province in China, No. 2014-056.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhang, ZH., Chen, WB. et al. TDUP: an approach to incremental mining of frequent itemsets with three-way-decision pattern updating. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 8, 441–453 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-015-0337-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-015-0337-6