Abstract
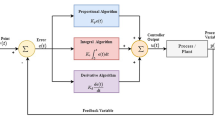
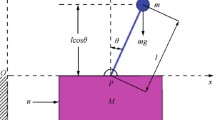
This study presents a robust self-learning proportional-integral-derivative (RSPID) control system design for nonlinear systems. This RSPID control system comprises a self-learning PID (SPID) controller and a robust controller. The gradient descent method is utilized to derive the on-line tuning laws of SPID controller; and the \( \, H_{\infty } \, \) control technique is applied for the robust controller design so as to achieve robust tracking performance. Moreover, in order to achieve fast learning of PID controller, a particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm is adopted to search the optimal learning-rates of PID adaptive gains. Finally, two nonlinear systems, a two-link manipulator and a chaotic system are examined to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed control algorithm. Simulation results show that the proposed control system can achieve favorable control performance for these nonlinear systems.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astrom KJ, Hagglund T (1988) Automatic tuning of PID controllers. Instrument Society of America, Research Triangle Park
Ho WK, Hang CC, Zhou JH (1997) Self-tuning PID control of a plant with under-damped response with specifications on gain and phase margins. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 5(4):446–452
Ren TJ, Chen TC, Chen CJ (2008) Motion control for a two-wheeled vehicle using a self-tuning PID controller. Control Eng Pract 16:365–375
Vagia M, Tzes A (2008) Robust PID control design for an electrostatic micromechanical actuator with structured uncertainty. IET Control Theory Appl 2(5):365–373
Yu DL, Chang TK, Yu DW (2005) Fault tolerant control of multivariable processes using auto-tuning PID controller. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B 35(1):32–43
Juang JG, Huang MT, Lin WK (2008) PID control using presearched genetic algorithms for a MIMO system. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern C 38(5):716–727
Wang J, Zhang C, Jing Y (2008) Fuzzy immune self-tuning PID control of HVAC system. IEEE Int Conf Mech Autom 678–683
Bandyopadhyay R, Chakraborty UK, Patranabis D (2001) Autotuning a PID controller: a fuzzy-genetic approach. J Syst Archit 47:663–673
Harinath E, Mann GKI (2008) Design and tuning of standard additive model based fuzzy PID controllers for multivariable process systems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B 38(3):667–674
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC (1995) Particle swarm optimization. IEEE Int Conf Neural Netw Perth, Australia 4:1942–1948
Eberhart RC, Shi Y (2001) Particle swarm optimization: developments, applications and resources. In: Proceedings of congress on evolution computation, Seoul, pp 81–75
Juang CF (2004) A hybrid of genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization for recurrent network design. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 34(2):997–1006
Heo JS, Wang K, Lee Y, Garduno-Ramirez R (2006) Multiobjective control of power plants using particle swarm optimization techniques. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 21(2):552–561
Lin FJ, Teng LT, Chu H (2008) A robust recurrent wavelet neural network controller with improved particle swarm optimization for linear synchronous motor drive. IEEE Trans Power Electron 23(6):3067–3078
Kim TH, Maruta I, Sugie T (2008) Robust PID controller tuning based on the constrained particle swarm optimization. Automatica 44:1104–1110
Chang WD, shih SP (2010) PID controller design of nonlinear systems using an improved particle swarm optimization approach. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 15:3632–3639
Chen BS, Lee CH (1996) H ∞ tracking design of uncertain nonlinear SISO systems: adaptive fuzzy approach. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 4(1):32–43
Wang SD, Lin CK (2000) Adaptive tuning of the fuzzy controller for robots. Fuzzy Sets Syst 110:351–363
Erlic M, Lu WS (1995) A reduced-order adaptive velocity observer for manipulator control. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 11(2):293–303
Lu J, Chen G, Cheng D (2002) Bridge the gap between the Lorenz system and the Chen system. Int J Bifurcat Chaos 12:2917–2926
Lin CM, Hsu CF (2004) Adaptive fuzzy sliding-mode control for induction servomotor systems. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 19(2):362–368
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, CM., Li, MC., Ting, AB. et al. A robust self-learning PID control system design for nonlinear systems using a particle swarm optimization algorithm. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 2, 225–234 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-011-0021-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-011-0021-4