Abstract
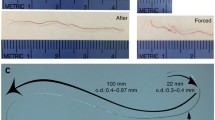
We developed a novel model of a rat embolic cerebral infarction with a quantifiable autologous arterial blood clot. The left femoral artery had 0.15 ml of blood withdrawn and mixed with 10 units of thrombin in 50 μl saline. After 30 min, the clot was suctioned into a 4-French polyvinyl chloride tube. A 24-gage catheter was inserted up through the internal carotid artery via the external carotid artery stump. The 1-cm clot, at a volume of 7.2 mm3, was pushed and inserted into the internal carotid artery via the catheter. After withdrawing the catheter, the ICA blood flow recovered. We checked neurological status after 24 h (neurological free was 15, and worst was 1) and measured the infarction volume by the TTC method. Twelve rats were examined, and five sham-operated rats were included. Two rats were not able to achieve an 80 % reduction in CBF. One rat died due to cerebral infarction. The success rate in producing infarction was 83 %. The total infarction volume was 368.5 mm3 ± 61.2 se. Median neurological score was 6. Hemorrhagic transformation was not detected. Sham-operated rats revealed no infarction and no neurological deficit. The volume of infarction correlated significantly with the neurological score. We conclude that this embolic stroke model is useful in producing a human, severe cardioembolic cerebral infarction.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
NINDS rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Engl J Med. 1995;333:1581–7.
Nogueira RG, Liebeskind DS, Sung G, Duckwiler G, Smith WS. Predictors of good clinical outcomes, mortality, and successful revascularization in patients with acute ischemic stroke undergoing thrombectomy: pooled analysis of the Mechanical Embolus Removal in Cerebral Ischemia (MERCI) and Multi MERCI Trials. Stroke. 2009;40:3777–83.
Shimamura N, Matchett G, Tsubokawa T, Ohkuma H, Zhang J. Comparison of silicon-coated nylon suture to plain nylon suture in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model. J Neurosci Methods. 2006;156:161–5.
Shimamura N, Matsuda N, Katayama K, Ohkuma H. Novel rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model: trans-femoral artery approach combined with preservation of the external carotid artery. J Neurosci Methods. 2009;184:195–8.
Kudo M, Aoyama A, Ichimori S, Fukunaga N. An animal model of cerebral infarction homologous blood clot emboli in rats. Stroke. 1982;13:505–8.
Overgaard K, Sereghy T, Boysen G, Pedersen H, Hoyer S, Diemer NH. A rat model of reproducible cerebral infarction using thrombotic blood clot emboli. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1992;12:484–90.
Overgaard K, Sereghy T, Boysen G, Pedersen H, Diemer NH. Reduction of infarct volume and mortality by thrombolysis in a rat embolic stroke model. Stroke. 1992;23:1167–73.
Overgaard K, Sereghy T, Boysen G, Pedersen H, Diemer NH. Reduction of infarct volume by thrombolysis with rt-PA in an embolic rat stroke model. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1993;53:383–93.
Sereghy T, Overgaard K, Boysen G. Neuroprotection by excitatory amino acid antagonist augments the benefit of thrombolysis in embolic stroke in rats. Stroke. 1993;24:1702–8.
Zhang Z, Zhang RL, Jiang Q, Raman SB, Cantwell L, Chopp M. A new rat model of thrombotic focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1997;17:123–35.
Shuaib A, Yang Y, Li Q, Siddiqui MM, Kalra J. Intraarterial urokinase produces significant attenuation of infarction volume in an embolic focal ischemia model. Exp Neurol. 1998;154:330–5.
Shimamura N, Matchett G, Yatsushige H, Calvert JW, Ohkuma H, Zhang J. Inhibition of integrin alphavbeta3 ameliorates focal cerebral ischemic damage in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model. Stroke. 2006;37:1902–9.
Buchan AM, Xue D, Slivka A. A new model of temporary focal neocortical ischemia in the rat. Stroke. 1992;23:273–9.
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20:84–91.
Coyle P. Middle cerebral artery occlusion in the young rat. Stroke. 1982;13:855–9.
Koizumi J, Yoshida Y, Nakazawa T, Oneda G. Experimental studies of ischemic brain edema 1. A new experimental model of cerebral embolism in rats in which recirculation can be introduced in the ischemia area. Jpn J Stroke. 1986;8:1–8.
Diness JG, Skibsbye L, Jespersen T, Bartels ED, Sorensen US, Hansen RS, et al. Effects on atrial fibrillation in aged hypertensive rats by Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channel inhibition. Hypertension. 2011;57:1129–35.
Sugiyama A, Takahara A, Honsho S, Nakamura Y, Hashimoto K. A simple in vivo atrial fibrillation model of rat induced by transesophageal atrial burst pacing. J Pharmacol Sci. 2005;98:315–8.
Zhang Z, Chopp M, Zhang RL, Goussev A. A mouse model of embolic focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1997;17:1081–8.
Shimamura N, Matchett G, Solaroglu I, Tsubokawa T, Ohkuma H, Zhang J. Inhibition of integrin alphavbeta3 reduces blood–brain barrier breakdown in focal ischemia in rats. J Neurosci Res. 2006;84:1837–47.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mark Inglin (University of Basel) for his editorial assistance. And this work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI grant number 40312491 for NS.
Compliance with Ethics Requirements
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI grant number 40312491 for NS. We have no conflict of interest. All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimamura, N., Matsuda, N., Kakuta, K. et al. A Model of Rat Embolic Cerebral Infarction with a Quantifiable, Autologous Arterial Blood Clot. Transl. Stroke Res. 4, 564–570 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-013-0262-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-013-0262-5