Abstract
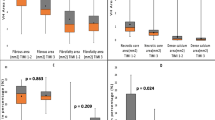
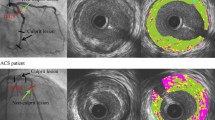
Distal embolization (DE) is a serious complication of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients with stable angina. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the coronary plaque characteristics that indicate DE during PCI in patients with stable angina using virtual histology intravascular ultrasound (VH-IVUS). Three hundred and sixty-four consecutive stable angina patients who underwent PCI were enrolled in this study. The patients were divided into two groups as follows: patients exhibiting DE (DE group, n = 10) and patients without DE (non-DE group, n = 354). Coronary plaque compositions were assessed by VH-IVUS. The fibro-fatty (FF) ratio (28 ± 17 vs. 11 ± 9 %, p < 0.0001) was higher in the DE group compared with the non-DE group. The best cut-off value of FF ratio for prediction of DE was 20 %, with a sensitivity of 0.80 and a specificity of 0.81 (odds ratio; 17.1, 95 % confidence interval 3.56–82.5, p = 0.0004). Coronary plaques with a high FF ratio may be the predictor of indicating DE in patients with stable angina during PCI.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartorelli AL, Koh TH, DiPede F, Reimers B, Thuesen L, Amann F, et al. Distal embolic protection during percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute coronary syndromes: RUBY study. Acute Card Care. 2006;8:148–54.
Gorog DA. The role of distal myocardial protection devices during percutaneous coronary interventions. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2007;9:52–9.
Fokkema ML, Vlaar PJ, Svilaas T, Vogelzang M, Amo D, Diercks GF, et al. Incidence and clinical consequences of distal embolization by the coronary angiogram after percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2009;30:908–15.
Peters RJ, Kok WE, Havenith MG, Rijsterborgh H, van der Wal AC, Visser CA. Histopathologic validation of intracoronary ultrasound imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1994;7:230–41.
Nair A, Kuban BD, Tuzcu EM, Schoenhagen P, Nissen SE, Vince DG. Coronary plaque classification with intravascular ultrasound radiofrequency data analysis. Circulation. 2002;106:2200–6.
Nair A, Calvetti D, Vince DG. Regularized autoregressive analysis of intravascular ultrasound backscatter: improvement in spatial accuracy of tissue maps. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2004;51:420–31.
Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Non-ST-Segment Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes of European Society of Cardiology, Bassand JP, Hamm CW, Ardissino D, Boersma E, Budaj A, Fernandez-Avilies F, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:1598–660.
Braunwald E, Antman EM, Beasley JW, Califf RM, Cheitlin MD, Hochman JS, et al. ACC/AHA 2002 guideline update for the management of patients with unstable angina and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction-summary article: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on practice guidelines (Committee on the Management of Patients with Unstable Angina). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;40:1366–74.
Nair A, Kuban BD, Obuchowski N, Vince DG. Assessing spectral algorithms to predict atherosclerotic plaque composition with normalized and raw intravascular ultrasound data. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2001;27:1319–31.
Falk E. Stable versus unstable atherosclerosis. Clinical aspects. Am Heart J. 1999;138:S421–5.
Virmani R, Burke AP, Farb A, Kolodgie FD. Pathology of the unstable plaque. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2002;44:349–56.
Nasu K, Tsuchikane E, Katoh O, Vince DG, Virmani R, Surmely JF, et al. Accuracy of in vivo coronary plaque morphology assessment. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:2405–12.
Schmermund A, Erbel R. Unstable coronary plaque and its relation to coronary calcium. Circulation. 2001;104:1682–7.
Kawaguchi R, Oshima S, Jingu M, Tsurugaya H, Toyama T, Hoshizaki H, et al. Usefulness of virtual histology intravascular ultrasound to predict distal embolization for ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50:1641–6.
Kawamoto T, Okura H, Koyama Y, Toda I, Taguchi H, Tamita K, et al. The relationship between coronary plaque characteristics and small embolic particles during coronary stent implantation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50:1635–40.
Surmely JF, Nasu K, Fujita H, Terashima M, Matsuda Tsuchikane E, et al. Coronary plaque composition of culprit/target lesions according to the clinical presentation. A virtual histology intravascular ultrasound analysis. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:2939–44.
Nakamura R, Ito K, Koide M, Taniguchi T, Irie H, Kinoshita N, et al. Coronary artery plaque assessment using volcano therapeutics virtual histology intravascular ultrasound and temperature guide wire. J Cardiol. 2006;48:85–92.
Nakamura T, Kubo N, Ako J, Momomura S. Angiographic no-reflow phenomenon and plaque characteristics by virtual histology intravascular ultrasound in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Interv Cardiol. 2007;20:335–9.
Fujii K, Carlier SG, Mintz GS, Wijns W, Colombo A, Bose D, et al. Association of plaque characterization by intravascular ultrasound virtual histology and arterial remodeling. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96:1476–83.
Galis ZS, Sukhova GK, Lark MW, Libby P. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinases and matrix degrading activity in vulnerable regions of human atherosclerotic plaque. J Clin Invest. 1994;94:2493–503.
Pasterkamp G, Schoneveld AH, Hijnen DJ, de Kleijn DP, Teepen H, van der Wal AC, et al. Atherosclerotic arterial remodeling and the localization of macrophages and matrix metalloproteases I, 2 and 9 in the human coronary artery. Atherosclerosis. 2000;150:245–53.
Nakamura M, Nishikawa H, Mukai S, Setsuda M, Nakajima K, Tamada H, et al. Impact of coronary artery remodeling on clinical presentation of coronary artery disease. An intravascular ultrasound study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;37:63–9.
Weissman NJ, Sheris SJ, Chari R, Mendelson FO, Anderson WD, Breall JA, et al. Intravascular ultrasonic analysis of plaque characteristics associated with coronary artery remodeling. Am J Cardiol. 1999;84:37–40.
Higashiguchi Y, Tanabe K, Yamamoto H, Aoki J, Nakazawa G, Onuma Y, et al. Relationship between coronary artery remodeling and plaque composition in culprit lesions. An intravascular ultrasound radiofrequency analysis. Circ J. 2007;71:654–60.
Nakamura M, Nishikawa H, Mukai S, Setsuda M, Nakajima K, Tamada H, et al. Impact of coronary artery remodeling on clinical presentation of coronary artery disease; an intravascular ultrasound study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;37:63–9.
von Birgelen C, Klinkhart W, Mintz GS, Papatheodorou A, Herrmann J, Baumgart D, et al. Plaque distribution and vascular remodeling of ruptured and nonruptured coronary plaques in the same vessel. An intravascular ultrasound study in vivo. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;37:1864–70.
Burke AP, Kolodgie FD, Farb A, Weber D, Virmani R. Morphologycal predictors of arterial remodeling in coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2002;105:297–303.
Bluestein D, Alemu Y, Avrahami I, Gharib M, Dumont K, Ricotta JJ, et al. Influence of microcalcifications on vulnerable plaque mechanics using FSI modeling. J Biomech. 2008;41:111–8.
Endo M, Hibi K, Shimizu T, Komura N, Kusama I, Otsuka F, et al. Impact of ultrasound attenuation and plaque rupture as detected by intravascular ultrasound on the incidence of no-reflow phenomenon after percutaneous coronary intervention in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2010;3:540–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, F., Ueshima, K., Fujimoto, T. et al. Coronary plaque characteristics that indicate distal embolization during percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with stable angina-virtual histology intravascular ultrasound study. Cardiovasc Interv and Ther 28, 227–234 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12928-013-0157-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12928-013-0157-0