Abstract
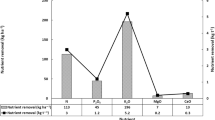
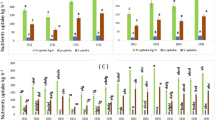
Field experiments were conducted in two growing seasons as a split plot based on a randomized complete block design with four replications. Irrigation intervals (irrigation after 70 and 170 mm evaporation from class A pan) were assigned to main plots and spraying of polyamines (putrescine 0.1 mM, spermidine 0.1 mM, and spermine 0.1 mM) were allocated to the subplots. T nitrogen and sulfur content of different parts of mung bean, nitrogen uptake, protein filling duration, protein percentage of grain, maximum protein content per grains, grain and protein yields per unit area, methionine and serine contents reduced under water limitation, but grain filling rate, isoleucine, leucine, threonine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, glycine, proline, tyrosine and arginine contents in grains raised. Treatment of plants with polyamines improved the contents of nitrogen and sulfur, nitrogen uptake, protein-filling duration, protein percentage, grain and protein yield per unit area, and histidine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, tyrosine, and arginine contents in grain. Putrescine had the highest grain and protein yields. Our results clearly indicated that polyamines with improving histidine, methionine, phenylalanine, and threonine content in mung bean grains improved the quality of mung bean protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akter N, Islam MR, Karim MA, Hossain T. 2014. Alleviation of drought stress in maize by exogenous application of gibberellic acid and cytokinin. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 17: 41–48
Apelbaum A, Burgoon AC, Anderson JD, Lieberman M, Ben-Arie R, Mattoo AK. 1981. Polyamines inhibit biosynthesis of ethylene in higher plant tissue and fruit protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 68: 453–456
Apelbaum A, Yang, SF. 1981. Biosynthesis of stress ethylene induced by water deficit. Plant Physiol. 68: 594–596
Beltrano J, Ronco MG, Montaldi ER. 1999. Drought stress syndrome in wheat is provoked by ethylene evolution imbalance and reversed by rewatering, aminoethoxyvinylglycine, or sodium benzoate. J. Plant Growth Regul. 18: 59–64
Berberich T, Sagor GHM, Kusano T. 2015. Polyamines in plant stress response. In: Polyamines, Springer Japan. pp 155–168
Butt MS, Batool R. 2010. Nutritional and functional properties of some promising legumes protein isolates. Pak. J. Nutr. 9: 373–379
Carrera C, Martinez MJ, Dardanelli J, Balzarini M. 2009. Water deficit effect on the relationship between temperatures during the grain fill period and soybean grain oil and protein concentrations. Crop Sci. 49: 990–998
Daneshian J, Zare D. 2005. Diversity for resistance drought on soybean. J. Agr. Sci. 1: 23–50
Farhangi-Abriz S, Torabian S. 2017. Antioxidant enzyme and osmotic adjustment changes in bean seedlings as affected by biochar under salt stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 137: 64–70
Fountoulakis M, Lahm HW. 1998. Hydrolysis and amino acid composition analysis of proteins. J. Chromatogr. A. 826: 109–134
Foyer CH, Valadier MH, Migge A, Becker TW. 1998. Droughtinduced effects on nitrate reductase activity and mRNA and on the coordination of nitrogen and carbon metabolism in maize leaves. Plant Physiol. 117: 283–292
Galston AW, Sawhney RK. 1990. Polyamines in plant physiology. Plant physiol. 94: 406–410
Girousse C, Bournoville R, Bonemain JL. 1996. Water deficitinduced changes in concentrations in proline and some other amino acids in the phloem sap of alfalfa. Plant Physiol. 111: 109–113
Groppa MD, Benavides MP. 2008. Polyamines and abiotic stress: recent advances. Amino Acids, 34: 35–45
Hawkwkesford M, Horst W, Kichey TMR, Schjorring JK, Muller IS, White P. 2012. Functions of macronutrients: In: Marschers’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. Elsevier Science 135–189
Hobbs EH, Muendel HH. 1983. Water requirements of irrigated soybeans in southern Alberta Can. J. Plant Sci. 63: 855–860
Hoffmann L, Maury S, Martz F, Geoffroy P, Legrand M. 2003. Purification, cloning, and properties of an acyltransferase controlling shikimate and quinate ester intermediates in phenylpropanoid metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 78: 95–103
Karr-Lilienthal LK, Grieshop CM, Spears JK, Fahey GC. 2005. Amino acid, carbohydrate, and fat composition of soybean meals prepared at 55 commercial US soybean processing plants. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 53: 2146–2150
Kotzabasis K, Fotinou C, Roubelakis-Angelakis KA, Ghanotakis D. 1993. Polyamines in the photosynthetic apparatus. Photosynth. Res. 38: 83–88
Kramer PJ, Boyer JS. 1995. Water relations of plants and soils. Academic Press.
San Diego Kumar A, Taylor M, Altabella T, Tiburcio AF. 1997. Recent advances in polyamine research. Trends Plant Sci. 2: 124–130
Liu JH, Kitashiba H, Wang J, Ban Y, Moriguchi T. 2007. Polyamines and their ability to provide environmental stress tolerance to plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 24: 117–126
Martin-Tanguy J. 2001. Metabolism and function of polyamines in plants: recent development (new approaches). Plant Growth Regul. 34: 135–148
Morgan JM. 1984. Osmoregulation and water stress in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 35: 299–319
Morgan PW, Drew MC. 1997. Ethylene and plant responses to stress. Physiol. Plant. 100: 620–630
Nayyar H, Satwinder K, Kumar S, Singh KJ, Dhir KK. 2005. Involvement of polyamines in the contrasting sensitivity of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) and soybean (Glycine max L.) to water deficit stress. Bot. Bull. Acad. Sin. 46: 333–338
Rady MM, El-Yazal MAS, Taie HA, Ahmed SM. 2016. Response of wheat growth and productivity to exogenous polyamines under lead stress. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 19: 363–371
Rosales EP, Iannone MF, Groppa MD, Benavides MP. 2012. Polyamines modulate nitrate reductase activity in wheat leaves: involvement of nitric oxide. Amino Acids, 42: 857–865
Sharp RE, LeNoble ME. 2002. ABA, ethylene and the control of shoot and root growth under water stress. J. Exp. Bot. 53: 33–37
Singh C, Kumar V, Prasad I, Patil VR, Rajkumar BK. 2016. Response of upland cotton (G. hirsutum L.) genotypes to drought stress using drought tolerance indices. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 1: 53–59
Somashekaraiah BV, Padmaja K, Prasad ARK. 1992. Phytotoxicity of cadmium ions on germinating grainlings of mung bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): Involvement of lipid peroxides in chlorphyll degradation. Physiol. Plant, 85: 85–89
Weiss M, Manneberg M, Juranville JF, Lahm HW, Fountoulakis M. 1998. Effect of the hydrolysis method on the determination of the amino acid composition of proteins. J. Chromatogr. A. 795: 263–275
Wilson RF. 2004. Grain composition Soybeans: improvement, production, and uses. USDA Agricultural Research Service, Beltsville-Maryland, 621–677
Wolf RB, Cavins JF, Kleiman R, Black LT. 1982. Effect of temperature on soybean grain constituents: oil, protein, moisture, fatty acids, amino acids and sugars. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 59: 230–232
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farhangi-Abriz, S., Faegi-Analou, R. & Nikpour-Rashidabad, N. Polyamines, affected the nitrogen partitioning, protein accumulation and amino acid composition of mung bean under water stress. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 20, 279–285 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-017-0079-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-017-0079-0