Abstract
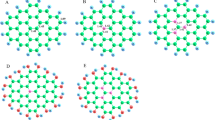
Utilizing the density functional theory (DFT) method, we investigated the catalytic activity of N-doped graphene quantum dots (NGQDs) with nitrogen (N) atoms strategically doped at various active sites on the surface. We focused on exploring their efficiency in the 2e− and 4e− reduction pathways for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). By introducing N-doping at the central benzene ring of carbon-based materials, we observed the formation of localized π-orbitals, significantly enhancing their electrocatalytic activity. In comparison to other reported catalysts, our N-doped GQD metal-free electrocatalyst displayed remarkable adsorption capability. Furthermore, we introduced the hydroxyl group (OH) into the functionalized N-doped GQDs, which further improved electrocatalytic performance. This enhancement was attributed to the decreased HOMO–LUMO energy gap and increased chemical reactivity. The calculated free energy (ΔG) values for each elementary reaction step in the 4e− reduction pathway were highly favorable and indicated the feasibility of the process. Our findings indicate that N-doped GQDs exhibit exceptional activity for the ORR, positioning them as promising carbon-based metal-free electrocatalysts. Consequently, they hold significant potential as an alternative to noble metal-based catalysts in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) and metal-air batteries.
Graphical Abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
M.H. Seo, D. Higgins, G. Jiang, S.M. Choi, B. Han, Z. Chen, Theoretical insight into highly durable iron phthalocyanine derived non-precious catalysts for oxygen reduction reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2(46), 19707–19716 (2014)
M. Winter, R.J. Brodd, What are batteries, fuel cells, and supercapacitors? Chem. Rev. 104(10), 4245–4270 (2004)
L. Qu, Y. Liu, J.B. Baek, L. Dai, Nitrogen-doped graphene as efficient metal-free electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction in fuel cells. ACS Nano. 4(3), 1321–1326 (2010)
C. Chowdhury, A. Datta, Silicon-doped nitrogen-coordinated graphene as electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C. 122(48), 27233–27240 (2018)
M. Shao, Q. Chang, J.P. Dodelet, R. Chenitz, Recent advances in electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Rev. 116(6), 3594–3657 (2016)
D. Liu, L. Tao, D. Yan, Y. Zou, S. Wang, Recent advances on non-precious metal porous carbon-based electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. ChemElectroChem. 5(14), 1775–1785 (2018)
Y. Nie, L. Li, Z. Wei, Recent advancements in Pt and Pt-free catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44(8), 2168–2201 (2015)
L.Y. Feng, Y.J. Liu, J.X. Zhao, Iron-embedded boron nitride nanosheet as a promising electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR): a density functional theory (DFT) study. J. Power. Sources 287, 431–438 (2015)
Q. Wei, X. Tong, G. Zhang, J. Qiao, Q. Gong, S. Sun, Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube and graphene materials for oxygen reduction reactions. Catalysts. 5(3), 1574–1602 (2015)
T. Thiruppathiraja, P.N. Senthan, S. Lakshmipathi, DFT study on a fluorine-functionalized nitrogen-and boron-doped triangulene as an electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Sustain. Energy. Fuels. 7(13), 3088–3095 (2023)
M. Kiani, J. Zhang, J. Chen, Y. Luo, Y. Chen, J. Fan, G. Wang, R. Wang, Facile synthesis of magnesium ferrite nanoparticles supported on nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon black as an efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. J. Nanopart. Res. 21, 1–12 (2019)
Z. Yang, Z. Yao, G. Li, G. Fang, H. Nie, Z. Liu, X. Zhou, X.A. Chen, S. Huang, Sulfur-doped graphene as an efficient metal-free cathode catalyst for oxygen reduction. ACS Nano 6(1), 205–211 (2012)
P. Chandran, A. Ghosh, S. Ramaprabhu, High-performance platinum-free oxygen reduction reaction and hydrogen oxidation reaction catalyst in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 3591 (2018)
W. Xia, A. Mahmood, Z. Liang, R. Zou, S. Guo, Earth-abundant nanomaterials for oxygen reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55(8), 2650–2676 (2016)
F. Li, H. Shu, C. Hu, Z. Shi, X. Liu, P. Liang, X. Chen, Atomic mechanism of electrocatalytically active Co–N complexes in graphene basal plane for oxygen reduction reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 7(49), 27405–27413 (2015)
P. Rao, D. Wu, J. Luo, J. Li, P. Deng, Y. Shen, X. Tian, A plasma bombing strategy to synthesize high-loading single-atom catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Cell. Rep. Phys. Sci. 3(5)(2022)
Y. Yu, P. Rao, S. Feng, M. Chen, P. Deng, J. Li, Z. Miao, Z. Kang, Y. Shen, X. Tian, Atomic co clusters for efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Acta. Phys. Chim. Sin. 39, 2210039 (2023)
P. Rao, T.J. Wang, J. Li, P.L. Deng, Y.J. Shen, Y. Chen, X.L. Tian, Plasma induced Fe-NX active sites to improve the oxygen reduction reaction performance. Adv. Sens. Energy. Mater. 1(1)(2022)
L. Dai, Y. Xue, L. Qu, H.J. Choi, J.B. Baek, Metal-free catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Rev. 115(11), 4823–4892 (2015)
X. Liu, L. Dai, Carbon-based metal-free catalysts. Nat. Rev. Mater. 1(11), 1–12 (2016)
Z. Wang, R. Jia, J. Zheng, J. Zhao, L. Li, J. Song, Z. Zhu, Nitrogen-promoted self-assembly of N-doped carbon nanotubes and their intrinsic catalysis for oxygen reduction in fuel cells. ACS Nano. 5(3), 1677–1684 (2011)
S. Ratso, I. Kruusenberg, M. Vikkisk, U. Joost, E. Shulga, I. Kink, T. Kallio, K. Tammeveski, Highly active nitrogen-doped few-layer graphene/carbon nanotube composite electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline media. Carbon. 73, 361–370 (2014)
D. Higgins, P. Zamani, A. Yu, Z. Chen, The application of graphene and its composites in oxygen reduction electrocatalysis: a perspective and review of recent progress. Energy Environ. Sci. 9(2), 357–390 (2016)
M. Reda, H.A. Hansen, T. Vegge, DFT study of stabilization effects on N-doped graphene for ORR catalysis. Catal. Today 312, 118–125 (2018)
S. Kattel, P. Atanassov, B. Kiefer, Density functional theory study of the oxygen reduction reaction mechanism in a BN co-doped graphene electrocatalyst. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2(26), 10273–10279 (2014)
A. Ferre-Vilaplana, E. Herrero, Why nitrogen favors oxygen reduction on graphitic materials. Sustain. Energy. Fuels. 3(9), 2391–2398 (2019)
T. Liu, X. Hao, J. Liu, P. Zhang, J. Chang, H. Shang, X. Liu, Graphdiyne and nitrogen-doped graphdiyne nanotubes as highly efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24(23), 16813 (2023)
M. Chen, Y. Ping, Y. Li, T. Cheng, Insights into the pH-dependent behavior of N-doped carbons for the oxygen reduction reaction by first-principles calculations. J. Phys. Chem. C. 125(48), 26429–26436 (2021)
Y. Gao, Z. Cai, X. Wu, Z. Lv, P. Wu, C. Cai, Graphdiyne-supported single-atom-sized Fe catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction: DFT predictions and experimental validations. ACS Catal. 8(11), 10364–10374 (2018)
T. Thiruppathiraja, A.L. Arokiyanathan, B. Aazaad, R. Silviya, S. Lakshmipathi, H, OH and COOH functionalized magnesium phthalocyanine as a catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR)–a DFT study. Int. J. Hydro. Energy. 45(15), 8540–8548 (2020)
Z. Zhang, S. Yang, M. Dou, H. Liu, L. Gu, F. Wang, Systematic study of transition-metal (Fe Co, Ni, Cu) phthalocyanines as electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction and their evaluation by DFT. RSC Adv. 6(71), 67049–67056 (2016)
B. Modak, K. Srinivasu, S.K. Ghosh, Exploring metal decorated porphyrin-like porous fullerene as catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction: a DFT study. Int. J. Hydro. Energy. 42(4), 2278–2287 (2017)
H. Tan, Y. Li, J. Kim, T. Takei, Z. Wang, X. Xu, J. Wang, Y. Bando, Y.M. Kang, J. Tang, Y. Yamauchi, Sub-50 nm iron–nitrogen-doped hollow carbon sphere-encapsulated iron carbide nanoparticles as efficient oxygen reduction catalysts. Adv. Sci. 5(7), 1800120 (2018)
G. Fazio, L. Ferrighi, C. Di Valentin, Boron-doped graphene as active electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction at a fuel-cell cathode. J. Catal. 318, 203–210 (2014)
X. Zou, L. Wang, B.I. Yakobson, Mechanisms of the oxygen reduction reaction on B-and/or N-doped carbon nanomaterials with curvature and edge effects. Nanoscale 10(3), 1129–1134 (2018)
L.S. Panchakarla, K.S. Subrahmanyam, S.K. Saha, A. Govindaraj, H.R. Krishnamurthy, U.V. Waghmare, C.N. Rao, Synthesis, structure, and properties of boron-and nitrogen-doped graphene. Adv. Mater. 21(46), 4726–4730 (2009)
T. Van Tam, S.G. Kang, K.F. Babu, E.S. Oh, S.G. Lee, W.M. Choi, Synthesis of B-doped graphene quantum dots as a metal-free electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A. 5(21), 10537–10543 (2017)
J. Zhang, Z. Wang, Z. Zhu, A density functional theory study on oxygen reduction reaction on nitrogen-doped graphene. J. Mol. Model. 19, 5515–5521 (2013)
T. Thiruppathiraja, A.L. Arokiyanathan, S. Lakshmipathi, Pyrrolic, pyridinic, and graphitic sumanene as metal-free catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction–a density functional theory study. Fuel Cells. 21(6), 490–501 (2021)
R. Liu, H. Liu, Y. Li, Y. Yi, X. Shang, S. Zhang, X. Yu, S. Zhang, H. Cao, G. Zhang, Nitrogen-doped graphdiyne as a metal-free catalyst for high-performance oxygen reduction reactions. Nanoscale 6(19), 11336–11343 (2014)
C. Zhang, N. Mahmood, H. Yin, F. Liu, Y. Hou, Synthesis of phosphorus-doped graphene and its multifunctional applications for oxygen reduction reaction and lithium ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 25(35), 4932–4937 (2013)
P. Zhang, Q. Hu, X. Yang, X. Hou, J. Mi, L. Liu, M. Dong, Size effect of oxygen reduction reaction on nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots. RSC Adv. 8(1), 531–536 (2018)
C. Xia, J. Feng, C. Ma, H. Xi, N. Song, H. Dong, L. Yu, L. Dong, Exploring the underlying oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalytic activities of pyridinic-N and pyrrolic-N doped graphene quantum dots. Mol. Catal. 535(2023)
A.D. Becke, Density functional thermochemistry. III. the role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 98(7), 5648–5652 (1993)
P.C. Hariharan, J.A. Pople, The influence of polarization functions on molecular orbital hydrogenation energies. Theoret. Chim. Acta 28, 213–222 (1973)
MJ Frisch GW Trucks HB Schlegel GE Scuseria MA Robb JR Cheeseman G Scalmani V Barone B Mennucci GA Petersson H Nakatsuji Gaussian 09. 2009 Gaussian Inc Wallingford CT USA
T.V. Pham, J.G. Kim, J.Y. Jung, J.H. Kim, H. Cho, T.H. Seo, H. Lee, N.D. Kim, M.J. Kim, High areal capacitance of N-doped graphene synthesized by arc discharge. Adv. Func. Mater. 29(48), 1905511 (2019)
S. Armaković, S.J. Armaković, J.P. Šetrajčić, V. Holodkov, Aromaticity, response, and nonlinear optical properties of sumanene modified with boron and nitrogen atoms. J. Mol. Model. 20, 1–13 (2014)
M. Cheviri, S. Lakshmipathi, Nitrogen-doped buckybowls as potential scaffold material for lithium-sulfur battery: a DFT study. Electrocatalysis 12(6), 678–690 (2021)
J.G. Manjunatha, M. Deraman, N.H. Basri, N.S. Nor, I.A. Talib, N. Ataollahi, Sodium dodecyl sulfate modified carbon nanotubes paste electrode as a novel sensor for the simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid, and uric acid. C. R. Chim. 17(5), 465–476 (2014)
F. Liu, G. Zhu, D. Yang, D. Jia, F. Jin, W. Wang, Systematic exploration of N, C configurational effects on the ORR performance of Fe–N doped graphene catalysts based on DFT calculations. RSC Adv. 9(39), 22656–22667 (2019)
X. Hu, Y. Wu, H. Li, Z. Zhang, Adsorption and activation of O2 on nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C. 114(21), 9603–9607 (2010)
L. Zhang, Z. Xia, Mechanisms of oxygen reduction reaction on nitrogen-doped graphene for fuel cells. J. Phys. Chem. C. 115(22), 11170–11176 (2011)
Y. Li, H. Shu, X. Niu, J. Wang, Electronic and optical properties of edge-functionalized graphene quantum dots and the underlying mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. C. 119(44), 24950–24957 (2015)
V. Sharma, B. Roondhe, S. Saxena, A. Shukla, Role of functionalized graphene quantum dots in hydrogen evolution reaction: a density functional theory study. Int. J. Hydro. Energy. 47(99), 41748–41758 (2022)
Y. Meng, X. Qu, K. Li, Y. Yang, Y. Wang, Z. Wu, Rhodium and nitrogen codoped graphene as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction and CO2 reduction reaction: mechanism insights. J. Phys. Chem. C. 123(9), 5176–5187 (2019)
Z. Duan, G. Wang, A first principles study of oxygen reduction reaction on a Pt (111) surface modified by a subsurface transition metal M (M= Ni Co, or Fe). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13(45), 20178–20187 (2011)
J. Zhang, Z. Wang, Z. Zhu, The inherent kinetic electrochemical reduction of oxygen into H2O on FeN4-carbon: a density functional theory study. J. Power. Sources 255, 65–69 (2014)
X. Chen, F. Li, X. Wang, S. Sun, D. Xia, Density functional theory study of the oxygen reduction reaction on a cobalt–polypyrrole composite catalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C. 116(23), 12553–12558 (2012)
X. Sun, K. Li, C. Yin, Y. Wang, F. He, X. Bai, H. Tang, Z. Wu, The oxygen reduction reaction mechanism on Sn doped graphene as an electrocatalyst in fuel cells: a DFT study. RSC Adv. 7(2), 729–734 (2017)
S. Sun, N. Jiang, D. Xia, Density functional theory study of the oxygen reduction reaction on metalloporphyrins and metallophthalocyanines. J. Phys. Chem. C. 115(19), 9511–9517 (2011)
J. Zhao, Z. Chen, Carbon-doped boron nitride nanosheet: an efficient metal-free electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C. 119(47), 26348–26354 (2015)
X. Bai, E. Zhao, K. Li, Y. Wang, M. Jiao, F. He, X. Sun, H. Sun, Z. Wu, Theoretical insights on the reaction pathways for oxygen reduction reaction on phosphorus doped graphene. Carbon 105, 214–223 (2016)
B. Qin, Y. Tian, P. Zhang, Z. Yang, G. Zhang, Z. Cai, Y. Li, A density functional theory study of the oxygen reduction reaction on the (111) and (100) surfaces of cobalt(II) oxide. Prog. React. Kinet. Mech. 44(2), 122–131 (2019)
Y. Yang, K. Li, Y. Meng, Y. Wang, Z. Wu, A density functional study on the oxygen reduction reaction mechanism on FeN2-doped graphene. New J. Chem. 42(9), 6873–6879 (2018)
P. Zhang, B.B. Xiao, X.L. Hou, Y.F. Zhu, Q. Jiang, Layered SiC sheets: a potential catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Sci. Rep. 4(1), 3821 (2014)
A.M. Priya, L. Senthilkumar, P. Kolandaivel, Hydrogen-bonded complexes of serotonin with methanol and ethanol: a DFT study. Struct. Chem. 25, 139–157 (2014)
L. Wang, H. Dong, Z. Guo, L. Zhang, T. Hou, Y. Li, Potential application of novel boron-doped graphene nanoribbon as oxygen reduction reaction catalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C. 120(31), 17427–17434 (2016)
D.Y. Shin, Y.J. Shin, M.S. Kim, J.A. Kwon, D.H. Lim, Density functional theory–based design of a Pt-skinned PtNi catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction in fuel cells. Appl. Surf. Sci. 565, 150518 (2021)
K. Li, Y. Li, Y. Wang, F. He, M. Jiao, H. Tang, Z. Wu, The oxygen reduction reaction on Pt (111) and Pt (100) surfaces substituted by subsurface Cu: a theoretical perspective. J. Mater. Chem. A. 3(21), 11444–11452 (2015)
R. Ma, G. Lin, Y. Zhou, Q. Liu, T. Zhang, G. Shan, M. Yang, J. Wang, A review of oxygen reduction mechanisms for metal-free carbon-based electrocatalysts. Comput. Mater. 5(1), 78 (2019)
W.A. Saidi, Oxygen reduction electrocatalysis using N-doped graphene quantum-dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 4(23), 4160–4165 (2013)
M. Li, L. Zhang, Q. Xu, J. Niu, Z. Xia, N-doped graphene as catalysts for oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution reactions: theoretical considerations. J. Catal. 314, 66–72 (2014)
D. Chanda, A.S. Dobrota, J. Hnát, Z. Sofer, I.A. Pašti, N.V. Skorodumova, M. Paidar, K. Bouzek, Investigation of electrocatalytic activity on a N-doped reduced graphene oxide surface for the oxygen reduction reaction in an alkaline medium. Int. J. Hydro. Energy. 43(27), 12129–12139 (2018)
Funding
The Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India, provided financial support (DST-PURSE (II) Fellowship/2020/407).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Thangaraj Thiruppathiraja: Methodology, Software, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft. Senthilkumar Lakshmipathi: Methodology, Software, Data curation, Formal analysis, review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Thiruppathiraja, T., Lakshmipathi, S. OH-Functionalized N-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots as an Efficient Metal-Free Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction in PEMFCs. Electrocatalysis (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-024-00869-8
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-024-00869-8