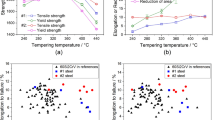
Abstract
As-received (AR) high strength low alloy (HSLA) steel in plate form was subjected to annealing, normalizing, and inter-critical annealing (IA) heat treatments to produce steels with different microstructures having different grain sizes. The AR steel was coated with nanocrystalline (NC) Ni using the pulse current electrodeposition technique. An optical microscope is used to investigate the microstructures of the AR HSLA steel and various heat-treated states. The electrochemical behaviour of the HSLA steels was evaluated by polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopic (EIS) studies in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. Furthermore, hydrogen embrittlement (HE) and stress corrosion cracking (SCC) behaviour of the HSLA steel of various states were evaluated by a slow strain rate tensile test (SSRT) at a strain rate of 2 ×\({10}^{-6}\) s−1 in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. A local electrochemical cell was constructed, and a cathodic overvoltage of 250 mV vs. SCE (saturated calomel electrode) was applied to the tensile specimen by a potentiostat/galvanostat. Potentiodynamic polarization and EIS studies confirmed that NC Ni coating had enhanced the corrosion resistance of the HSLA steel. SSRT results indicated that the AR HSLA steel tends to affect by HE, whereas HSLA steels deposited with NC Ni coating are immune to HE. Scanning electron microscopy fractographic features of the failed samples also exhibited the respective fracture features.
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
G. Xu, X. Gan, G. Ma, F. Luo, H. Zou, The development of Ti-alloyed high strength microalloy steel. Mater. Des. 31(6), 2891–2896 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2009.12.032
F. Jie, Z.B. Wang, Y.L. Kang, Research and development of HSLC steels produced by EAF-CSP technology. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 25(5), 449-454 (2003). https://doi.org/10.13374/j.issn1001-053x.2003.05.042
I.A. Yakubtsov, P. Poruks, J.D. Boyd, Microstructure and mechanical properties of bainitic low carbon high strength plate steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 480(1–2), 109–116 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.06.069
M.C. Zhao, K. Yang, Y.Y. Shan, Comparison on strength and toughness behaviors of microalloyed pipeline steels with acicular ferrite and ultrafine ferrite. Mater. Lett. 57(9–10), 1496–1500 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(02)01013-3
F. Xiao, B. Liao, D. Ren, Y. Shan, K. Yang, Acicular ferritic microstructure of a low-carbon Mn-Mo-Nb microalloyed pipeline steel. Mater. Charact. 54(4–5), 305–314 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2004.12.011
B.K. Panigrahi, Processing of low carbon steel plate and hot strip-an overview. Bull. Mater. Sci. 24(4), 361-371 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02708632
R. Song, D. Ponge, D. Raabe, J. G. Speer, and D. K. Matlock, Overview of processing, microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine grained bcc steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. Elsevier. 441(1–2), 1–17 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.08.095
R. Priestner, L. Ali, Strain induced transformation in C-Mn steel during single pass rolling. Mater. Sci. Technol. (United Kingdom) 9(2), 135–141 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1179/mst.1993.9.2.135
K.S. Ghosh, N. Gao, M.J. Starink, Characterisation of high pressure torsion processed 7150 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 552, 164–171 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.05.026
D.H. Shin, W.J. Kim, W.Y. Choo, Grain refinement of a commercial 0.15%C steel by equal-channel angular pressing. Scr. Mater. 41(3), 259–262 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(99)00156-6
Y. Saito, N. Tsuji, H. Utsunomiya, T. Sakai, R.G. Hong, Ultra-fine grained bulk aluminum produced by accumulative roll-bonding (ARB) process. Scr. Mater. 39(9), 1221–1227 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(98)00302-9
A. Belyakov, Y. Sakai, T. Hara, Y. Kimura, and K. Tsuzaki, Effect of dispersed particles on microstructure evolved in iron under mechanical milling followed by consolidating rolling. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 32(7), 1769–1776, (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-001-0153-3
B.Q. Han, S. Yue, Processing of ultrafine ferrite steels. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 136(1–3), 100–104 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(02)01014-2
K.S. Ghosh, D.K. Mondal, Effect of grain size on mechanical electrochemical and hydrogen embrittlement behaviour of a micro-alloy steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 559, 693–705 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.09.011
P.K. Rout, M.M. Ghosh, K.S. Ghosh, Effect of solution pH on electrochemical and stress corrosion cracking behaviour of a 7150 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 604, 156–165 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.02.036
K.S. Ghosh, D.K. Mondal, Mechanical and electrochemical behavior of a high strength low alloy steel of different grain sizes. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 44(8), 3608–3622 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-1745-4
B.R. Kumar, A review on the importance of microalloying in steel. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. 5(2), 187–193 (2014)
N. Eliaz, A. Shachar, B. Tal, D. Eliezer, Characteristics of hydrogen embrittlement, stress corrosion cracking and tempered martensite embrittlement in high-strength steels. Eng. Fail. Anal. 9(2), 167–184 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1350-6307(01)00009-7
W.K. Kim, S.U. Koh, B.Y. Yang, K.Y. Kim, Effect of environmental and metallurgical factors on hydrogen induced cracking of HSLA steels. Corros. Sci. 50(12), 3336–3342 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2008.09.030
P. Kar, P. Siva Prasad, M.M. Ghosh, and K. S. Ghosh, Electrochemical and hydrogen embrittlement of a micro-alloy steel coated with nanocrystalline nickel by pulse electrodeposition. Philos. Mag. Lett. 100(4), 162–170 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/09500839.2020.1736356
C. Park, N. Kang, S. Liu, Effect of grain size on the resistance to hydrogen embrittlement of API 2W Grade 60 steels using in situ slow-strain-rate testing. Corros. Sci. 128(September), 33–41 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2017.08.032
K. Banerjee, U.K. Chatterjee, Hydrogen embrittlement of a HSLA-100 steel in seawater. ISIJ Int. 39(1), 47–55 (1999). https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.39.47
H.J. Cleary, N.D. Greene, Corrosion properties of iron and steel. Corros. Sci. 7(12), 821–831 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-938X(67)80115-X
R.W. Revie, H.H. Uhlig, Corrosion and Corrosion Control: An Introduction to Corrosion Science and Engineering (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1985)
H. Luo, Y.C. Guan, K.N. Han, Inhibition of mild steel corrosion by sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate and sodium oleate in acidic solutions. Corrosion 54(8), 619–627 (1998). https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3287638
J.L. Albarran, L. Martinez, H.F. Lopez, Effect of heat treatment on the stress corrosion resistance of a microalloyed pipeline steel. Corros. Sci. 41(6), 1037–1049 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-938X(98)00139-5
K.S. Kumar, H. Van Swygenhoven, S. Suresh, Mechanical behavior of nanocrystalline metals and alloys. Acta Mater. 51(19), 5743–5774 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2003.08.032
D.O. Northwood, A.T. Alpas, Mechanical and tribological properties of nanocrystalline and nanolaminated surface coatings. Nanostructured Mater. 10(5), 777–793 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0965-9773(98)00115-9
Z.B. Wang, N.R. Tao, W. Wang, G. Liu, J. Lu and K. Lu, Effect of surface nanocrystallization on friction and wear properties in low carbon steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 352(1–2), 144–149 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(02)00870-5
H.S. Kim, M.B. Bush, Effects of grain size and porosity on the elastic modulus of nanocrystalline materials. Nanostructured Mater. 11(3), 361–367 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0965-9773(99)00052-5
A. Balyanov et al., Corrosion resistance of ultra fine-grained Ti. Scr. Mater. 51(3), 225–229 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2004.04.011
R. Rofagha, R. Langer, A.M. El-Sherik, U. Erb, G. Palumbo, K.T. Aust, The corrosion behaviour of nanocrystalline nickel. Scr. Metall. Mater. 25(12), 2867–2872 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-716X(91)90171-V
L. Wang, Y. Gao, T. Xu, Q. Xue, A comparative study on the tribological behavior of nanocrystalline nickel and cobalt coatings correlated with grain size and phase structure. Mater. Chem. Phys. 99(1), 96–103 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.10.014
H. Natter, M. Schmelzer, R. Hempelmann, Nanocrystalline nickel and nickel-copper alloys: synthesis, characterization, and thermal stability. J. Mater. Res. 13(5), 1186–1197 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1998.0169
L. Wang, J. Zhang, Y. Gao, Q. Xue, L. Hu, T. Xu, Grain size effect in corrosion behavior of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Ni coatings in alkaline solution. Scr. Mater. 55(7), 657–660 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2006.04.009
K. Takasawa, Y. Wada, R. Ishigaki, R. Kayano, Effects of grain size on hydrogen environment embrittlement of high strength low alloy steel in 45 MPa gaseous hydrogen. Mater. Trans. 51(2), 347–353 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2320/MATERTRANS.M2009241
Y.H. Jang, S.S. Kim, C.D. Yim, C. Lee, S.J. Kim, Corrosion behaviour of friction stir welded AZ31B Mg in 3·5%NaCl solution. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 42(2), 119–122 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1179/174327807X196834
E. Sikora, X.J. Wei, B.A. Shaw, Corrosion behavior of nanocrystalline bulk Al-Mg-based alloys. Corrosion 60(4), 387–398 (2004). https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3287748
S.G. Wang, C.B. Shen, K. Long, T. Zhang, F.H. Wang, Z.D. Zhang, The electrochemical corrosion of bulk nanocrystalline ingot iron in acidic sulfate solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 110(1), 377–382 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0538971
P.Q. Dai, C. Zhang, J.C. Wen, H.C. Rao, Q.T. Wang, Tensile properties of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Ni-Cu alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 25(2), 594–600 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-1881-2
Y. Li, F. Wang, G. Liu, Grain size effect on the electrochemical corrosion behavior of surface nanocrystallized low-carbon steel. Corrosion 60(10), 891–896 (2004). https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3287822
L. Shi, C. Sun, P. Gao, F. Zhou, W. Liu, Mechanical properties and wear and corrosion resistance of electrodeposited Ni-Co/SiC nanocomposite coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252(10), 3591–3599 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.05.035
S.A. Lajevardi, T. Shahrabi, Effects of pulse electrodeposition parameters on the properties of Ni-TiO 2 nanocomposite coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256(22), 6775–6781 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.04.088
C.A. Huang, C.Y. Chen, C.C. Hsu, C.S. Lin, Characterization of Cr-Ni multilayers electroplated from a chromium(III)-nickel(II) bath using pulse current. Scr. Mater. 57(1), 61–64 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2007.02.004
R. Rofagha, S. Splinter, U. Erb, N. Mclntyre, materials, and undefined 1994, XPS characterization of the passive films formed on nanocrystalline nickel in sulphuric acid. Elsevier. Accessed: Jan. 30, 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0965977394901295
W.A. Badawy, F.M. Al-Kharafi and J.R. Al-Ajmi, Electrochemical behaviour of cobalt in aqueous solutions at different pH. J. Appl. Electrochem. 30(6), 693-704 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003893122201
L. Wang, Y. Gao, Q. Xue, H. Liu, T. Xu, Graded composition and structure in nanocrystalline Ni-Co alloys for decreasing internal stress and improving tribological properties. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 38(8), 1318–1324 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/38/8/033
C.-C. Yang, Pulsed electrodeposition of copper/nickel multilayers on a rotating disk electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 142(9), 3034 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2048681
W. Hui, H. Zhang, Y. Zhang, X. Zhao, C. Shao, Effect of nickel on hydrogen embrittlement behavior of medium-carbon high strength steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 674, 615–625 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.08.028
A.J. West, M.I.R. Louthan, Hydrogen effects on the tensile properties of 21–6–9 stainless steel. Met.Trans. a, 13(11), 2049–2058 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02645950
D.P. Abraham, C.J. Altstetter, The effect of hydrogen on the yield and flow stress of an austenitic stainless steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 26(11), 2849–2858 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02669643
K.S. Ghosh, D.K. Mondal, Effect of grain size on mechanical electrochemical and hydrogen embrittlement behaviour of a micro-alloy steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 559, 693–705 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.09.011
G.M. Pressouyre, I.M. Bernstein, A quantitative analysis of hydrogen trapping. Metall. Trans. A 9(11), 1571–1580 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02661939
S. Lynch, Hydrogen embrittlement phenomena and mechanisms. Corr. Rev. Walter de Gruyter, 30(3–4), 105–123 (2012) https://doi.org/10.1515/corrrev-2012-0502
C.F. Dong, X.G. Li, Z.Y. Liu, Y.R. Zhang, Hydrogen-induced cracking and healing behaviour of X70 steel. J. Alloys Compd. 484(1–2), 966–972 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.05.085
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge M/s Tata Steel, Jamshedpur, India, for providing the micro-alloy steel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, P.S., Ghosh, K.S. Effect of Heat Treatment and NC Ni Coating on Electrochemical and Hydrogen Embrittlement Behaviour of a High Strength Low Alloy (HSLA) Steel. Electrocatalysis 13, 551–566 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-022-00744-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-022-00744-4