Abstract
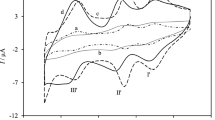
This study deals with the use of a COOH-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube–coated glassy carbon electrode (f-MWCNT-coated GCE) to investigate the electrochemical oxidation of ciprofloxacin (CIP). The electrochemical behavior of CIP is investigated using cyclic voltammetry and square wave voltammetry in PBS buffer aqueous solutions. Cyclic voltammograms have shown that (1) CIP provided a well-defined irreversible oxidation peak at a potential of around 1 V and (2) modifying glassy carbon electrode surface by MWCNT leads to a significant improvement 3.6 and 1.5 folds of the electrochemical response as compared to that at bare GCE, and MWCNT-coated GCE, respectively. This improvement in the electrocatalytic activity of the electrode is attributed to the decrease of the charge transfer resistance. The influence of some controlled parameters (scan rate, pH, successive potential scans, and SMX concentration) on the electrochemical oxidation of CIP is studied. It has been shown that CIP oxidizes according to a diffusion-controlled mechanism involving the transfer of one electron and two protons. Furthermore, this study demonstrates that the zwitterionic form of CIP is thermodynamically more reactive to electrochemical oxidation than the cationic and anionic forms. Under optimized conditions, a linear calibration curve was obtained by square wave voltammetry for CIP in the concentration range 5–100 µM with a detection limit of 0.16 µM. The f-MWCNT-coated GCE showed great improvement, as compared to bare GCE, in the anodic oxidation reactivity of CIP with high simplicity of preparation, selectivity, repeatability, and reproducibility. Also, CIP analytical determination was performed successfully, using f-MWCNT-coated GCE, in-hospital effluent, treated domestic wastewater effluent, and natural water source, allowing promising and feasible applications in on-site environmental monitoring.
Graphical Abstract
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.A. Brown, Fluoroquinolones in animal health. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 19, 1–14 (1996)
P.C. Appelbaum, P.A. Hunter, The fluoroquinolone antibacterials: past, present and future perspectives. Int. J. Antimicrob. Ag. 16, 5–15 (2000)
L.J. Zivanovic, G. Zigic, M. Zecevic, Investigation of chromatographic conditions for the separation of ofloxacin and its degradation products. J. Chromatogr. A 1119, 224–230 (2006)
F. Tewes, J. Brillault, B. Lamy, P.O. Connell, J.C. Olivier, W. Couet, A.M. Healy, Ciprofloxacin-loaded inorganic-organic composite microparticles to treat bacterial lung infection. Mol. Pharmaceut. 13, 100–112 (2016)
S. Suryoprabowo, L. Liu, J. Peng, H. Kuang, C. Xu, Development of a broad specific monoclonal antibody for fluoroquinolone analysis. Food Anal. Methods 7, 2163–2168 (2014)
B. Huang, Y. Yin, L. Lu, H. Ding, L. Wang, T. Yu, J.J. Zhu, X.D. Zheng, Y.Z. Zhang, Preparation of high-affinity rabbit monoclonal antibodies for ciprofloxacin and development of an indirect competitive ELISA for residues in milk. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 11, 812–818 (2010)
X.V. Doorslaer, J. Dewulf, H.V. Langenhove, K. Demeestere, Fluoroquinolone antibiotics: an emerging class of environmental micropollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 16(5–15), 5–15 (2014)
R.H.O. Montes, M.C. Marra, M.M. Rodrigues, E.M. Richter, R.A.A. Munoz, Fast determination of ciprofloxacin by batch injection analysis with amperometric detection and capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection. Electroanalysis 26, 432–438 (2014)
M. Tumini, O. Nagel, M.P. Molina, R. Althaus, Microbiological assay with bacillus licheniformis for the easy detection of quinolones in milk. Int. Dairy J. 64, 9–13 (2017)
J.-H. Choi, M.I.R. Mamun, A.M.A. El-Aty, J.-H. Park, E.-H. Shin, J.Y. Park, S.-K. Cho, S.C. Shin, K.B. Lee, J.-H. Shim, Development of a single-step precipitation cleanup method for the determination of enrofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and danofloxacin in porcine plasma. Food Chem. 127, 1878–1883 (2011)
A. Zotou, N. Miltiadou, Sensitive LC determination of ciprofloxacin in pharmaceutical preparations and biological fluids with fluorescence detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 28, 559–568 (2002)
S. Watabe, Y. Yokoyama, K. Nakazawa, K. Shinozaki, R. Hiraoka, K. Takeshita, Yukio Suzuki, Simultaneous measurement of pazufloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and levofloxacin in human serum by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B. 878, 1555–1561 (2010)
M.Y. Pinero, M. Fuenmayor, L. Arce, R. Bauza, M. Valcarcel, A simple sample treatment for the determination of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in raw goat milk. Microchem. J. 110, 533–537 (2013)
B. Chen, J. Han, Y. Wang, C. Sheng, Y. Liu, G. Zhang, Y. Yan, Separation, enrichment and determination of ciprofloxacin using thermoseparating polymer aqueous two-phase system combined with high performance liquid chromatography in milk, egg, and shrimp samples. Food Chem. 148, 105–111 (2014)
J. Vella, F. Busuttil, N.S. Bartolo, C. Sammut, V. Ferrito, A. Serracino-Inglotta, L.M. Azzopardia, G. LaFerla, A simple HPLC–UV method for the determination of ciprofloxacin in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B. 989, 80–85 (2015)
H.J. Kim, K.A. Seo, H.M. Kim, E.S. Jeong, J.L. Ghim, S.H. Lee, Y.M. Lee, D.H. Kim, J.G. Shin, Simple and accurate quantitative analysis of 20 anti-tuberculosis drugs in human plasma using liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 102, 9–16 (2015)
K. Jindal, M. Narayanam, S. Singh, A systematic strategy for the identification and determination of pharmaceuticals in environment using advanced LC–MS tools: application to ground water samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 108, 86–96 (2015)
L. Lucatello, P. Cagnardi, F. Capolongo, C. Ferraresi, F. Bernardi, C. Montesissa, Development and validation of an LC–MS/MS/MS method for the quantification of fluoroquinolones in several matrices from treated turkeys. Food Control 48, 2–11 (2015)
L. Fotouhi, M. Aahyari, Electrochemical behavior and analytical application of ciprofloxacin using a multi-walled nanotube composite film-glassy carbon electrode. Colloids Surf. B. 81, 110–114 (2010)
A.A. Ensafi, M. Taei, T. Khayamian, F. Hasanpour, Simultaneous voltammetric determination of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in urine and plasma using multiwall carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode by least-squares support vector machines. Anal. Sci. 26, 803–808 (2010)
J.M.P.J. Garrido, M. Melle-Franco, K. Strutynski, F. Borges, C.M.A. Brett, E.M.P.J. Garrido, β–Cyclodextrin carbon nanotube-enhanced sensor for ciprofloxacin detection. J. Environ Sci. Health C. 52, 313–319 (2016)
C. Yan, J. Li, T. Meng, X. Liu, R. Zhang, Y. Chen, G. Wang, Selective recognition of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride based on molecular imprinted sensor via electrochemical copolymerization of pyrrole and o-phenylenediamine. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 11, 6466–6476 (2016)
H. Bagheri, H. khoshsafar, S. Amidi, Y. Hosseinzadeh Ardakani, Fabrication of an electrochemical sensor based on magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes for the determination of ciprofloxacin. Anal. Methods. 8, 3383–3390 (2016)
M. Radicova, M. Behul, M. Marton, M. Vojs, R. Bodor, R. Redhammer, A.V. Stanova, Heavily boron doped diamond electrodes for ultra-sensitive determination of ciprofloxacin in human urine. Electroanalysis 29, 1612–1617 (2017)
C. Wu, R. Chen, J. Wang, Y. Wang, X. Jing, R. Chen, L. Sun, Y. Yun, Fluorescent molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for selective and rapid detection of ciprofloxacin in aquaculture water. J. Sep. Sci. 41, 3782–3790 (2018)
N. Yuphintharakun, P. Nurerk, K. Chullasat, P. Kanatharana, F. Davis, D. Sooksawat, O. Bankoed, A nanocomposite optosensor containing carboxylic functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes and quantum dots incorporated into a molecularly imprinted polymer for highly selective and sensitive detection of ciprofloxacin. Spectroc. Acta A. 201, 382–391 (2018)
K.R. Reddy, P.K. Brahman, L. Suresh, Fabrication of high performance disposable screen printed electrochemical sensor for ciprofloxacin sensing in biological samples. Measurement 127, 175–186 (2018)
X. Hu, K.Y. Goud, V.S. Kumar, G. Katanante, Z. Li, Z. Zhu, J.L. Marty, Disposable electrochemical aptasensor based on carbon nanotubes-V2O5-chitosan nanocomposite for detection of ciprofloxacin. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 286, 278–286 (2018)
S.G. Surya, S. Khatoon, A.A. Lahcen, A.T.H. Nguen, B.B. Dzantiev, N. Tarannum, K.N. Salama, A chitosan gold nanoparticles molecularly imprinted polymer based ciprofloxacin sensor. R. Soc. Chem. 10, 12823–12832 (2020)
E. Sari, R. Uzek, M. Duman, A. Denizil, Detection of ciprofloxacin through surface Plasmon resonance nanosensor with specific recognition sites. J. Biomater. Sci. 29(1302–1318), 1302–1318 (2018)
X. Xu, P. Guo, Z. Luo, Y. Ge, Y. Zhou, R. Chang, W. Du, C. Chang, Q. Fu, Preparation and characterization of surface molecularly imprinted films coated on multiwall carbon nanotubes for recognition and separation of lysozyme with high binding capacity and selectivity. RSC Adv. 7, 18765–18744 (2017)
P. Gayen, B.P. Chaplin, Selective electrochemical detection of ciprofloxacin with a porous nafion/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite film electrode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(3), 1615–1626 (2016)
R. Barabás, G. Katona, E.S. Bogya, M.V. Diudea, A. Szentes, B. Zsirka, J. Kovács, L. Kékedy-Nagy, M. Czikó, Preparation and characterization of carboxyl functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes–hydroxyapatite composites. Ceram. Int. 41, 12717–12727 (2015)
S. Tajik, H. Beitollahi, R. Zaeimbashi, M. Sheikhshoaei, M.B. Askari, P. Salarizadah, An electrochemical sensor based on V2O5 nanoparticles for the detection of ciprofloxacin. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 17558–17567 (2021)
M. Sabeti, A.A. Ensafi, K.S. Mousaabadi, B. Rezaei, A selective electrochemical sensor based on a modified-glassy carbon electrode using f-MWCNTs-polydopamine for ciprofloxacin detection. IEEE Sens. J. 12, 19714–19721 (2021)
R. Karthik, R. Sasikumar, S. M. Chen, J. V. kumar, A. Elangovan, V. Muthuraj, P. Muthukrishnan, F. M. A. Al-Hemaid, M. A. Ali, M. S. Elshikh, A highly sensitive and selective electrochemical determination of non-steroidal prostate anti-cancer drug nilutamide based on ƒ-MWCNT in tablet and human blood serum sample. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1095, 226–234 (2018)
C. Slim, N. Tlili, C. Richard, S. Griveau, F. Bedioui, Amperometric detection of diclofenac at a nano-structured multi-wall carbon nanotubes sensing films. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 107, 107454 (2019)
P.J. Britto, K.S.V. Santhanam, P.M. Ajayan, Carbon nanotube electrode for oxidation of dopamine. Bioelectrochem. Bioenergetics. 41, 121–125 (1996)
C.M.A. Brett, A.M. Oliveira Brett, Electrochemistry: principles, methods and aplications, Oxford Science University Publications, Oxford (1993)
M. Gattrell, D.W. Kirk, A study of electrode passivation during aqueous phenol electrolysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 140, 903–911 (1993)
H. Li, D. Zhang, X. Han, B. Xing, Adsorption of antibiotic ciprofloxacin on carbon nanotubes: pH dependence and thermodynamics. Chemosphere 95, 150–155 (2014)
L. Fotouhi, A.B. Hashkavayi, M.M. Heravi, Electrochemical behaviour and voltammetric determination of sulphadiazine using a multi-walled carbon nanotube composite film-glassy carbon electrode. J. Exp. Nanosci. 8(947–956), 947–956 (2013)
F. Yu, S. Sun, S. Han, J. Zheng, J. Ma, Adsorption removal of ciprofloxacin by multi-walled carbon nanotubes with different oxygen contents from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 28, 588–595 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaabani, A., Ben Jabrallah, T. & Belhadj Tahar, N. Electrochemical Oxidation of Ciprofloxacin on COOH-Functionalized Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube–Coated Vitreous Carbon Electrode. Electrocatalysis 13, 402–413 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-022-00725-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-022-00725-7