Abstract
Divided electrochemical reactors allow the design of strategies to take advantage of the two reactions of the redox pair involved for wastewater treatment. Nafion membranes are the most used separators in these cells. These membranes have demonstrated high efficiency, but their high costs make the process more expensive. The present work focuses on the evaluation of the technical and economic feasibility of replacing the Nafion 117® membrane with a commercial polymeric membrane used in reverse osmosis (RO) treatments. In this study, a divided electrochemical cell was constructed with electrodes made of galvanized steel. The Fenton reaction was developed in the anode compartment using electrogenerated iron as a catalyst. An experimental design 23 was used to study the influence of three operating parameters (initial H2O2, membrane, voltage) on the H2O2 activation kinetics. The results demonstrated that the activation of H2O2 followed a pseudo-zero-order kinetic. The maximum rate constants obtained for Nafion 117® and RO membrane were 2.76 mM min−1 and 2.45 mM min−1, respectively. The optimization of H2O2 activation process was performed using a response surface methodology, where multiple regression models were used to figure out the best operation conditions when using both membranes. Finally, an extensive cost analysis of the process is included.
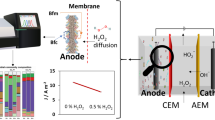
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
X. Zhang, Y. Ding, H. Tang, X. Han, L. Zhu, N. Wang, Degradation of bisphenol A by hydrogen peroxide activated with CuFeO2 microparticles as a heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst: efficiency stability and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 236, 251–262 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.09.051
M. Davoudi, M. Gholami, S. Naseri, A. Hossein Mahvi, M. Farzadkia, A. Esrafili, H. Alidadi, Application of electrochemical reactor divided by cellulosic membrane for optimized simultaneous removal of phenols chromium and ammonia from tannery effluents. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 96, 1310–1332 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2014.942311
S. Ellouze, S. Kessemtini, D. Clematis, G. Cerisola, M. Panizza, S. Chaabane Elaoud, Application of Doehlert design to the electro-Fenton treatment of Bismarck Brown Y. J. Electroanal. Chem. 799, 34–39 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.05.042
A. Fernandes, L. Labiadh, L. Ciríaco, M.J. Pacheco, A. Gadri, S. Ammar, A. Lopes, Electro-Fenton oxidation of reverse osmosis concentrate from sanitary landfill leachate: evaluation of operational parameters. Chemosphere. 184, 1223–1229 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.06.088
S. Rodríguez, D. Lorenzo, A. Santos, A. Romero, Comparison of real wastewater oxidation with Fenton/Fenton-like and persulfate activated by NaOH and Fe(II). J. Environ. Manag. 255, 109926 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109926
H. He, Q. Ji, Z. Gao, S. Yang, C. Sun, S. Li, L. Zhang, Degradation of tri(2-chloroisopropyl) phosphate by the UV/H2O2 system: kinetics mechanisms and toxicity evaluation. Chemosphere. 236, 124388 (2019)
Y. Zhang, Y. Xiao, Y. Zhong, T.-T. Lim, Comparison of amoxicillin photodegradation in the UV/H2O2 and UV/persulfate systems: reaction kinetics degradation pathways and antibacterial activity. Chem. Eng. J. 372, 420–428 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.160
J. Wang, H. Chen, Catalytic ozonation for water and wastewater treatment: recent advances and perspective. Sci. Total. Environ. 704, 135249 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135249
K.I. Hamid, P.J. Scales, A. Sebastien, J.-P. Croue, S. Muthukumaran, M. Duke, Ozone combined with ceramic membranes for water treatment: impact on HO radical formation and mitigation of bromate. J. Environ. Manage. 253, 109655 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109655
L. Labiadh, S. Ammar, A.R. Kamali, Oxidation/mineralization of AO7 by electro-Fenton process using chalcopyrite as the heterogeneous source of iron and copper catalysts with enhanced degradation activity and reusability. J. Electroanal. Chem. 853, 113532 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113532
L. Feng, E.A. Serna-Galvis, N. Oturan, S. Giannakis, R.A. Torres-Palma, M.A. Oturan, Evaluation of process influencing factors, degradation products, toxicity evolution and matrix-related effects during electro-Fenton removal of piroxicam from waters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 7(5), 103400 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103400
M.G. Lak, M.R. Sabour, E. Ghafari, A. Amiri, Energy consumption and relative efficiency improvement of photo-Fenton – optimization by RSM for landfill leachate treatment a case study. Waste. Manag. 79, 58–70 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.07.029
J-H. Kim, H –K. Lee, Y-J. Park, S-B. Lee, S-J. Choi, W. Oh, H-S. Kim, C–R. Kim, K–C. Kim, B-C. Seo, Studies on decomposition behavior of oxalic acid waste by UVC photo-Fenton advanced oxidation process. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 51(8), 1957–1963 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.net.2019.06.011
R. Andreozzi, A. D’Apuzzo, R. Marotta, A kinetic model for the degradation of benzothiazole by Fe3+ photo-assisted Fenton process in a completely mixed batch reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 80(1–3), 241–257 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(00)00308-3
J.J. Pignatello, E. Oliveros, A. MacKay, Advanced oxidation processes for organic contaminant destruction based on the Fenton reaction and related chemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36(1), 1–84 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380500326564
J. Casado, Towards industrial implementation of electro-Fenton and derived technologies for wastewater treatment: a review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 7(1), 102823 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.102823
A.A. Najafpoor, M. Davoudi, E.R. Salmani, Decolorization of synthetic textile wastewater using electrochemical cell divided by cellulosic separator. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng. 15, 11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40201-017-0273-3
comparison of two electrochemical systems, A. Ochoa-Chavez, A. Pieczynska, A. Fiszka Borzyszkowska, P. Espinoza-Montero, E. Siedlecka, Electrochemical degradation of 5-FU using a flow reactor with BDD electrode. Chemosphere. 201, 816–825 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.050
A.J. Mendez-Martínez, M.M. Dávila-Jiménez, O. Ornelas-Dávila, M.P. Elizalde-González, U. Arroyo-Abad, I. Sirés, E. Brillas, Electrochemical reduction and oxidation pathways for Reactive Black 5 dye using nickel electrodes in divided and undivided cells. Electrochim. Acta. 59(1), 140–149 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2011.10.047
A.Y. Bagastyo, D.J. Batstone, I. Kristiana, B.I. Escher, C. Joll, J. Radjenovic, Electrochemical treatment of reverse osmosis concentrate on boron-doped electrodes in undivided and divided cell configurations. J. Hazard. Mater. 279, 111–116 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.06.060
B. Ramírez, V. Rondán, L. Ortiz-Hernández, S. Silva-Martínez, A. Alvarez-Gallegos, Semi-empirical chemical model for indirect advanced oxidation of Acid Orange 7 using an unmodified carbon fabric cathode for H2O2 production in an electrochemical reactor. J. Environ. Manage. 171, 29–34 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.02.004
Y.A. Bustos, J.G. Rangel-Peraza, M.N. Rojas-Valencia, E.R. Bandala, A. Álvarez-Gallegos, L. Vargas-Estrada, Treatment of industrial effluents by electrochemical generation of H2O2 using an RVC cathode in a parallel plate reactor. Environ. Technol. 37(7), 815–827 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2015.1086820
J. Mora-Gómez, M. García-Gabaldón, J. Carrillo-Abad, M. Montañés, S. Mestre, V. Pérez-Herranz, Influence of the reactor configuration and the supporting electrolyte concentration on the electrochemical oxidation of Atenolol using BDD and SnO2 ceramic electrodes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 241, 116684 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116684
B. Ramírez-Pereda, A.A. Álvarez-Gallegos, S. Silva-Martinez, J.G. Rangel-Peraza, Y.A. Bustos-Terrones, Evaluation of the simultaneous use of two compartments of an electrochemical reactor for the elimination of azo dyes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 855, 113593 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113593
V. Rondan, B. Ramírez, S. Silva-Martínez, J. Hernández, M. Kumar Tiwari, A. Alvarez-Gallegos, High removal efficiency of dye pollutants by anodic Fenton treatment. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 15, 52–67 (2020). https://doi.org/10.20964/2020.01.21
C. Agarwal, A. Mhatre, A. Goswami, Transport studies of monovalent ions through Nafion-117 ion exchange membrane in presence of polyacrylate. Sep. Sci. Technol. 49(17), 2650–2656 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2014.940047
J. Hu, H. Zhang, W. Xu, Z. Yuan, X. Li, Mechanism and transfer behavior of ions in Nafion membranes under alkaline media. J. Membr. Sci. 566(15), 8–14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.08.057
I. Navarro-Solis, L. Villalba-Almendra, A. Alvarez-Gallegos, H2 production by PEM electrolysis, assisted by textile effluent treatment and a solar photovoltaic cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 35(20), 10833–10841 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.07.086
M.J. Parnian, S. Rowshanzamir, J.A. Moghaddam, Investigation of physicochemical and electrochemical properties of recast Nafion nanocomposite membranes using different loading of zirconia nanoparticles for proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1(2), 146–154 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2018.06.008
C. Agarwal, S. Chaudhury, A.G. Pandey, Kinetic aspects of Donnan dialysis through Nafion-117 membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 415, 681–685 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2012.05.049
S. Sevda, X. Dominguez-Benetton, K. Vanbroekhoven, T. Sreekrishnan, D. Pant, Characterization and comparison of the performance of two different separator types in air–cathode microbial fuel cell treating synthetic wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 228, 1–11 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.05.014
W. Yang, R. Rossi, Y. Tian, K.-Y. Kim, B.E. Logan, Mitigating external and internal cathode fouling using a polymer bonded separator in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 249, 1080–1084 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.109
A.A. Najafpoor, M. Davoudi, R. Salmani, Optimization of copper removal from aqueous solutions in a continuous electrochemical cell divided by cellulosic separator. Water. Sci. Technol. 75(5–6), 1233–1242 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.619
K. Hara, N. Kishimoto, M. Kato, H. Otsu, Efficacy of a two-compartment electrochemical flow cell introduced into a reagent-free UV/chlorine advanced oxidation process. Chem. Eng. J. 388, 124385 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124385
G. Syed Ibrahim, A. M. Isloor, R. Farnood, Fundamentals and basics of reverse osmosis. Current trends and future developments on (bio-) membranes fundamentals and basics of reverse osmosis. (Elsevier, 2020), pp 141–163.
Y-N. Wang, R. Wang, Reverse osmosis membrane separation technology Membrane Separation Principles and Applications. (Elsevier, 2019), pp 1–45.
B. Ooi, J. Sum, J. Beh, W. J. Lau, S. Lai, Materials and engineering design of interfacial polymerized thin film composite nanofiltration membrane for industrial applications. (Elservier, 2019), pp 47–83.
D. Ankoliya, B. Mehta, H. Raval, Advances in surface modification techniques of reverse osmosis membrane over the years. Sep. Sci. Technol. 54, 293–310 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1483404
A. García, Y. Quintero, N. Vicencio, B. Rodríguez, D. Ozturk, E. Mosquera, T.P. Corrales, U. Volkmann, Influence of Tio2 nanostructures on anti-adhesion and photoinduced bactericidal properties of thin film composites membranes. RSC. Adv. 6(86), 82941–82948 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA17999A
M. Armendariz Ontiveros, Y. Quintero, A. Llanquilef, M. Morel, L. Argentel Martínez, A. García García, A. García, Anti-biofouling and desalination properties of thin film composite reverse osmosis membranes with copper and iron nanoparticles. Materials. 12(13), 2081 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132081
A. Elhalil, H. Tounsadi, R. Elmoubarki, F. Mahjoubi, M. Farnane, M. Sadiq, M. Abdennouri, S. Qourzal, N. Barka, Factorial experimental design for the optimization of catalytic degradation of malachite green dye in aqueous solution by Fenton process. Water. Resour. Ind. 15, 41–48 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2016.07.002
D. E. Santiago, O. González-Díaz, J. Araña, E. Pulido Melián, J. Pérez-Peña, J. Doña-Rodríguez, Factorial experimental design of imazalil-containing wastewater to be treated by Fenton-based processes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A. 353, 240–250 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.11.038
J. D. García-Espinoza, I. Robles, V. Gil, E. Becerril-Bravo, J. A. Barrios, L. A. Godínez, Electrochemical degradation of triclosan in aqueous solution. A study of the performance of an electro-Fenton reactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 7(4), 103228 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103228
I. Kolthoff, R. Belcher, G. Matsuyama, V. Stenger, Volumetric analysis Vol 3. (Interscience Publishers, New York, 1957). https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.3030470330
H. Lin, H. Zhang, X. Wang, L. Wang, J. Wu, Electro-Fenton removal of Orange II in a divided cell: reaction mechanism, degradation pathway and toxicity evolution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 122, 533–540 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.12.010
P. Liang, M. Rivallin, S. Cerneaux, S. Lacour, E. Petit, M. Cretin, Coupling cathodic Electro-Fenton reaction to membrane filtration for AO7 dye degradation: a successful feasibility study. J. Membr. Sci. 510, 182–190 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.02.071
G. Varank, S.Y. Guvenc, A. Demir, A comparative study of electrocoagulation and electro-Fenton for food industry wastewater treatment: multiple response optimization and cost analysis. Sep. Sci. Technol. 53(17), 2727–2740 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1470643
T. Yatagai, Y. Ohkawa, D. Kubo, Y. Kawase, Hydroxyl radical generation in electro-Fenton process with a gas-diffusion electrode: linkages with electro-chemical generation of hydrogen peroxide and iron redox cycle. J. Environ. Sci. Health. A. 52(1), 74–83 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2016.1229935
L. Jimenez-Lima, S. Silva-Martínez, J. Hernández, F. Sierra, A. Alvarez-Gallegos, Modeling methylene blue oxidation by means of Fenton chemistry enhanced by UV irradiation at mild conditions. Desalination. Water. Treat. 55(13), 3646–3652 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.939864
F. Sopaj, N. Oturan, J. Pinson, F. Podvorica, M.A. Oturan, Effect of the anode materials on the efficiency of the electro-Fenton process for the mineralization of the antibiotic sulfamethazine. Appl. Catal. B. 199, 331–341 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.06.035
A.-R.A. Giwa, I.A. Bello, A.B. Olabintan, O.S. Bello, T.A. Saleh, Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of fenton oxidative decolorization of methylene blue. Heliyon. 6(8), e04454 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04454
F.Z. Saidi, M. Mokhtari, Central composite design to optimize the degradation of methylene blue by Fenton process. ChemistrySelect. 4(38), 11288–11293 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201902466
G. Buftia, E. Rosales, M. Pazos, G. Lazar, M.A. Sanromán, Electro-Fenton process for implementation of acid black liquor waste treatment. Sci. Total. Environ. 635, 397–404 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.139
K. Cruz-González, O. Torres-López, A.M. García-León, E. Brillas, A. Hernández-Ramírez, J.M. Peralta-Hernández, Optimization of electro-Fenton/BDD process for decolorization of a model azo dye wastewater by means of response surface methodology. Desalination. 286, 63–68 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.11.005
S. Toshio Fujiwara, K. Ribeiro, T. María de Andrade, Preparation and application of cellulose acetate/Fe films in the degradation of Reactive Black 5 dye through photo-Fenton reaction. Environ. Technol. 37(13), 1664–1675 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2015.1127290
T. Wang, Y. Zhou, S. Cao, J. Lu, Y. Zhou, Degradation of sulfanilamide by Fenton-like reaction and optimization using response surface methodology. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 172, 334–340 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.01.106
R. Davarnejad, M. Mohammadi, A.F. Ismail, Petrochemical wastewater treatment by elector-Fenton process using aluminum and iron electrodes: statistical comparison. J. Water Process. Eng. 3, 18–25 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2014.08.002
S. Yazici Guvenc, K. Dincer, G. Varank, Performance of electrocoagulation and electro-Fenton processes for treatment of nanofiltration concentrate of biologically stabilized landfill leachate. J. Water Process. Eng. 31, 100863 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100863
P. Kaur, V. Sangal, J. Kushwaha, Parametric study of electro-Fenton treatment for real textile wastewater disposal study and its cost analysis. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 801–810 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1696-9
Acknowledgements
The authors thank TECNM/Instituto Tecnológico de Culiacán for providing the entire infrastructure for conducting this work.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Council of Science and Technology of Mexico through a doctoral scholarship: CONACYT PhD scholarship 2018–2022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hermosillo-Nevárez, J.J., Bustos-Terrones, Y.A., Rangel-Peraza, J.G. et al. Technical–Economic Analysis of Hydrogen Peroxide Activation by a Sacrificial Anode: Comparison of Two Exchange Membranes. Electrocatalysis 13, 11–25 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-021-00689-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-021-00689-0