Abstract
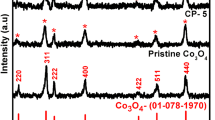
The sluggish reaction rate of the oxygen electrode is always the main obstacle impeding the practical energy conversion efficiency of the metal-air batteries. In this work, a novel and simple strategy is reported to transform conventional cotton fabrics into metal-doped oxygen electrocatalysts. Through a chemical adsorption approach, cobalt metal ions are uniformly loaded on the cotton fibre surface. By a subsequent carbonisation and oxidisation procedures, the cobalt-doped cotton carbon catalysts are obtained. Thereinto, the cobalt oxides doped cotton carbon catalyst (CoO/CC) exhibits the best ORR performance, with an onset potential of 0.85 V (vs. RHE) and the limiting current density of 5.7 mA/cm2 in 0.1 M KOH. Notably, the OER performance is also greatly improved under the same conditions, suggesting great potential to be used as bifunctional materials. Structural and elemental characterisations demonstrate that these good results are ascribed to two aspects: the macropore generation in the cotton carbon due to the metal etching effect, and the cobalt metals transforming into cobalt oxides after the oxidisation process. Thus, this work provides a simple approach to recycle conventional textiles into valuable products.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Huang, J. Wang, Y. Peng, C. Jung, A. Fisher, X. Wang, Design of efficient bifunctional oxygen reduction/evolution electrocatalyst: recent advances and perspectives. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1700544 (2017)
C.R. Raj, A. Samanta, S.H. Noh, S. Mondal, T. Okajima, T. Ohsaka, Emerging new generation electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 11156–11178 (2016)
X. Tian, X.F. Lu, B.Y. Xia, X.W. Lou, Advanced electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction in energy conversion technologies. Joule 4, 45–68 (2020)
D. Yang, L. Zhang, X. Yan, X. Yao, Recent progress in oxygen electrocatalysts for zinc–air batteries. Small Methods 1, 1700209 (2017)
I.C. Man, H.Y. Su, F. Calle-Vallejo, H.A. Hansen, J.I. Martínez, N.G. Inoglu, J. Kitchin, T.F. Jaramillo, J.K. Nørskov, J. Rossmeisl, Universality in oxygen evolution electrocatalysis on oxide surfaces. Chem. Cat. Chem. 3, 1159–1165 (2011)
J. Xiao, Q. Kuang, S. Yang, F. Xiao, S. Wang, L. Guo, Surface structure dependent electrocatalytic activity of Co3O4 anchored on graphene sheets toward oxygen reduction reaction. Sci. Rep. 3, 2300 (2013)
X. Han, G. He, Y. He, J. Zhang, X. Zheng, L. Li, C. Zhong, W. Hu, Y. Deng, T.Y. Ma, Engineering catalytic active sites on cobalt oxide surface for enhanced oxygen electrocatalysis. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1702222 (2018)
Y. Wang, J. Li, Z. Wei, Transition-metal-oxide-based catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 6, 8194–8209 (2018)
Y. Liang, Y. Li, H. Wang, J. Zhou, J. Wang, T. Regier, H. Dai, Co3O4 nanocrystals on graphene as a synergistic catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Nat. Mater. 10, 780–786 (2011)
M. Borghei, J. Lehtonen, L. Liu, O.J. Rojas, Advanced biomass-derived electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Mater. 30, 1703691 (2018)
S. De, A.M. Balu, J.C. van der Waal, R. Luque, Biomass-derived porous carbon materials: synthesis and catalytic applications. Chem. Cat. Chem. 7, 1608–1629 (2015)
J. Wang, M. Liu, C. Duan, J. Sun, Y. Xu, Preparation and characterization of cellulose-based adsorbent and its application in heavy metal ions removal. Carbohydr. Polym. 206, 837–843 (2019)
S. Hokkanen, A. Bhatnagar, M. Sillanpää, A review on modification methods to cellulose-based adsorbents to improve adsorption capacity. Water Res. 91, 156–173 (2016)
L.L. Xu, M.X. Guo, S. Liu, S.-W. Bian, Graphene/cotton composite fabrics as flexible electrode materials for electrochemical capacitors. RSC Adv. 5, 25244–25249 (2015)
I. Kubovský, D. Kačíková, F. Kačík, Structural changes of oak wood main components caused by thermal modification. Polymers (Basel) 12, 485 (2020)
L. Chen, T. Ji, L. Mu, J. Zhu, Cotton fabric derived hierarchically porous carbon and nitrogen doping for sustainable capacitor electrode. Carbon 111, 839–848 (2017)
X. Xia, M. Li, T. Liu, P. Liang, X. Huang, Facile synthesis of cobalt oxide as electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction in microbial fuel cells. Chem. Engr. J. 342, 395–400 (2018)
K. Lu, G. Chang, H. Zhang, X.-Y. Yu, Accelerating the oxygen evolution reaction kinetics of Co3O4 in neutral electrolyte by decorating RuO2. Chem. Commun. 57, 2907–2910 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, S., Liu, Y. & Fang, J. Controllable Adsorption of Cobalt Metal Ions on Cotton Fabrics and Their Carbonised Oxygen Electrocatalysts. Electrocatalysis 12, 667–677 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-021-00677-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-021-00677-4