Abstract
Objectives
There is an increasing recognition of mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) as a promising way to reduce burnout. However, inconsistent results were found on the effect among college students. In addition, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. The aims of this study were to explore the effect of a mindfulness-based training program on burnout in college student population and to examine if changes in mindfulness mediate the intervention effect.
Method
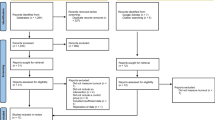
A total of 128 college students (M = 21.36 years, SD = 2.76 years) were randomized into an intervention group (n = 64) or a wait-list control group (n = 64). The intervention consisted of eight sections of mindfulness training courses. Measures on mindfulness and burnout were administered at the baseline, post-intervention, and 3-month follow-up.
Results
Compared to those in the control group, participants in the intervention group reported a significant increase in mindfulness and a decrease in burnout both at post-intervention (mindfulness: F = 22.41, p < 0.01, partial η2 = 0.15; burnout: F = 8.24, p < 0.01, partial η2 = 0.06) and 3-month follow-up (mindfulness: F = 16.29, p < 0.01, partial η2 = 0.12; burnout: F = 9.24, p < 0.01, partial η2 = 0.07). Mediation analyses demonstrated that the increase in mindfulness fully mediated the intervention effect on burnout.
Conclusions
Mindfulness-based training programs can effectively reduce burnout among college students, and the effect appears to be mediated by changes in mindfulness levels.
Preregistration
This study is not preregistered.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated for this study are available on request to the corresponding author.
References
Al-Alawi, M., Al-Sinawi, H., Al-Qubtan, A., Al-Lawati, J., Al-Habsi, A., Al-Shuraiqi, M., Al-Adawi, S., & Panchatcharam, S. M. (2019). Prevalence and determinants of burnout syndrome and depression among medical students at Sultan Qaboos University: A cross-sectional analytical study from Oman. Archives of Environmental & Occupational Health, 74(3), 130–139. https://doi.org/10.1080/19338244.2017.1400941
Almeida, G. d. C., de Souza, H. R., de Almeida, P. C., Almeida, B. d. C., & Almeida, G. H. (2016). The prevalence of burnout syndrome in medical students. Archives of Clinical Psychiatry, 43(1), 6–10. https://doi.org/10.1590/0101-60830000000072
Appelbaum, N. P., Lee, N., Amendola, M., Dodson, K., & Kaplan, B. (2019). Surgical resident burnout and job satisfaction: The role of workplace climate and perceived support. Journal of Surgical Research, 234, 20–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2018.08.035
Appels, A., & Schouten, E. (1991). Burnout as a risk factor for coronary heart-disease. Behavioral Medicine, 17(2), 53–59. https://doi.org/10.1080/08964289.1991.9935158
Armon, G., Melamed, S., Shirom, A., & Shapira, I. (2010). Elevated burnout predicts the onset of musculoskeletal pain among apparently healthy employees. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 15(4), 399–408. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0020726
Atalayin, C., Balkis, M., Tezel, H., Onal, B., & Kayrak, G. (2015). The prevalence and consequences of burnout on a group of preclinical dental students. European Journal of Dentistry, 9(3), 356–363. https://doi.org/10.4103/1305-7456.163227
Baer, R. A. (2003). Mindfulness training as a clinical intervention: A conceptual and empirical review. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 10(2), 125–143. https://doi.org/10.1093/clipsy/bpg015
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., Hopkins, J., Krietemeyer, J., & Toney, L. (2006). Using self-report assessment methods to explore facets of mindfulness. Assessment, 13(1), 27–45. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191105283504
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., Lykins, E., Button, D., Krietemeyer, J., Sauer, S., Walsh, E., Duggan, D., & Williams, J. M. G. (2008). Construct validity of the five facet mindfulness questionnaire in meditating and nonmeditating samples. Assessment, 15(3), 329–342. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191107313003
Bakker, A. B., & de Vries, J. D. (2021). Job demands-resources theory and self-regulation: New explanations and remedies for job burnout. Anxiety Stress and Coping, 34(1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/10615806.2020.1797695
Barbosa, P., Raymond, G., Zlotnick, C., Wilk, J., Toomey, R., 3rd., & Mitchell, J., 3rd. (2013). Mindfulness-based stress reduction training is associated with greater empathy and reduced anxiety for graduate healthcare students. Education for Health, 26(1), 9–14. https://doi.org/10.4103/1357-6283.112794
Bishop, S. R., Lau, M., Shapiro, S., Carlson, L., Anderson, N. D., Carmody, J., Segal, Z. V., Abbey, S., Speca, M., Velting, D., & Devins, G. (2004). Mindfulness: A proposed operational definition. Clinical Psychology-Science and Practice, 11(3), 230–241. https://doi.org/10.1093/clipsy/bph077
Brown, K. W., & Ryan, R. M. (2003). The benefits of being present: Mindfulness and its role in psychological well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84(4), 822–848. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.84.4.822
Capri, B., Ozkendir, O. M., Ozkurt, B., & Karakus, F. (2012). General self-efficacy beliefs, life satisfaction and burnout of university students. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences, 47, 968–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.06.76
Chang, E., Eddins-Folensbee, F., & Coverdale, J. (2012). Survey of the prevalence of burnout, stress, depression, and the use of supports by medical students at one school. Academic Psychiatry, 36(3), 177–182. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ap.11040079
Cook, A. F., Arora, V. M., Rasinski, K. A., Curlin, F. A., & Yoon, J. D. (2014). The prevalence of medical student mistreatment and its association with burnout. Academic Medicine, 89(5), 749–754. https://doi.org/10.1097/acm.0000000000000204
Dahlin, M., Joneborg, N., & Runeson, B. (2007). Performance-based self-esteem and burnout in a cross-sectional study of medical students. Medical Teacher, 29(1), 43–48. https://doi.org/10.1080/01421590601175309
Davies, J. N., Sharpe, L., Day, M. A., & Colagiuri, B. (2021). Mindfulness-based analgesia or placebo effect? The development and evaluation of a sham mindfulness intervention for acute experimental pain. Psychosomatic Medicine, 83(6), 557–565. https://doi.org/10.1097/psy.0000000000000886
de Vibe, M., Solhaug, I., Tyssen, R., Friborg, O., Rosenvinge, J. H., Sorlie, T., & Bjorndal, A. (2013). Mindfulness training for stress management: A randomised controlled study of medical and psychology students. BMC Medical Education, 13, 107. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6920-13-107
Demerouti, E., Bakker, A. B., Nachreiner, F., & Schaufeli, W. B. (2001). The job demands-resources model of burnout. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86(3), 499–512. https://doi.org/10.1037//0021-9010.86.3.499
dos Santos Boni, R. A., Paiva, C. E., de Oliveira, M. A., Lucchetti, G., Tavares Guerreiro Fregnani, J. H., & Ribeiro Paiva, B. S. (2018). Burnout among medical students during the first years of undergraduate school: Prevalence and associated factors. PLoS ONE, 13(3), e0191746. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0191746
Dyrbye, L., & Shanafelt, T. (2016). A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents. Medical Education, 50(1), 132–149. https://doi.org/10.1111/medu.12927
Dyrbye, L. N., Thomas, M. R., Massie, F. S., Power, D. V., Eacker, A., Harper, W., Durning, S., Moutier, C., Szydlo, D. W., Novotny, P. J., Sloan, J. A., & Shanafelt, T. D. (2008). Burnout and suicidal ideation among US medical students. Annals of Internal Medicine, 149(5), 334-W370. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-149-5-200809020-00008
Fendel, J. C., Burkle, J. J., & Goritz, A. S. (2021). Mindfulness-based interventions to reduce burnout and stress in physicians: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Academic Medicine, 96(5), 751–764. https://doi.org/10.1097/acm.0000000000003936
Fitzpatrick, O., Biesma, R., Conroy, R. M., & McGarvey, A. (2019). Prevalence and relationship between burnout and depression in our future doctors: A cross-sectional study in a cohort of preclinical and clinical medical students in Ireland. BMJ Open, 9(4), e023297. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023297
Flook, L., Goldberg, S. B., Pinger, L., Bonus, K., & Davidson, R. J. (2013). Mindfulness for teachers: A pilot study to assess effects on stress, burnout, and teaching efficacy. Mind Brain and Education, 7(3), 182–195. https://doi.org/10.1111/mbe.12026
Garneau, K., Hutchinson, T. A., Zhao, Q., Dobkin, P. L. J. E. J., & f. P. C. H. (2013). Cultivating person-centered medicine in future physicians. European Journal for Person Centered Healthcare, 1, 468–477. https://doi.org/10.5750/EJPCH.V1I2.688
Green, A. A., & Kinchen, E. V. (2021). The effects of mindfulness meditation on stress and burnout in nurses. Journal of Holistic Nursing, 39(4), 356–368. https://doi.org/10.1177/08980101211015818
Hakanen, J. J., Bakker, A. B., & Schaufeli, W. B. (2006). Burnout and work engagement among teachers. Journal of School Psychology, 43(6), 495–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2005.11.001
Hakanen, J. J., Schaufeli, W. B., & Ahola, K. (2008). The job demands-resources model: A three-year cross-lagged study of burnout, depression, commitment, and work engagement. Work and Stress, 22(3), 224–241. https://doi.org/10.1080/02678370802379432
Harker, R., Pidgeon, A. M., Klaassen, F., & King, S. (2016). Exploring resilience and mindfulness as preventative factors for psychological distress burnout and secondary traumatic stress among human service professionals. Work, 54(3), 631–637. https://doi.org/10.3233/wor-162311
Hathaisaard, C., Wannarit, K., & Pattanaseri, K. (2022). Mindfulness-based interventions reducing and preventing stress and burnout in medical students: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian Journal of Psychiatry, 69, 102997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajp.2021.102997
Hayes, A. F. (2013). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach. Guilford Press.
Hayes, A. F., & Rockwood, N. J. (2017). Regression-based statistical mediation and moderation analysis in clinical research: Observations, recommendations, and implementation. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 98, 39–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2016.11.001
Heyting, A., Tolboom, J. T. B. M., & Essers, J. G. A. (1992). Statistical handling of drop-outs in longitudinal clinical trials. Statistics in Medicine, 11(16), 2043–2061. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.4780111603
Hu, Q., & Schaufeli, W. B. (2009). The factorial validity of the Maslach Burnout Inventory-Student Survey in China. Psychological Reports, 105(2), 394–408. https://doi.org/10.2466/pr0.105.2.394-408
Ishak, W., Nikravesh, R., Lederer, S., Perry, R., Ogunyemi, D., & Bernstein, C. (2013). Burnout in medical students: A systematic review. The Clinical Teacher, 10(4), 242–245. https://doi.org/10.1111/tct.12014
Kabat-Zinn, J. (1982). An outpatient program in behavioral medicine for chronic pain patients based on the practice of mindfulness meditation - Theoretical considerations and preliminary - Results. General Hospital Psychiatry, 4(1), 33–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/0163-8343(82)90026-3
Kabat-Zinn, J. (2003). Mindfulness-based interventions in context: Past, present, and future. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 10(2), 144–156. https://doi.org/10.1093/clipsy/bpg016
Kemper, K. J., McClafferty, H., Wilson, P. M., Serwint, J. R., Batra, M., Mahan, J. D., Schubert, C. J., Staples, B. B., Schwartz, A., & Pediat Resident, B.-R. (2019). Do mindfulness and self-compassion predict burnout in pediatric residents? Academic Medicine, 94(6), 876–884. https://doi.org/10.1097/acm.0000000000002546
Kinnunen, S. M., Puolakanaho, A., Tolvanen, A., Makikangas, A., & Lappalainen, R. (2020). Improvements in mindfulness facets mediate the alleviation of burnout dimensions. Mindfulness, 11(12), 2779–2792. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-020-01490-8
Koutsimani, P., Montgomery, A., & Georganta, K. (2019). The relationship between burnout, depression, and anxiety: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 284. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00284
Langballe, E. M., Innstrand, S. T., Hagtvet, K. A., Falkum, E., & Aasland, O. G. (2009). The relationship between burnout and musculoskeletal pain in seven Norwegian occupational groups. Work, 32(2), 179–188. https://doi.org/10.3233/wor-2009-0804
Lee, K. P., Yeung, N., Wong, C., Yip, B., Luk, L. H. F., & Wong, S. (2020). Prevalence of medical students’ burnout and its associated demographics and lifestyle factors in Hong Kong. PLoS ONE, 15(7), e0235154. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0235154
Li, C. X., Zhu, Y. X., Zhang, M. G., Gustafsson, H., & Chen, T. (2019). Mindfulness and athlete burnout: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(3), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030449
Li, X., Wuyuntena, Yuan, F.-z., Liu, Z.-h., & Fan, L.-l. (2017). A analysis of reliability and validity of FFMQ by clasical test theory and the generalizability theory. Journal of Inner Mongolia Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 46(05), 776–780.
Lian, R. Y. L. W. L. (2005). Relationship between professional commitment and learning burnout of undergraduates and scales developing. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 37(05), 632.
Little, R., & Yau, L. (1996). Intent-to-treat analysis for longitudinal studies with drop-outs. Biometrics, 52(4), 1324–1333. https://doi.org/10.2307/2532847
Liu, W., Zhao, S., Shi, L., Zhang, Z., Liu, X., Li, L., Duan, X., Li, G., Lou, F., Jia, X., Fan, L., Sun, T., & Ni, X. (2018). Workplace violence, job satisfaction, burnout, perceived organisational support and their effects on turnover intention among Chinese nurses in tertiary hospitals: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open, 8(6), e019525. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019525
Luken, M., & Sammons, A. (2016). Systematic review of mindfulness practice for reducing job burnout. American Journal of Occupational Therapy, 70(2), 7002250020p1–7002250020p10. https://doi.org/10.5014/ajot.2016.016956
Mafla, A. C., Villa-Torres, L., Polychronopoulou, A., Polanco, H., Moreno-Juvinao, V., Parra-Galvis, D., Duran, C., Villalobos, M. J., & Divaris, K. (2015). Burnout prevalence and correlates amongst Colombian dental students: The STRESSCODE study. European Journal of Dental Education, 19(4), 242–250. https://doi.org/10.1111/eje.12128
Maslach, C., Schaufeli, W. B., & Leiter, M. P. (2001). Job burnout. Annual Review of Psychology, 52, 397–422. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.52.1.397
Mazurkiewicz, R., Korenstein, D., Fallar, R., & Ripp, J. (2012). The prevalence and correlations of medical student burnout in the pre-clinical years: A cross-sectional study. Psychology Health & Medicine, 17(2), 188–195. https://doi.org/10.1080/13548506.2011.597770
Melamed, S. (2009). Burnout and risk of regional musculoskeletal pain-a prospective study of apparently healthy employed adults. Stress and Health, 25(4), 313–321. https://doi.org/10.1002/smi.1265
Noone, C., & Hogan, M. J. (2018). A randomised active-controlled trial to examine the effects of an online mindfulness intervention on executive control, critical thinking and key thinking dispositions in a university student sample. BMC Psychology, 6(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-018-0226-3
Oro, P., Esquerda, M., Mas, B., Vinas, J., Yuguero, O., & Pifarre, J. (2021). Effectiveness of a mindfulness-based programme on perceived stress, psychopathological symptomatology and burnout in medical students. Mindfulness, 12(5), 1138–1147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-020-01582-5
Pagnin, D., de Queiroz, V., Carvalho, Y., Dutra, A. S. S., Amaral, M. B., & Queiroz, T. T. (2014). The relation between burnout and sleep disorders in medical students. Academic Psychiatry, 38(4), 438–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40596-014-0093-z
Rahmati, Z. (2015). The study of academic burnout in students with high and low level of self-efficacy. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 171, 49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.087
Roeser, R. W., Schonert-Reichl, K. A., Jha, A., Cullen, M., Wallace, L., Wilensky, R., Oberle, E., Thomson, K., Taylor, C., & Harrison, J. (2013). Mindfulness training and reductions in teacher stress and burnout: Results from two randomized, waitlist-control field trials. Journal of Educational Psychology, 105(3), 787–804. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0032093
Salvado, M., Marques, D. L., Pires, I. M., & Silva, N. M. (2021). Mindfulness-based interventions to reduce burnout in primary healthcare professionals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Healthcare, 9(10), 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9101342
Salvarani, V., Rampoldi, G., Ardenghi, S., Bani, M., Blasi, P., Ausili, D., Di Mauro, S., & Strepparava, M. G. (2019). Protecting emergency room nurses from burnout: The role of dispositional mindfulness, emotion regulation and empathy. Journal of Nursing Management, 27(4), 765–774. https://doi.org/10.1111/jonm.12771
Santen, S. A., Holt, D. B., Kemp, J. D., & Hemphill, R. R. (2010). Burnout in medical students: Examining the prevalence and associated factors. Southern Medical Journal, 103(8), 758–763. https://doi.org/10.1097/SMJ.0b013e3181e6d6d4
Scanlan, J. N., & Still, M. (2019). Relationships between burnout, turnover intention, job satisfaction, job demands and job resources for mental health personnel in an Australian mental health service. Bmc Health Services Research, 19, 62. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-018-3841-z
Schaufeli, W. B., Martinez, I. M., Pinto, A. M., Salanova, M., & Bakker, A. B. (2002). Burnout and engagement in university students - A cross-national study. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 33(5), 464–481. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022022102033005003
Schutte, N., Toppinen, S., Kalimo, R., & Schaufeli, W. (2000). The factorial validity of the Maslach Burnout Inventory-General Survey (MBI-GS) across occupational groups and nations. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 73, 53–66. https://doi.org/10.1348/096317900166877
Suleiman-Martos, N., Gomez-Urquiza, J. L., Aguayo-Estremera, R., Canadas-De La Fuente, G. A., De La Fuente-Solana, E. I., & Albendin-Garcia, L. (2020). The effect of mindfulness training on burnout syndrome in nursing: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 76(5), 1124–1140. https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.14318
Sun, J., Jin, Y., & Dai, M. (2013). Discussion on testing the mechanism of missing data. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 43(12), 166–173.
Taylor, N. Z., & Millear, P. M. R. (2016). The contribution of mindfulness to predicting burnout in the workplace. Personality and Individual Differences, 89, 123–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2015.10.005
Toker, S., Melamed, S., Berliner, S., Zeltser, D., & Shapira, I. (2012). Burnout and risk of coronary heart disease: A prospective study of 8838 employees. Psychosomatic Medicine, 74(8), 840–847. https://doi.org/10.1097/PSY.0b013e31826c3174
Toppinen-Tanner, S., Ahola, K., Koskinen, A., & Vaananen, A. (2009). Burnout predicts hospitalization for mental and cardiovascular disorders: 10-year prospective results from industrial sector. Stress and Health, 25(4), 287–296. https://doi.org/10.1002/smi.1282
Van der Heijden, B., Mahoney, C. B., & Xu, Y. (2019). Impact of job demands and resources on nurses’ burnout and occupational turnover intention towards an age-moderated mediation model for the nursing profession. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(11), 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16112011
Vela-Bueno, A., Moreno-Jimenez, B., Rodriguez-Munoz, A., Olavarrieta-Bernardino, S., Fernandez-Mendoza, J., Jose De la Cruz-Troca, J., Bixler, E. O., & Vgontzas, A. N. (2008). Insomnia and sleep quality among primary care physicians with low and high burnout levels. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 64(4), 435–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychores.2007.10.014
Vidhukumar, K., & Hamza, M. (2020). Prevalence and correlates of burnout among undergraduate medical students - A cross-sectional survey. Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine, 42(2), 122–127. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpsym.Ijpsym_192_19
Vilardaga, R., Luoma, J. B., Hayes, S. C., Pistorello, J., Levin, M. E., Hildebrandt, M. J., Kohlenberg, B., Roget, N. A., & Bond, F. (2011). Burnout among the addiction counseling workforce: The differential roles of mindfulness and values-based processes and work-site factors. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 40(4), 323–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2010.11.015
Yang, H. J. (2004). Factors affecting student burnout and academic achievement in multiple enrollment programs in Taiwan’s technical-vocational colleges. International Journal of Educational Development, 24(3), 283–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedudev.2003.12.001
Zhu, T., Xue, J., Montuclard, A., Jiang, Y., Weng, W., & Chen, S. (2019). Can mindfulness-based training improve positive emotion and cognitive ability in Chinese non-clinical population? A Pilot Study. Front Psychol, 10, 1549. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01549
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Grant Number GF21C090006) and the Humanities and Social Sciences Youth Foundation, Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China (Grant Number 22YJCZH209).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ruochen Gan: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, project administration, formal analysis, writing — original draft. Jiang Xue: writing — review and editing. Shulin Chen: funding acquisition, writing — review and editing. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Statement
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Research Ethics Committee of the Department of Psychology and Behavioral Sciences, Zhejiang University (No. [2021]027).
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gan, R., Xue, J. & Chen, S. Do Mindfulness-Based Interventions Reduce Burnout of College Students in China? A Randomized Controlled Trial. Mindfulness 14, 880–890 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-023-02092-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-023-02092-w