Abstract
Objectives
We aimed to examine how a standardized compassion meditation program would induce changes in the patterns of interactions among psychological variables.
Methods
We conducted network analyses on psychological variables before and after 96 participants completed an 8-week Compassion Cultivation Training (CCT) program.
Results
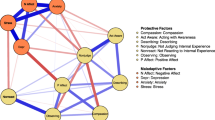
After the CCT program, self-compassion variables increased their importance and influence in the network (i.e., centrality), whereas psychopathology and negative functioning variables (e.g., stress, anxiety, depression, and rumination) decreased their centrality. More importantly, self-compassion increased its associations with other adaptive variables (e.g., emotional reappraisal and mindfulness) after the program. Also, self-compassion, non-attachment, and decentering were the nodes connecting different sub-networks (i.e., bridge nodes), decoupling psychopathological variables (i.e., psychological distress and rumination) from the rest of the network. The variance of compassion, mindfulness, and well-being was mostly explained by other nodes in the network (i.e., predictability), whereas psychopathology-related constructs diminished in their predictability after the program.
Conclusions
These results highlight the role of self-compassion and other adaptive variables as the key mechanisms through which compassion meditation may produce its effects.
Trial Registration
ClinicalTrial.org (NCT03920241)




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., Hopkins, J., Krietemeyer, J., & Toney, L. (2006). Using self-report assessment methods to explore facets of mindfulness. Assessment, 13(1), 27–45. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191105283504.
Blanco, I., Roca, P., Duque, A., Pascual, T., & Vázquez, C. (2020). The effects of a 1-month meditation retreat on selective attention towards emotional faces. An eye-tracking study. Mindfulness, 11, 219–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-019-01247-y.
Borsboom, D., & Cramer, A. O. (2013). Network analysis: an integrative approach to the structure of psychopathology. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 9, 91–121. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-050212-185608.
Brito-Pons, G., Campos, D., & Cebolla, A. (2018). Implicit or explicit compassion? Effects of compassion cultivation training and comparison with mindfulness-based stress reduction. Mindfulness, 9(5), 1494–1508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-018-0898-z.
Brito-Pons, G., Waibel, A., Rosenberg, E., & Chun, J. (2019). Compassion Cultivation Training (CCT): program description, research, and potential benefit for health care and palliative care professionals. In L. Galiana & N. Sansó (Eds.), The Power of Compassion. Nova Science.
Castellanos, N., Diez, G. G., Antúnez-Almagro, C., Bailén, M., Bressa, C., González Soltero, R., Pérez, M., & Larrosa, M. (2020). A critical mutualism – competition interplay underlies the loss of microbial diversity in sedentary lifestyle. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 3142. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.03142.
Chapin, H. L., Darnall, B. D., Seppala, E. M., Doty, J. R., Hah, J. M., & Mackey, S. C. (2014). Pilot study of a compassion meditation intervention in chronic pain. Journal of Compassionate Health Care, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40639-014-0004-x.
Condon, P., Desbordes, G., Miller, W. B., & DeSteno, D. (2013). Meditation increases compassionate responses to suffering. Psychological Science, 24(10), 2125–2127. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797613485603.
Cosley, B. J., McCoy, S. K., Saslow, L. R., & Epel, E. S. (2010). Is compassion for others stress buffering? Consequences of compassion and social support for physiological reactivity to stress. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 46(5), 816–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2010.04.008.
Crocker, J., & Canevello, A. (2008). Creating and undermining social support in communal relationships: the role of compassionate and self-image goals. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 95(3), 555–575. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.95.3.555.
Dahl, C. J., & Davidson, R. J. (2019). Mindfulness and the contemplative life: pathways to connection, insight, and purpose. Current Opinion in Psychology, 28, 60–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2018.11.007.
Dahl, C. J., Lutz, A., & Davidson, R. J. (2015). Reconstructing and deconstructing the self: cognitive mechanisms in meditation practice. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 19(9), 515–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2015.07.001.
Davidson, R. J., & Dahl, C. J. (2018). Outstanding challenges in scientific research on mindfulness and meditation. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 13(1), 62–65. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691617718358.
Davis, M. H. (1980). A multidimensional approach to individual differences in empathy. Catalog of Selected Documents in Psychology, 10(2124), 85.
Derryberry, D., & Reed, M. A. (2002). Anxiety-related attentional biases and their regulation by attentional control. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 111(2), 225–236. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.111.2.225.
Diener, E., Emmons, R. A., Larsen, R. J., & Griffin, S. (1985). The Satisfaction with Life Scale. Journal of Personality Assessment, 49(1), 71–75.
Finlay-Jones, A. L. (2017). The relevance of self-compassion as an intervention target in mood and anxiety disorders: a narrative review based on an emotion regulation framework. Clinical Psychologist, 21(2), 90–103. https://doi.org/10.1111/cp.12131.
Fresco, D. M., Moore, M. T., van Dulmen, M. H. M., Segal, Z. V., Ma, S. H., Teasdale, J. D., & Williams, J. M. G. (2007). Initial psychometric properties of the experiences questionnaire: validation of a self-report measure of decentering. Behavior Therapy, 38(3), 234–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beth.2006.08.003.
Fried, E. I., Eidhof, M. B., Palic, S., Costantini, G., Huisman-van Dijk, H. M., Bockting, C. L., Engelhard, I., Armour, C., Nielsen, A. B. S., & Karstoft, K.-I. (2018). Replicability and generalizability of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) networks: a cross-cultural multisite study of PTSD symptoms in four trauma patient samples. Clinical Psychological Science, 6(3), 335–351. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167702617745092.
Gao, Z. K., Small, M., & Kurths, J. (2017). Complex network analysis of time series. Europhysics Letters, 116(5), 50001. https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/116/50001.
Gilbert, P. (2019). Explorations into the nature and function of compassion. Current Opinion in Psychology, 28, 108–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2018.12.002.
Gilbert, P., Catarino, F., Duarte, C., Matos, M., Kolts, R., Stubbs, J., Ceresatto, L., Duarte, J., Pinto-Gouveia, J., & Basran, J. (2017). The development of compassionate engagement and action scales for self and others. Journal of Compassionate Health Care, 4(1), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40639-017-0033-3.
Goetz, J. L., Keltner, D., & Simon-Thomas, E. (2010). Compassion: an evolutionary analysis and empirical review. Psychological Bulletin, 136(3), 351–374. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0018807.
Goldberg, S. B., Tucker, R. P., Greene, P. A., Davidson, R. J., Wampold, B. E., Kearney, D. J., & Simpson, T. L. (2018). Mindfulness-based interventions for psychiatric disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 59, 52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2017.10.011.
Goldin, P. R., & Jazaieri, H. (2017). The Compassion Cultivation Training (CCT) program. In E. M. Seppala, E. Simon Thomas, S. L. Brown, M. C. Worline, C. D. Cameron, & J. R. Doty (Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Compassion Science. Oxford University Press.
Gross, J. J. (2001). Emotion regulation in adulthood: timing is everything. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 10(6), 214–219. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8721.00152.
Gross, J. J., & John, O. P. (2003). Individual differences in two emotion regulation processes: implications for affect, relationships, and well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 85(2), 348–362. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.85.2.348.
Gu, J., Strauss, C., Bond, R., & Cavanagh, K. (2015). How do mindfulness-based cognitive therapy and mindfulness-based stress reduction improve mental health and wellbeing? A systematic review and meta-analysis of mediation studies. Clinical Psychology Review, 37, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2015.01.006.
Gu, J., Cavanagh, K., Baer, R., & Strauss, C. (2017). An empirical examination of the factor structure of compassion. PLoS ONE, 12(2), e0172471. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0172471.
Gunaratana, H. (2009). Beyond mindfulness in plain English: an introductory guide to deeper states of meditation. Wisdom Publications.
Hair, J. F. J., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2014). Multivariate data analysis (7th ed.) Pearson-Prentice Hall International Edition.
Haslbeck, J. M., & Fried, E. I. (2017). How predictable are symptoms in psychopathological networks? A reanalysis of 18 published datasets. Psychological Medicine, 47(16), 2267–2276. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291717001258.
Heeren, A., & McNally, R. J. (2016). An integrative network approach to social anxiety disorder: the complex dynamic interplay among attentional bias for threat, attentional control, and symptoms. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 42, 95–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2016.06.009.
Hervás, G., & Vázquez, C. (2013). Construction and validation of a measure of integrative well-being in seven languages: the Pemberton Happiness Index. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes, 11(1), 66. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-11-66.
Hofmann, S. G., Curtiss, J. E., & Hayes, S. C. (2020). Beyond linear mediation: toward a dynamic network approach to study treatment processes. Clinical Psychology Review, 76, 101824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2020.101824.
Hölzel, B. K., Lazar, S. W., Gard, T., Schuman-Olivier, Z., Vago, D. R., & Ott, U. (2011). How does mindfulness meditation work? Proposing mechanisms of action from a conceptual and neural perspective. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 6(6), 537–559. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691611419671.
Inwood, E., & Ferrari, M. (2018). Mechanisms of change in the relationship between self-compassion, emotion regulation, and mental health: a systematic review. Applied Psychology. Health and Well-Being, 10(2), 215–235. https://doi.org/10.1111/aphw.12127.
Jazaieri, H., Jinpa, G. T., McGonigal, K., Rosenberg, E. L., Finkelstein, J., Simon-Thomas, E., Cullen, M., Doty, J. R., Gross, J. J., & Goldin, P. R. (2013). Enhancing compassion: a randomized controlled trial of a compassion cultivation training program. Journal of Happiness Studies, 14(4), 1113–1126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-012-9373-z.
Jazaieri, H., McGonigal, K., Jinpa, T., Doty, J. R., Gross, J. J., & Goldin, P. R. (2014). A randomized controlled trial of compassion cultivation training: effects on mindfulness, affect, and emotion regulation. Motivation and Emotion, 38(1), 23–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11031-013-9368-z.
Jazaieri, H., Lee, I. A., McGonigal, K., Jinpa, T., Doty, J. R., Gross, J. J., & Goldin, P. R. (2015). A wandering mind is a less caring mind: daily experience sampling during compassion meditation training. Journal of Positive Psychology, 11(1), 37–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/17439760.2015.1025418.
Jazaieri, H., McGonigal, K., Lee, I. A., Jinpa, T., Doty, J. R., Gross, J. J., & Goldin, P. R. (2018). Altering the trajectory of affect and affect regulation: the impact of compassion training. Mindfulness, 9(1), 283–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-017-0773-3.
Jinpa, T. (2010). Compassion cultivation training (CCT): instructor’s manual. Unpublished, Stanford.
Jones, P. J., Mair, P., & McNally, R. J. (2018). Visualizing psychological networks: a tutorial in R. Frontiers in Psychology, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01742.
Kazdin, A. E. (2009). Understanding how and why psychotherapy leads to change. Psychotherapy Research, 19(4–5), 418–428. https://doi.org/10.1080/10503300802448899.
Kim, J. J., Cunnington, R., & Kirby, J. N. (2020a). The neurophysiological basis of compassion: an fMRI meta-analysis of compassion and its related neural processes. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 108, 112–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.10.023.
Kim, J. J., Parker, S. L., Doty, J. R., Cunnington, R., Gilbert, P., & Kirby, J. N. (2020b). Neurophysiological and behavioural markers of compassion. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63846-3.
Kirby, J. N. (2017). Compassion interventions: the programmes, the evidence, and implications for research and practice. Psychology and Psychotherapy: Theory, Research and Practice, 90(3), 432–455. https://doi.org/10.1111/papt.12104.
Kirby, J. N., Tellegen, C. L., & Steindl, S. R. (2017). A meta-analysis of compassion-based interventions: current state of knowledge and future directions. Behavior Therapy, 48(6), 778–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beth.2017.06.003.
Klimecki, O. M., Leiberg, S., Ricard, M., & Singer, T. (2014). Differential pattern of functional brain plasticity after compassion and empathy training. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 9(6), 873–879. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nst060.
Lovibond, P. F., & Lovibond, S. H. (1995). The structure of negative emotional states: comparison of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS) with the Beck Depression and Anxiety Inventories. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 33(3), 335–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-7967(94)00075-U.
Luberto, C. M., Shinday, N., Song, R., Philpotts, L. L., Park, E. R., Fricchione, G. L., & Yeh, G. Y. (2018). A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of meditation on empathy, compassion, and prosocial behaviors. Mindfulness, 9(3), 708–724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-017-0841-8.
MacBeth, A., & Gumley, A. (2012). Exploring compassion: a meta-analysis of the association between self-compassion and psychopathology. Clinical Psychology Review, 32(6), 545–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2012.06.003.
Malinowski, P. (2013). Neural mechanisms of attentional control in mindfulness meditation. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 7, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2013.00008.
McNally, R. J. (2016). Can network analysis transform psychopathology? Behaviour Research and Therapy, 86, 95–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2016.06.006.
McNally, R. J. (2020). Network analysis of psychopathology: controversies and challenges. The Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 17, 1.1–1.23. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-081219-092850
Mehling, W. E., Price, C., Daubenmier, J. J., Acree, M., Bartmess, E., & Stewart, A. (2012). The Multidimensional Assessment of Interoceptive Awareness (MAIA). PLoS ONE, 7(11), e48230. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048230.
Menon, V. (2011). Large-scale brain networks and psychopathology: a unifying triple network model. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15(10), 483–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2011.08.003.
Neff, K. (2003a). The development and validation of a scale to measure self-compassion. Self and Identity, 2(3), 223–250. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298860309027.
Neff, K. (2003b). Self-compassion: an alternative conceptualization of a healthy attitude toward oneself. Self and Identity, 2(2), 85–101. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298860309032.
Neff, K. (2011). Self-compassion, self-esteem, and well-being. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 5(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-9004.2010.00330.x.
Neff, K. D., Kirkpatrick, K. L., & Rude, S. S. (2007). Self-compassion and adaptive psychological functioning. Journal of Research in Personality, 41(1), 139–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2006.03.004.
Nielsen, L., Riddle, M., King, J. W., Aklin, W. M., Chen, W., Clark, D., Collier, E., Czajkowski, S., Esposito, L., Ferrer, R., Green, P., Hunter, C., Kehl, K., King, R., Onken, L., Simmons, J. M., Stoeckel, L., Stoney, C., Tully, L., & Weber, W. (2018). The NIH Science of Behavior Change Program: transforming the science through a focus on mechanisms of change. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 101, 3–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2017.07.002.
Nolen-Hoeksema, S., & Morrow, J. (1991). A prospective study of depression and posttraumatic stress symptoms after a natural disaster: the 1989 of Loma Prieta earthquake. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61, 115–121.
Papini, S., Rubin, M., Telch, M. J., Smits, J. A. J., & Hien, D. A. (2020). Pretreatment posttraumatic stress disorder symptom network metrics predict the strength of the association between node change and network change during treatment. Journal of Traumatic Stress, 33(1), 64–71. https://doi.org/10.1002/jts.22379.
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J.-Y., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88(5), 879–903. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879.
Pommier, E., Neff, K. D., & Tóth-Király, I. (2019). The development and validation of the Compassion Scale. Assessment, 27(1), 21–39. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191119874108.
Raes, F., Pommier, E., Neff, K. D., & Van Gucht, D. (2011). Construction and factorial validation of a short form of the Self-Compassion Scale. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 18(3), 250–255. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.702.
Robinaugh, D. J., Millner, A. J., & McNally, R. J. (2016). Identifying highly influential nodes in the complicated grief network. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 125(6), 747–757. https://doi.org/10.1037/abn0000181.
Roca, P., & Vazquez, C. (2020). Brief meditation trainings improve performance in the emotional attentional blink. Mindfulness, 11, 1613–1622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-020-01374-x.
Roca, P., Diez, G., Castellanos, N., & Vazquez, C. (2019). Does mindfulness change the mind? A novel psychonectome perspective based on network analysis. PLoS ONE, 14(7), e0219793. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0219793.
Sahdra, B. K., Shaver, P. R., & Brown, K. W. (2010). A scale to measure nonattachment: a Buddhist complement to Western research on attachment and adaptive functioning. Journal of Personality Assessment, 92(2), 116–127. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223890903425960.
Scarlet, J., Altmeyer, N., Knier, S., & Harpin, R. E. (2017). The effects of Compassion Cultivation Training (CCT) on health-care workers. Clinical Psychologist, 21(2), 116–124. https://doi.org/10.1111/cp.12130.
Scheier, M. F., Carver, C. S., & Bridges, M. W. (1994). Distinguishing optimism from neuroticism (and trait anxiety, self-mastery, and self-esteem): a reevaluation of the Life Orientation Test. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 67(6), 1063–1078. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.67.6.1063.
Strauss, C., Lever Taylor, B., Gu, J., Kuyken, W., Baer, R., Jones, F., & Cavanagh, K. (2016). What is compassion and how can we measure it? A review of definitions and measures. Clinical Psychology Review, 47, 15–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2016.05.004.
Tanay, G., Lotan, G., & Bernstein, A. (2012). Salutary proximal processes and distal mood and anxiety vulnerability outcomes of mindfulness training: a pilot preventive intervention. Behavior Therapy, 43(3), 492–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beth.2011.06.003.
Tang, Y. Y., Hölzel, B. K., & Posner, M. I. (2015). The neuroscience of mindfulness meditation. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 16(4), 213–225. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3916.
van Bork, R., Rhemtulla, M., Waldorp, L., Kruis, J., Rezvanifar, S., & Borsboom, D. (in press). Latent variable models and networks: statistical equivalence and testability. Multivariate Behavioral Research.
van Borkulo, C., Boschloo, L., Kossakowski, J., & Tio, P. (2017). Comparing network structures on three aspects: a permutation test. Manuscript Submitted for Publication. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.29455.38569
Wallace, B. A., & Shapiro, S. L. (2006). Mental balance and well-being: building bridges between Buddhism and Western psychology. American Psychologist, 61(7), 690–701. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.61.7.690.
Watkins, E. (2015). Psychological treatment of depressive rumination. Current Opinion in Psychology, 4, 32–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2015.01.020.
Wegner, D. M., & Zanakos, S. (1994). Chronic thought suppression. Journal of Personality, 62(4), 615–640. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6494.1994.tb00311.x.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank all participants for their generosity in voluntarily participating in the study. We thank all the Nirakara Lab members for their immense help and inspiration throughout the project. Finally, we also thank the MBSR and CCT instructors: Agustín Moñivas, Ana Arrabé, Gonzalo Brito, and Silvia Fernández.
Funding
This research was partially supported by a Spanish Ministry of Economy (MINECO) and Ministry of Science grants (PID2019-108711GB-I00) to CV and Real Colegio Complutense at Harvard/Santander Bank grant (CT27/16-CT28/16) to PR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PR and CV developed the study conception and design. Testing and data collection were performed by PR and GD. Data analysis and interpretation were performed by GD and PR. The first draft of the manuscript was written by PR, under the close supervision of CV and RM. PR, CV, and RM drafted the manuscript. All the authors approved the final version of the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Participants provided informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study. Furthermore, the study was approved by the Complutense University ethics committee prior to participant recruitment and was registered at ClinicalTrial.org (NCT03920241).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 3023 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roca, P., Diez, G., McNally, R.J. et al. The Impact of Compassion Meditation Training on Psychological Variables: a Network Perspective. Mindfulness 12, 873–888 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-020-01552-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-020-01552-x