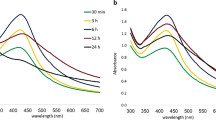
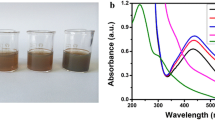
Abstract
Recently, Ag/ZnO nanocomposite (Ag/ZnONC) has been known as one of effective antimicrobial agents. However, its interesting aspects could cause several health effects. This problem can be rectified by capping its surface via the addition of a biomolecule which form a “bio-capped layer” around the particles and prevent them from interacting human cells. In this study, a new fabrication of bio-capped Ag/ZnONCs in various amounts of silver has been reported. Stable and spherical bio-capped Ag/ZnONCs were produced using extract which acts as a reducing and capping agent. The physicochemical, properties of the fabricated NCs was characterized by UV-Vis, XRD, DLS, zeta potential, SEM, XRD, EDX, and FTIR, antioxidant activity. In addition, the mechanism of fabrication has been suggested. Our method of fabrication could be an eco-friendly technique and considered as an alternative to other techniques such as electro- and photo-chemical, chemical, and physical techniques. Our results show that the as-synthesized Ag/ZnONCs possess antioxidant activity and the secondary metabolites of the extract adsorbed on the NC reacts with DPPH. Moreover, the cytotoxicity of bio-capped Ag/ZnONCs (0.15% of Ag) to treat cell lines was evaluated by using cell viability test of human A549 cell line. The obtained results demonstrated that concentrations of up to 0.1 mg/mL of bio-capped Ag/ZnONCs induced no significant harmful to the cells. Hence, the present study proved that the fabricated NCs have the potential to use in industrial and pharmacological applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ibănescu, M., Muşat, V., Textor, T., Badilita, V., & Mahltig, B. (2014). Photocatalytic and antimicrobial Ag/ZnO nanocomposites for functionalization of textile fabrics. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 610, 244–249.
Vandebriel, R. J., & De Jong, W. H. (2012). A review of mammalian toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotechnology, Science and Applications, 5, 61–71.
Zhou, Y., Fang, X., Gong, Y., Xiao, A., Xie, Y., Liu, L., & Cao, Y. (2017). The interactions between ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) and α-linolenic acid (LNA) complexed to BSA did not influence the toxicity of ZnO NPs on HepG2 cells. Nanomaterials, 7, 91–98.
Szekeres, M., Illés, E., Janko, C., Farkas, K., Tóth, I. Y., Nesztor, D., Zupkó, I., Földesi, I., Alexiou, C., & Tombácz, E. (2015). Hemocompatibility and biomedical potential of Poly (Gallic Acid) coated iron oxide nanoparticles for theranostic use. Journal of Nanomedicine and Nanotechnology, 6, 252–259.
Zhang, G., Zheng, H., Shen, M., Wang, L., & Wang, X. (2015). Green synthesis and characterization of Au@Pt core–shell bimetallic nanoparticles using gallic acid. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 81, 79–87.
Yadav, R. S., Kuřitka, I., Vilcakova, J., Havlica, J., & Hajdúchová, M. (2017). Structural, magnetic, dielectric, and electrical properties of NiFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles prepared by honey-mediated sol-gel combustion. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 107, 150–161.
Mahakham, W., Theerakulpisu, P., Maensiri, S., Phumying, S., & Sarmah, A. K. (2016). Environmentally benign synthesis of phytochemicals-capped gold nanoparticles as nanopriming agent for promoting maize seed germination. Science of the Total Environment, 573, 1089–1102.
Xiong, J., Wang, Y., Xue, Q., & Wu, X. (2011). Synthesis of highly stable dispersions of nanosized copper particles using L-ascorbic acid. Green Chemistry, 13, 900–904.
Pawlaczyk, I., Czerchawski, L., Pilecki, W., Lamer-Zarawska, E., & Gancarz, R. (2009). Polyphenolic-polysaccharide compounds from selected medicinal plants of Asteraceae and Rosaceae families: chemical characterization and blood anticoagulant activity. Carbohydrate Polymers, 77, 568–575.
Yadav, R. S., Kuřitka, I., Vilcakova, J., Urbánek, P., & Holek, M. (2017). Structural, magnetic, optical, dielectric, electrical and modulus spectroscopic characteristics of ZnFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles synthesized via honey-mediated sol-gel combustion method. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 110, 87–99.
Balachandran, S., Selvam, K., Babu, B., & Swaminathan, M. (2013). The simple hydrothermal synthesis of Ag–ZnO–SnO2 nanochain and its multiple applications. Dalton Transactions, 42(46), 16365–16374.
Mao, P., Wu, S., Li, J., Fu, W., He, W., Liu, X., Slutsky, A. S., Zhang, H., & Li, Y. (2015). Human alveolar epithelial type II cells in primary culture. Physiological Reports, 3, e12288.
Demir, N., Yildiz, O., Alpaslan, M., & Hayaloglu, A. A. (2014). Evaluation of volatiles, phenolic compounds and antioxidant activities of rose hip (Rosa L.) fruits in Turkey. LWT- Food Science and Technology, 57, 126–133.
Jafarirad, S., Mehrabi, M., Divband, B., & Kosari-Nasab, M. (2016). Biofabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using fruit extract of Rosa canina and their toxic potential against bacteria: a mechanistic approach. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 59, 296–302.
Jafarirad, S., Salmasi, M., Divband, B., & Sarabchi, M. (2019). Systematic study of Nd3 on structural properties of ZnO nanocomposite for biomedical applications; in-vitro biocompatibility, bioactivity, photoluminescence and antioxidant properties. Journal of Rare Earths, 37, 508–514.
Ahn, B. D., Kang, H. S., Kim, J. H., Kim, G. H., Chang, H. W., & Lee, S. Y. (2006). Synthesis and analysis of Ag-doped ZnO. Journal of Applied Physics, 100, 93701. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2364041.
Murali, S., Kumar, S., Koh, J., Seena, S., Singh, P., Ramalho, A., & Sobral, A. J. F. N. (2019). Bio-based chitosan/gelatin/Ag@ZnO bionanocomposites: synthesis and mechanical and antibacterial properties. Cellulose, 26, 5347–5361.
Georgekutty, R., Seery, M. K., & Pillai, S. C. (2008). A highly efficient Ag-ZnO photocatalyst: synthesis, properties, and mechanism. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 112, 13563.
Nyquist, R. A., & Kagel, R. (1971). Infrared spectra of inorganic compounds. New York/London: Academic Press Inc..
Khorrami, S., Jafari Najafabadi, F., Zarepour, A., & Zarrabi, A. (2019). Is astragalus gossypinus honey a natural antibacterial and cytotoxic agent? An investigation on A. gossypinus honey biological activity and its green synthesized silver nanoparticles. BioNanoScience. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-019-00646-8.
Ebadollahi, R., Jafarirad, S., Kosari-Nasab, M., & Mahjouri, S. (2019). Effect of explant source, perlite nanoparticles and TiO2/perlite nanocomposites on phytochemical composition of metabolites in callus cultures of Hypericum perforatum. Scientific Reports, published online. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49504-3.
Stebounova, L. V., Adamcakova-dodd, A., Kim, J. S., Park, H., Shaughnessy, P. T. O., Grassian, V. H., & Thorne, P. S. (2011). Nanosilver induces minimal lung toxicity or inflammation in a subacute murine inhalation model Part. Particle and Fibre Toxicology, 8, 5–11.
Park, S., Lee, Y. K., Jung, M., Kim, K. H., Chung, N., Ahn, E. K., Lim, Y., & Lee, K. H. (2007). Cellular toxicity of various inhalable metal nanoparticles on human alveolar epithelial cells. Inhalation Toxicology, 19, 59–65.
Herzog, F., Clift, M. J., Piccapietra, F., Behra, R., Schmid, O., Petri-Fink, A., & Rothen-Rutishauser, B. (2013). Exposure of silver-nanoparticles and silver-ions to lung cells in vitro at the air-liquid interface. Particle and Fibre Toxicology, 10, 11–19.
Mahdavi Rad, M., Najafzadeh, N., Tata, N., & Jafari, A. (2018). Ag–ZnO nanocomposites cause cytotoxicity and induce cell cycle arrest in human gastric and melanoma cancer cells. Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, 52(Suppl. 5). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-018-1774-9.
Arooj, S., Nazir, S., Nadhman, A., Ahmad, N., Muhammad, B., Ahmad, I., Mazhar, K., & Abbasi, R. (2015). Novel ZnO:Ag nanocomposites induce significant oxidative stress in human fibroblast malignant melanoma (Ht144) cells. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology, 6, 570–582.
Rasoulpour, I., & Jafarirad, S. (2017). Synthesis of biocapped CuO nanoparticles: an investigation on biorganic-Cu2+ interactions, in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial aspects. Inorganic and Nano-Metal Chemistry, 47, 1599–1604.
Funding
This project is financially supported by the University of Tabriz (grant no. 3381).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Research involving humans and animals statement
None.
Informed consent
None.
Funding statement
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jafarirad, S., Taghizadeh, P.M. & Divband, B. Biosynthesis, Characterization and Structural Properties of a Novel Kind of Ag/ZnO Nanocomposites In Order to Increase Its Biocompatibility Across Human A549 Cell Line. BioNanoSci. 10, 42–53 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-019-00685-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-019-00685-1