Abstract
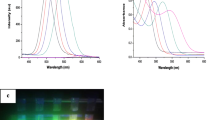
The present work reports the aqueous synthesis of l-cysteine (2-amino 3-mercaptopropionic acid) capped manganese-doped cadmium sulphide quantum dots (QDs). l-Cysteine functions both as a sulfur source and the stabilizer during the synthesis. The product collected at different time intervals during the reaction showed red shifts in their absorption onsets (peak shifts 380 → 395 → 420 nm) and respective emission (peak shifts 585 → 610 → 660 nm) onsets. Nanoparticles of the average size of 3 ± 0.5 nm were obtained. Based on the theoretical calculations, the maximum band gap energy of the synthesized nanocrystals is found to be 2.83 eV. Fourier transform infrared and Raman spectroscopic studies have confirmed the presence of carboxylic and amine functional groups. Atomic force and electron microscopic techniques have verified the formation of the nanosized QDs. Energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry has confirmed the doping of manganese in the CdS structure, while X-ray diffractometry established the crystal structure as of zinc blend type. The proposed l-cysteine capped CdS:Mn QDs can be termed as multifunctional crystals, which are useful for the assembly of fluorescent molecular probes for clinical analysis and disease diagnosis. The proposed nanocrystals can also be potentially used as contrast agents in the magnetic resonance imaging due to the presence of manganese.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Michalet, X., Pinaud, F. F., Bentolila, L. A., Tsay, J. M., Doose, S., Li, J. J., et al. (2005). Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science, 307(5709), 538–544. doi:10.1126/science.1104274.
Kumar, P., Deep, A., Sharma, S. C., Bharadwaj, L. M. (2012). Bioconjugation of InGaP quantum dots for molecular sensing. Analytical Biochemistry, 421(1), 285–290. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2011.10.037.
Chen, Y., & Rosenzweig, Z. (2002). Luminescent CdS quantum dots as selective ion probes. Analytical Chemistry, 74(19), 5132–5138. doi:10.1021/ac0258251.
Yu, W. W., & Peng, X. (2002). Formation of high-quality CdS and other II–VI semiconductor nanocrystals in noncoordinating solvents: tunable reactivity of monomers. Angewandte Chemie, International Edition, 41(13), 2368–2371. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20020703)41.
Sun, W.-T., Yu, Y., Pan, H.-Y., Gao, X.-F., Chen, Q., Peng, L.-M. (2008). CdS quantum dots sensitized TiO2 nanotube-array photoelectrodes. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 130(4), 1124–1125. doi:10.1021/ja0777741.
Li, H., Shih, W. Y., Shih, W.-H. (2007). Synthesis and characterization of aqueous carboxyl-capped CdS quantum dots for bioapplications. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 46(7), 2013–2019. doi:10.1021/ie060963s.
De, M., Ghosh, P. S., Rotello, V. M. (2008). Applications of nanoparticles in biology. Advanced Materials, 20(22), 4225–4241. doi:10.1002/adma.200703183.
Li, Z., & Du, Y. (2003). Biomimic synthesis of CdS nanoparticles with enhanced luminescence. Materials Letters, 57(16–17), 2480–2484. doi:10.1016/s0167-577x(02)01297-1.
Murray, C. B., Norris, D. J., Bawendi, M. G. (1993). Synthesis and characterization of nearly monodisperse CdE (E = sulfur, selenium, tellurium) semiconductor nanocrystallites. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 115(19), 8706–8715. doi:10.1021/ja00072a025.
Peng, Z. A., & Peng, X. (2000). Formation of high-quality CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals using CdO as precursor. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 123(1), 183–184. doi:10.1021/ja003633m.
Foglia, S., Suber, L., Righini, M. (2001). Size tailoring of CdS nanoparticles by different colloidal chemical techniques. Colloids and Surfaces Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 177(1), 3–12. doi:10.1016/s0927-7757(00)00673-7.
Silva, G.A. (2009). Quantum dot nanotechnologies for neuroimaging. In HS Sharma (Ed.), Nanoneuroscience and Nanoneuropharmacology, vol 180. Progress in Brain Research (pp 19–34). doi:10.1016/s0079-6123(08)80002-7
Santra, S., Yang, H., Holloway, P. H., Stanley, J. T., Mericle, R. A. (2005). Synthesis of water-dispersible fluorescent, radio-opaque, and paramagnetic CdS:Mn/ZnS quantum dots: a multifunctional probe for bioimaging. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 127(6), 1656–1657. doi:10.1021/ja0464140.
Ladizhansky, V., & Vega, S. (2000). Doping of CdS nanoparticles by Co2+ ions studied by NMR. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 104(22), 5237–5241. doi:10.1021/jp993951b.
Yang, Y., Chen, O., Angerhofer, A., Cao, Y. C. (2006). Radial-position-controlled doping in CdS/ZnS core/shell nanocrystals. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 128(38), 12428–12429. doi:10.1021/ja064818h.
Galicka, M., Buczko, R., Kacman, P. (2011). Structure-dependent ferromagnetism in Mn-doped III–V nanowires. Nano Letters, 11(8), 3319–3323. doi:10.1021/nl201687q.
Yang, H., & Holloway, P. H. (2003). Electroluminescence from hybrid conjugated polymer CdS:Mn/ZnS core/shell nanocrystals devices. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 107(36), 9705–9710. doi:10.1021/jp034749i.
Nag, A., & Sarma, D. D. (2007). White light from Mn2+-doped CdS nanocrystals: a new approach. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 111(37), 13641–13644. doi:10.1021/jp074703f.
Cao, L., Qu, H., Sun, D., Su, G., Liu, W., Sun, Y. (2009). Solvothermal synthesis and luminescence properties of CdS:Mn nanorods. Science in China Series B: Chemistry, 52(12), 2134–2140. doi:10.1007/s11426-009-0170-4.
Levy, L., Feltin, N., Ingert, D., Pileni, M. P. (1999). Isolated Mn2+ in CdS quantum dots. Langmuir, 15(10), 3386–3389. doi:10.1021/la981633i.
Yang, Y., Chen, O., Angerhofer, A., Cao, Y. C. (2006). Radial-position-controlled doping in CdS/ZnS core/shell nanocrystals. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 128(38), 12428–12429. doi:10.1021/ja064818h.
Yang, Y., Chen, O., Angerhofer, A., Cao, Y. C. (2008). On doping CdS/ZnS core/shell nanocrystals with Mn. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 130(46), 15649–15661. doi:10.1021/ja805736k.
Counio, G., Gacoin, T., Boilot, J. P. (1998). Synthesis and photoluminescence of Cd1-xMnxS (x ≤ 5) nanocrystals. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 102(27), 5257–5260. doi:10.1021/jp980511w.
Mederos, A., Saysell, D. M., Sanchiz, J., Sykes, A. G. (1998). Potentiometric studies on the formation and dissociation of the l-cysteine complexes of di-μ-sulfido and di-μ-oxo molybdenum (V) [Mo2O2(μ-S)2(cys)2]2− and [Mo2O2(μ-O)2(cys)2]2−. Journal of the Chemical Society Dalton Transactions, 16, 2723–2725. doi:10.1039/A802002G.
Zhou, M., Nakatani, E., Gronenberg, L. S., Tokimoto, T., Wirth, M. J., Hruby, V. J., et al. (2007). Peptide-labeled quantum dots for imaging GPCRs in whole cells and as single molecules. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 18(2), 323–332. doi:10.1021/bc0601929.
Buchholz, D. B., Proffit, D. E., Wisser, M. D., Mason, T. O., Chang, R. P. H. (2012). Electrical and band-gap properties of amorphous zinc–indium–tin oxide thin films. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 22(1), 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.pnsc.2011.12.001.
Mansur, H. S., & Mansur, A. A. P. (2011). CdSe quantum dots stabilized by carboxylic-functionalized PVA: synthesis and UV–vis spectroscopy characterization. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 125(3), 709–717. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.09.068.
Zhang, L. Z., Sun, W., Peng, C. (2003). Spectroscopic and theoretical studies of quantum and electronic confinement effects in nanostructured materials. Molecules, 8(1), 207–222. doi:10.3390/80100207.
Mizel, A., & Cohen, M. L. (1997). Electronic energy levels in semiconductor nanocrystals: a Wannier function approach. Physical Review B, 56(11), 6737–6741. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.56.6737.
Sobhana, S. S. L., Devi, M. V., Sastry, T. P., Mandal, A. B. (2011). CdS quantum dots for measurement of the size-dependent optical properties of thiol capping. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 13(4), 1747–1757. doi:10.1007/s11051-010-9934-1.
Andreas, F. T. (2006). Size-dependent band gap of colloidal quantum dots. Journal of Applied Physics, 99, 013708. doi:10.1063/1.2158502.
Barglik-Chory, C., Buchold, D., Schmitt, M., Kiefer, W., Heske, C., Kumpf, C., et al. (2003). Synthesis, structure and spectroscopic characterization of water-soluble CdS nanoparticles. Chemical Physics Letters, 379(5–6), 443–451. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2003.08.068.
Zhang, J., Sun, L., Liao, C., Yan, C. (2002). Size control and photoluminescence enhancement of CdS nanoparticles prepared via reverse micelle method. Solid State Communication, 124(1–2), 45–48. doi:10.1016/S0038-1098(02)00448-9.
Haj Mohamed, N. B., Haouari, M., Jaballah, N., Bchetnia, A., Hriz, K., Majdoub, M., et al. (2012). Optical and IR study of CdS nanoparticles dispersed in a new confined p-phenylenevinylene. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 407(18), 3849–3855. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2012.06.004.
Abdulkhadar, M., & Thomas, B. (1995). Study of Raman spectra of nanoparticles of CdS and ZnS. Nanostructured Materials, 5(3), 289–298. doi:10.1016/0965-9773(95)00237-9.
Acknowledgments
One of the authors (Parveen Kumar) is grateful to the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, India for providing the Senior Research Fellowship. Thanks are due to the Director, CSIO Chandigarh, India for providing necessary facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, P., Kumar, P., Bharadwaj, L.M. et al. Aqueous Synthesis of l-Cysteine Stabilized Water-Dispersible CdS:Mn Quantum Dots for Biosensing Applications. BioNanoSci. 3, 95–101 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-013-0078-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-013-0078-5