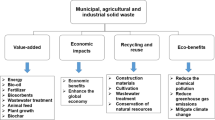
Abstract
In this paper, an operational optimization model is introduced which analyzes electricity generation and its environmental effects in Karachi metropolitan by LEAP model with two different scenarios: business-as-usual and sustainable waste management (SWM). The base and final year planning of this work are 2015 and 2050 respectively. Two different models of Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and LEAP are integrated to estimate the methane flow rate and Karachi energy for non-energy emissions respectively. The GE10 Gas turbine is selected to estimate the electricity production of the landfill gas (LFG) plants. Moreover, engineering equation solver (EES) code is developed which is based on the methane flow rate and composition data gained from the IPCC default method in the SWM scenario. The results obtained from combining EES code and LEAP model demonstrates that the LFG plants can generate upto 0.4 GWh electric powers that is 1.3% of total demand in 2015. Furthermore, it will grow up to 0.8 GWh which is 1.7% of total electricity demand in 2050. However, the utilization of LFG plants escalates the cost of electricity generation but the accumulated difference of 50 years global warming intensity in planned scenarios will be upto 80.1 Mt CO2 equivalents from 2015 to 2050.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barati, B., et al.: Recent progress in genetically modified microalgae for enhanced carbon dioxide sequestration. Biomass Bioenergy 145(1), 105927 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2020.105927
Nojedehi, P., Heidari, M., Ataei, A., Nedaei, M., Kurdestani, E.: Environmental assessment of energy production from landfill gas plants by using long-range energy alternative planning (LEAP) and IPCC methane estimation methods: a case study of Tehran. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 16(2016), 33–42 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2016.04.001
Maria, C., Góis, J., Leitão, A.: Challenges and perspectives of greenhouse gases emissions from municipal solid waste management in Angola. Energy Rep. 6(1), 364–369 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2019.08.074
Shin, H., Park, J., Kim, H., Shin, E.: Environmental and economic assessment of landfill gas electricity generation in Korea using LEAP model. Energy Policy 33(10), 1261–1270 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2003.12.002
Vincent, N., Chaiechi, T., Alam, A.B.M.R.: Are emission reduction policies effective under climate change conditions ? A backcasting and exploratory scenario approach using the LEAP-OSeMOSYS Model. Appl Energy 236(November 2018), 1183–1217 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.12.045
Global Methane Initiative: Global methane emissions and mitigation opportunities. Glob. Methane Initiate., vol. 2020, pp. 1–4 (2010). Accessed date; 2021-01-05. [Online]. https://www.globalmethane.org/documents/gmi-mitigation-factsheet.pdf
Sohail, M., Makhdum, A., Sadaf, T.: A time series analysis of energy consumption, energy prices and economic growth in Pakistan A time series analysis of energy consumption, energy prices and economic growth in Pakistan (2019)
Pohekar, S.D.Ã., Ramachandran, M.: Application of multi-criteria decision making to sustainable energy planning—a review. Renew Sustainable Energy Rev 8(4), 365–381 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2003.12.007
Waqas, M., Abbas, Z., Imran, M. et al. Numerical investigation of impact of hot climate conditions on the performance of Darrieus vertical axis wind turbine. Energy Syst (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-022-00539-y
Dyner, I.: Energy demand and greenhouse gas emissions analysis in Colombia: a LEAP model application. Energy 169, 380–397 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.12.051
Hu, G., Ma, X., Ji, J.: Scenarios and policies for sustainable urban energy development based on LEAP model—a case study of a postindustrial city: Shenzhen China. Appl. Energy 238(October 2018), 876–886 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.01.162
Kowalski, K., Stagl, S., Madlener, R., Omann, I.: Sustainable energy futures: methodological challenges in combining scenarios and participatory multi-criteria analysis q. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 197(3), 1063–1074 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2007.12.049
Isa, S., et al.: International biodeterioration & biodegradation economic and environmental evaluation of land fill gas utilisation: a multi-period optimisation approach for low carbon regions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.04.008
Vincent, N., Comfort, C., Panchakshara, G., Saratu, A., Emodi, A.: Application crossmark. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 68(August 2016), 247–261 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.09.118
Kumar, A., Bhattacharya, S.C., Pham, H.L.: Greenhouse gas mitigation potential of biomass energy technologies in Vietnam using the long range energy alternative planning system model. Energy 28(7), 627–654 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-5442(02)00157-3
Mirjat, N.H., Uqaili, M.A., Harijan, K., Das-Walasai, G., Mondal, A.H., Sahin, H.: Long-term electricity demand forecast and supply side scenarios for Pakistan (2015–2050): a LEAP model application for policy analysis. Energy (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.10.012
Zuberi, M.J.S., Ali, S.F.: Greenhouse effect reduction by recovering energy from waste land fi lls in Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 44, 117–131 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.12.028
Abbas, Z., Waqas, M.: Environmental effects strategy on coal consumption and GHGs emission analysis based on the LEAP model: a case study. Energy Sourc. Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1783392
Mirjat, N.H., Uqaili, M.A., Harijan, K., Das-Walasai, G., Mondal, M.A.H., Sahin, H.: Long-term electricity demand forecast and supply side scenarios for Pakistan (2015–2050): a LEAP model application for policy analysis. Energy 165(October), 512–526 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.10.012
Hainoun, A., Seif-Aldin, M., Almoustafa, S.: Formulating an optimal long-term energy supply strategy for Syria using MESSAGE model. Energy Policy 38(4), 1701–1714 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.11.032
Mangi, M.Y., Yue, Z., Kalwar, S., Lashari, Z.A.: Comparative analysis of urban development trends of Beijing and Karachi metropolitan areas. Sustainability (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020451
Siddiqi, M.M., et al.: Potential in urban Pakistan 1–13
Yah, N.F., Oumer, A.N., Idris, M.S.: Small scale hydro-power as a source of renewable energy in Malaysia: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 72(January), 228–239 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.01.068
Bautista, S.: A sustainable scenario for Venezuelan power generation sector in 2050 and its costs. Energy Policy 44, 331–340 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.01.060
Ghauri, W.U.: Waste to energy potential in presented by (2018)
Mirjat, N.H., Uqaili, M.A., Harijan, K., Das Valasai, G.: A review of energy and power planning and policies of Pakistan A review of energy and power planning and policies of Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 79(October), 110–127 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.040
Zaigham, N.A., Nayyar, Z.A.: Prospects of renewable energy sources in Pakistan. Prosp. Renew. Energy Sources Pak. (2019)
Khan, M.M., Khan, H.: An assessment of the problems faced by Karachi and Pakistan due to the rapid population growth of the city (2016)
Hasan, A.: Land contestation in Karachi and the impact on housing and urban development. Environ. Urban. 27(1), 217–230 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1177/0956247814567263
Uddin, W., et al.: Biogas potential for electric power generation in Pakistan: a survey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 54, 25–33 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.09.083
Hasan, A.: Land contestation in Karachi and the impact on housing and urban development. Environ Urbanization 27(1), 1–14 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1177/0956247814567263
Uzair Ali, M., Gong, Z., Ali, M.U., Asmi, F., Muhammad, R.: CO2 emission, economic development, fossil fuel consumption and population density in India, Pakistan and Bangladesh: a panel investigation. Int. J. Financ. Econ. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/ijfe.2134
Ullah, W., et al.: Present status and potential of biomass energy in Pakistan based on existing and future renewable resources (2020)
Abbas, Z., Harijan, K., Shaikh, P.H., Walasai, G.D., Ali, F.: Effect of ambient temperature and relative humidity on solar PV system performance: a case study of Quaid-e-Azam Solar Park, Pakistan. Sindh Univ. Res. J. Sci. Ser. 49(4), 721–726 (2017). https://doi.org/10.26692/surj/2017.12.47
Bharathiraja, B., Sudharsana, T., Jayamuthunagai, J., Praveenkumar, R., Chozhavendhan, S., Iyyappan, J.: Biogas production—a review on composition, fuel properties, feed stock and principles of anaerobic digestion biogas production—a review on composition, fuel properties, feed stock and principles of anaerobic digestion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 90(July), 570–582 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.03.093
Forest, C., Paper, A., Council, I., Forest, A.: Calculation tools for estimating greenhouse gas emissions from pulp and paper mills (2005)
Mahmood, H., Khan, M.M.: Urban solid waste management in Karachi, Pakistan (2019)
Nojedehi, P., Heidari, M., Ataei, A., Nedaei, M., Kurdestani, E.: Environmental assessment of energy production from landfill gas plants by using long-range energy alternative planning (LEAP) and IPCC methane estimation methods: a case study of Tehran. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 16(2016), 33–42 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2016.04.001
Ali, M.: Integrating recycling and disposal system (2001)
Rice, A.T., Li, P.Y., Sanckens, C.J.: Optimal efficiency-power tradeoff for an air compressor/expander. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. Trans. ASME 140(2), 1–10 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4037652
Meltzer, D.E.: Investigation of students’ reasoning regarding heat, work, and the first law of thermodynamics in an introductory calculus-based general physics course, pp. 1432–1446 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1119/1.1789161
Ur Rehman, S.A., Cai, Y., Mirjat, N.H., Das Walasai, G., Shah, I.A., Ali, S.: The future of sustainable energy production in Pakistan: a system dynamics-based approach for estimating hubbert peaks. Energies (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111858
Acknowledgements
The authors are well acquainted with Dalian University of Technology Dalian 116024, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300350, China and Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Technology, Multan, Pakistan, for their technical support for the completion of this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abbas, Z., Waqas, M. & He, S. Environmental evaluation of electricity generation from landfill gas by using LEAP and IPCC model: a case study of Karachi. Energy Syst (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-023-00574-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-023-00574-3