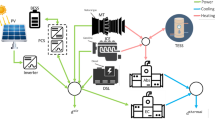
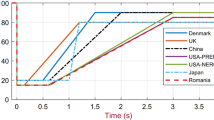
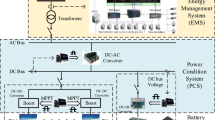
Abstract
Various stochastic programming methods have been used to account for penetration of uncertain renewable energy generation in microgrids. However, these stochastic methods may be unnecessary. Energy storage combined with rescheduling based on a rolling time horizon gives a microgrid powerful tools to adapt to any unexpected events. Add to that the natural tendency to over-engineer new systems and one begins to wonder how much value can be gained by stochastic optimization over deterministic methods. We investigated this question by looking at an existing residential microgrid in Hoover, AL. We compare various stochastic approaches for scheduling with deterministic approaches and show that there is little value of using stochastic programming. Instead, we find that considering longer time horizons is a better use of computational resources.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(u_{gt}^s\) :
-
Commitment status for each generator g in time t, for scenario s, \(\in \{0,1\}\)
- \(v_{gt}^s\) :
-
Generator start up indicator for each generator g in time t, scenario s \(\in \{0,1\}\)
- \(u_{bt}^{Cs},u_{bt}^{Ds}\) :
-
Battery charging/discharging status, respectively in time t, scenario s, \(\in \{0,1\}\)
- \(P_{gt}^s\) :
-
Total power (kW) at each generator g in time t, for scenario s, \(\in \mathbb {R}^+\)
- \(P_{bt}^{Cs},P_{bt}^{Ds}\) :
-
Battery charging/discharging power (kW), respectively, \(\in \mathbb {R}^+\)
- \(p_{gt}^{ms}\) :
-
Power at mth generator interval (kW), \(\in \mathbb {R}^+\)
- \(P_{vt}^s\) :
-
PV power which is not curtailed at time t, scenario s (kW), \(\in \mathbb {R}^+\)
- \(E_{bt}^s\) :
-
Energy in battery b at time t for scenario s (kWh), \(\in \mathbb {R}^+\)
- \(E_{bt}^{EX,s}\) :
-
Amount of battery extreme energy in time t, scenario s (kWh), \(\in \mathbb {R}^+\)
- \(P^{Vs}_{bt}\) :
-
Difference in battery power between time t and \(t-1\), scenario s, \(\in \mathbb {R}\)
- \(L_t^s\) :
-
Load shed at time t scenario s, \(\in \mathbb {R}^+\)
- \(k_{g}\) :
-
minimum up cost of generator g
- \(C_{gt}^m\) :
-
Marginal cost for mth generator interval (strictly increasing)
- \(C^{v}_{gt}\) :
-
Start up cost for generator g
- \(C_{bt}\) :
-
Battery operational cost
- \(\eta _b^C\) :
-
Charging efficiency of battery b
- \(\eta _b^D\) :
-
Discharging efficiency of batter b
- \(P_g^{min}\) :
-
Generator min up power
- \(P_{b,INIT}\) :
-
Initial power output of battery b
- \(D_{t}\) :
-
Real demand at time t
- \(P_{vt}^{Fs}\) :
-
Forecasted PV power at time t for scenario s
- \(E_b^{min}\) :
-
Minimum allowable energy for battery b
- \(E_b^{max}\) :
-
Maximum allowable energy for battery b
- \(E^{cap}_b\) :
-
Maximum energy capacity for battery b
- \(E_{b,INIT}\) :
-
Initial state of charge of batter b
- \(TU_g\) :
-
Minimum up-time for generator g
- \(g \in \mathcal {G}\) :
-
Set of generators
- \(b \in \mathcal {B}\) :
-
Set of batteries
- \(v \in \mathcal {V}\) :
-
Set of PV panels
- \(m \in \mathcal {I}\) :
-
Set of piecewise generator power components
- \(t \in \mathcal {T}\) :
-
Set of timeperiods
- \(s \in \mathcal {S}\) :
-
Set of scenarios
References
Bie, Z., Zhang, P., Li, G., Hua, B., Meehan, M., Wang, X.: Reliability evaluation of active distribution systems including microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 27(4), 2342 (2012)
Hatziargyriou, N., Asano, H., Iravani, R., Marnay, C.: Microgrids. IEEE Power Energy Mag 5(4), 78 (2007)
D.E. Olivares, C.A. Ca nizares, M. Kazerani, A centralized energy management system for isolated microgrids, IEEE Trans Smart Grid 5(4), 1864 (2014)
Hatziargyriou, N.: Microgrids: architectures and control. Wiley, Hoboken (2014)
Moretti, L., Astolfi, M., Vergara, C., Macchi, E., Pérez-Arriaga, J.I., Manzolini, G.: A design and dispatch optimization algorithm based on mixed integer linear programming for rural electrification. Appl. Energy 233, 1104 (2019)
Zia, M.F., Elbouchikhi, E., Benbouzid, M.: Microgrids energy management systems: A critical review on methods, solutions, and prospects. Appl. Energy 222, 1033 (2018)
Van Slyke, R.M., Wets, R.: L-shaped linear programs with applications to optimal control and stochastic programming. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 17(4), 638 (1969)
Geoffrion, A.M.: Generalized benders decomposition. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 10(4), 237 (1972)
Rockafellar, R.T., Wets, R.J.B.: Scenarios and policy aggregation in optimization under uncertainty. Math. Oper. Res. 16(1), 119 (1991)
CarøE, C.C., Schultz, R.: Dual decomposition in stochastic integer programming. Oper. Res. Lett. 24(1–2), 37 (1999)
Mulvey, J.M., Ruszczyński, A.: A new scenario decomposition method for large-scale stochastic optimization. Operat. Res. 43(3), 477 (1995)
Hytowitz, R.B., Hedman, K.W.: Managing solar uncertainty in microgrid systems with stochastic unit commitment. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 119, 111 (2015)
Mohammadi, S., Soleymani, S., Mozafari, B.: Scenario-based stochastic operation management of microgrid including wind, photovoltaic, micro-turbine, fuel cell and energy storage devices. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 54, 525 (2014)
Shen, J., Jiang, C., Liu, Y., Wang, X.: A microgrid energy management system and risk management under an electricity market environment. IEEE Access 4, 2349 (2016)
Asensio, M., Contreras, J.: Stochastic unit commitment in isolated systems with renewable penetration under cvar assessment. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 7(3), 1356 (2015)
Farzin, H., Fotuhi-Firuzabad, M., Moeini-Aghtaie, M.: Stochastic energy management of microgrids during unscheduled islanding period. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 13(3), 1079 (2016)
Mazidi, M., Zakariazadeh, A., Jadid, S., Siano, P.: Integrated scheduling of renewable generation and demand response programs in a microgrid. Energy Convers. Manag. 86, 1118 (2014)
Rezaei, N., Kalantar, M.: Stochastic frequency-security constrained energy and reserve management of an inverter interfaced islanded microgrid considering demand response programs. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 69, 273 (2015)
Zakariazadeh, A., Jadid, S., Siano, P.: Smart microgrid energy and reserve scheduling with demand response using stochastic optimization. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 63, 523 (2014)
D.E. Olivares, J.D. Lara, C.A. Ca nizares, M. Kazerani, Stochastic-predictive energy management system for isolated microgrids, IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 6(6), 2681 (2015)
Su, W., Wang, J., Roh, J.: Stochastic energy scheduling in microgrids with intermittent renewable energy resources. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 5(4), 1876 (2013)
Palma-Behnke, R., Benavides, C., Lanas, F., Severino, B., Reyes, L., Llanos, J., Sáez, D.: A microgrid energy management system based on the rolling horizon strategy. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 4(2), 996 (2013)
Silvente, J., Kopanos, G.M., Dua, V., Papageorgiou, L.G.: A rolling horizon approach for optimal management of microgrids under stochastic uncertainty. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 131, 293 (2018)
J. Silvente, G.M. Kopanos, E.N. Pistikopoulos, A. Espu na, A rolling horizon optimization framework for the simultaneous energy supply and demand planning in microgrids, Appl. Energy 155, 485 (2015)
McIlvenna, A., Ostrowski, J., Herron, A., King, D., Irminger, P., Hambrick, J., Ollis, B.: Practice summary: Improved reliability via optimization in residential microgrids. INFORMS J. Appl. Anal. 50(2), 112 (2020)
A. McIlvenna, A. Herron, J. Hambrick, B. Ollis, J. Ostrowski, Reducing the computational burden of a microgrid energy management system, Comput. Ind. Eng. 106384 (2020)
Xu, B., Oudalov, A., Ulbig, A., Andersson, G., Kirschen, D.S.: Modeling of lithium-ion battery degradation for cell life assessment. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 9(2), 1131 (2016)
W.E. Hart, C.D. Laird, J.P. Watson, D.L. Woodruff, G.A. Hackebeil, B.L. Nicholson, J.D. Siirola, Pyomo–optimization modeling in python, vol. 67, 2nd edn. (Springer Science & Business Media, 2017)
Hart, W.E., Watson, J.P., Woodruff, D.L.: Pyomo: modeling and solving mathematical programs in python. Math. Program. Comput. 3(3), 219 (2011)
Sharma, I., Dong, J., Malikopoulos, A.A., Street, M., Ostrowski, J., Kuruganti, T., Jackson, R.: A modeling framework for optimal energy management of a residential building. Energy Build. 130, 55 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Notice: This manuscript has been authored by UT-Battelle, LLC under Contract No. DE-AC05-00OR22725 with the U.S. Department of Energy. The United States Government retains and the publisher, by accepting the article for publication, acknowledges that the United States Government retains a non-exclusive, paid-up, irrevocable, world-wide license to publish or reproduce the published form of this manuscript, or allow others to do so, for United States Government purposes. The Department of Energy will provide public access to these results of federally sponsored research in accordance with the DOE Public Access Plan (http://energy.gov/downloads/doe-public-access-plan)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McIlvenna, A., Ollis, B. & Ostrowski, J. Investigating the impact of stochasticity in microgrid energy management. Energy Syst 13, 493–508 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-021-00437-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-021-00437-9