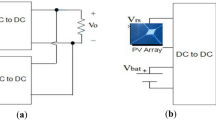
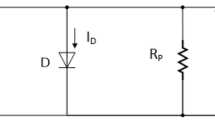
Abstract
The adaptability of maximum power point tracking (MPPT) of a solar PV system is important for integration to a microgrid. Depending on what fixed step-size the MPPT controller implements, there is an impact on settling time to reach the maximum power point (MPP) and the steady state operation for conventional tracking techniques. This paper presents experimental results of an adaptive tracking technique based on Perturb and Observe (P&O) and Incremental Conductance (IC) for standalone Photovoltaic (PV) systems under uniform irradiance and partial shading conditions. Analysis and verification of measured and MATLAB/Simulink simulation results have been carried out. The adaptive tracking technique splits the operational region of the solar PV’s power–voltage characteristic curve into four and six operational sectors to understand the MPP response and stability of the technique. By implementing more step-sizes at sector locations based on the distance of the sector from the MPP, the challenges associated with fixed step-size is improved on.The measured and simulation results clearly indicate that the proposed system tracks MPP faster and displays better steady state operation than conventional system. The proposed system’s tracking efficiency is over 10% greater than the conventional system for all techniques. The proposed system has been under partial shading condition has been and it outperforms other techniques with the GMPP achieved in 0.9 s which is better than conventional techniques.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
BP Energy Economics, 2018 BP Energy Outlook 2018 BP Energy Outlook. 2018, BP Energy Outlook p. 125 (2018)
UK Renewable Energy Roadmap. Department of Energy and Climate Change (2011)
Tawil, T.E., Charpentier, J.F., Benbouzid, M.: Sizing and rough optimization of a hybrid renewable-based farm in a stand-alone marine context. Renew. Energy 115, 1134 (2018)
Sheng, L., Zhou, Z., Charpentier, J., Benbouzid, M.: Stand-alone island daily power management using a tidal turbine farm and an ocean compressed air energy storage system. Renew. Energy 103, 286 (2017)
Moluguri, N.Kumar, Murthy, C.Rama, Harshavardhan, V.: Solar energy system and design—review. Mater. Today Proc. 3(10), 3637 (2016)
Kabir, E., Kumar, P., Kumar, S., Adelodun, A.A., Kim, K.H.: Solar energy: potential and future prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 82, 894 (2018)
Solangi, K.H., Islam, M.R., Saidur, R., Rahim, N.A., Fayaz, H.: A review on global solar energy policy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 15, 2149 (2011)
Huynh, D.C., Dunnigan, M.W.: Development and comparison of an improved incremental conductance algorithm for tracking the MPP of a solar PV panel. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 7(4), 1421 (2016)
Grancini, G.: A new era for solar energy: hybrid perovskite rocks. Photoniques, pp. 24–31 (2019)
Racharla, S., Rajan, K.: Solar tracking system—a review. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 10(2), 72 (2017)
Eldin, S.S., Abd-Elhady, M., Kandil, H.: Feasibility of solar tracking systems for PV panels in hot and cold regions. Renew. Energy 85, 228 (2016)
Tan, C.W.T.C.W., Green, T., Hernandez-Aramburo, C.: Analysis of perturb and observe maximum power point tracking algorithm for photovoltaic applications. 2008 IEEE 2nd International Power and Energy Conference (PECon 08), 237 (2008)
Ramli, M.A., Twaha, S., Ishaque, K., Al-Turki, Y.A.: A review on maximum power point tracking for photovoltaic systems with and without shading conditions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 67, 144 (2017)
Ishaque, K., Salam, Z.: A review of maximum power point tracking techniques of PV system for uniform insolation and partial shading condition. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 19, 475–488 (2013)
Liu, Y.H., Huang, S.C., Huang, J.W., Liang, W.C.: A particle swarm optimization-based maximum power point tracking algorithm for PV systems operating under partially shaded conditions. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 27(4), 1027 (2012)
Masoum, M.A.S., Dehbonei, H., Fuchs, E.F.: Theoretical and experimental analyses of photovoltaic systems with voltage- and current-based maximum power-point tracking. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 17(May), 514 (2014)
Algarín, C.R., Giraldo, J.T., Álvarez, O.R.: Fuzzy logic based MPPT controller for a PV system. Energies 10(12) (2017)
Penella, M.T., Gasulla, M.: A simple and efficient MPPT method for low-power PV cells. Int. J. Photoenergy 2014(1), 1 (2014)
Islam, H., Mekhilef, S., Shah, N., Soon, T., Seyedmahmousian, M., Horan, B., Stojcevski, A.: Performance evaluation of maximum power point tracking approaches and photovoltaic systems. Energies 11(2), 365 (2018)
Houssamo, I., Locment, F., Sechilariu, M.: Maximum power tracking for photovoltaic power system: development and experimental comparison of two algorithms. Renew. Energy 35(10), 2381 (2010)
Piegari, L., Rizzo, R., Spina, I., Tricoli, P.: Optimized adaptive perturb and observe maximum power point tracking control for photovoltaic generation. Energies 8(5), 3418 (2015)
Jaen, C., Moyano, C., Santacruz, X., Pou, J., Arias, A.: Overview of maximum power point tracking control techniques used in photovoltaic systems. In: Proceedings of the 15th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems, ICECS 2008, pp. 1099–1102 (2008)
Putri, R.I., Wibowo, S., Rifa’i, M.: .Maximum power point tracking for photovoltaic using incremental conductance method. Energy Procedia 68, 22–30 (2015)
Visweswara, K.: An investigation of incremental conductance based maximum power point tracking for photovoltaic system. Energy Procedia 54, 11 (2014)
Ghassami, A.Akbar, Sadeghzadeh, S.Mohammad, Soleimani, A.: A high performance maximum power point tracker for PV systems. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 53, 237 (2013)
Ganesh, V., Jadhav, C.B., Choudhari, Y.R., Kate, O.N., Rajguru, V.S.: 2017 7th International Conference on Power Systems (ICPS), pp. 7–12 (2017)
Yüksek, G., Mete, A.N.: A novel variable step size adaptive conductance ratio algorithm for MPPT in solar PV systems. In: 2017 10th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ELECO), pp. 949–953 (2017)
Anya, I.F., Saha, C., Ahmed, H., Huda, N., Sujan, R.: Performance improvement of perturb and observe maximum power point tracking technique for solar PV applications, chap. 8. In: Eltamaly, A.A.Y., Ali, M. (eds.) Modern MPPT Techniques for Photovoltaic Energy Systems, 1st edn. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2019)
Lappalainen, K., Valkealahti, S.: Output power variation of different PV array configurations during irradiance transitions caused by moving clouds. Appl. Energy 190, 902 (2017)
Ramli, M.Z., Salam, Z.: Performance evaluation of dc power optimizer (DCPO) for photovoltaic (PV) system during partial shading. Renew. Energy 139, 1336 (2019)
Alonso, R., Ibá nez, P., Martínez, V., Román, E., Sanz, A.: 13th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, 2009. EPE ’09, pp. 1–8 (2009)
Sundareswaran, K., Palani, S., Vigneshkumar, V.: An innovative perturb, observe and check algorithm for partially shaded PV systems. IET Renew. Power Gen. 9(7), 757 (2015)
Lian, K.L., Jhang, J.H., Tian, I.S.: A maximum power point tracking method based on perturb-and-observe combined with particle swarm optimization. IEEE J. Photovolt. 4(2), 626 (2014)
Jiang, L.L., Nayanasiri, D., Maskell, D.L., Vilathgamuwa, D.: A hybrid maximum power point tracking for partially shaded photovoltaic systems in the tropics. Renew. Energy 76, 53 (2015)
Benlahbib, B., Bouarroudj, N., Mekhilef, S., Abdelkrim, T., Lakhdari, A., Bouchafaa, F.: A fuzzy logic controller based on maximum power point tracking algorithm for partially shaded PV array-experimental validation. Elektronika ir Elektrotechnika, pp. 38–44 (2018)
Sundareswaran, K., Vignesh kumar, V., Palani, S.: Application of a combined particle swarm optimization and perturb and observe method for MPPT in PV systems under partial shading conditions. Renew. Energy 75, 308 (2015)
Abdullahi, N., Saha, C., Jinks, R.: Modelling and performance analysis of a silicon PV module. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 033501, 1 (2017)
Ramyar, A., Iman-Eini, H., Farhangi, S.: Global maximum power point tracking method for photovoltaic arrays under partial shading conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64(4), 2855 (2017)
Femia, N., Petrone, G., Spagnuolo, G., Vitelli, M.: Power electronics and control techniques for maximum energy harvesting in photovoltaic systems. In: Power Electronics and Control Techniques for Maximum Energy Harvesting in Photovoltaic Systems, 1st edn. CRC Press (2013)
Erickson, R.W., Maksimovic, D.: Fundamentals of Power Electronics, 2nd edn. Springer (2001)
Luo, F.L., Ye, H.: Small signal analysis of energy factor and mathematical modeling for power DC–DC converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 22(1), 69 (2007)
Ramani, S., Kollimalla, S.K., Arundhati, B.: Comparative study of P&O and incremental conductance method for PV system. In: 2017 International Conference on Circuit, Power and Computing Technologies (ICCPCT), pp. 1–7 (2017)
Jha, K., Dahiya, R.: Numerical Optimization in Engineering and Sciences. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing. Springer International Publishing, Singapore (2020)
Ahmed, J., Salam, Z.: Comparative study of perturb & observe (P&O) and incremental conductance (IC) MPPT technique of PV system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 11(6), 1378 (2015)
Alajmi, B.N., Ahmed, K.H., Finney, S.J., Williams, B.W.: A maximum power point tracking technique for partially shaded photovoltaic systems in microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 60(4), 1596 (2013)
Manickam, C., Raman, G.R., Raman, G.P., Ganesan, S.I., Nagamani, C.: A hybrid algorithm for tracking of GMPP based on P&O and PSO with reduced power oscillation in string inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 63(10), 6097 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anya, I., Saha, C., Ahmed, H. et al. Experimental evaluation of adaptive maximum power point tracking for a standalone photovoltaic system. Energy Syst 13, 835–853 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-021-00436-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-021-00436-w