Abstract
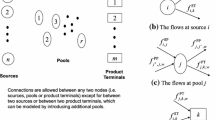
This work reports on modeling and numerical experience in solving the long-term design and operation planning problem of the Brazilian natural gas network. The considered planning problem involves a large amount of money to be invested in production, imports, shipping and delivery of natural gas for several uses in Brazil. In order to account for uncertainties related to the gas demand, mainly due to the use of gas for power production, we model the network planning problem by adopting a two-stage stochastic linear programming approach. We calculate the value of incorporating stochasticity into the problem and assess its numerical tractability in a real-life case by applying optimal scenario reduction techniques and a decomposition strategy based on bundle methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birge, J.R., Louveaux, F.V.: Introduction to Stochastic Programming. Springer Series in Operations Research Series. Springer, London (1997)
Bonnans, J., Gilbert, J., Lemaréchal, C., Sagastizábal, C.: Numerical Optimization: Theoretical and Practical Aspects, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2006)
Correa, R., Lemaréchal, C.: Convergence of some algorithms for convex minimization. Math. Program. 62(2), 261–275 (1993)
Dupacová, J., Gröwe-Kuska, N., Römisch, W.: Scenario reduction in stochastic programming: an approach using probability metrics. Math. Program. 95, 493–511 (2003)
Fábián, C., Szőke, Z.: Solving two-stage stochastic programming problems with level decomposition. Comput. Manag. Sci. 4, 313–353 (2007)
Fábián, C.I.: Bundle-type methods for inexact data. In: Csendes T., Rapcsk T. (eds.) Proceedings of the XXIV Hungarian Operations Research Conference (Veszprém, 1999), vol. 8 (special issue), pp. 35–55 (2000)
Heitsch, H., Römisch, W.: Scenario reduction algorithms in stochastic programming. Comput. Optim. Appl. 24, 187–206 (2003)
Heitsch, H., Römisch, W.: Scenario tree reduction for multistage stochastic programs. Comput. Manag. Sci. 6, 117–133 (2009)
Hellemo, L., Midthun, K., Tomasgard, A., Werner, A.: Multi-Stage Stochastic Programming for Natural Gas Infrastructure Design with a Production Perspective, chapter 10, pp. 259–288
Hellemo, L., Midthun, K., Tomasgard, A., Werner, A.: Natural gas infrastructure design with an operational perspective. Energy Proc. 26(0), 67–73 (2012). 2nd Trondheim Gas Technology Conference
Hiriart-Urruty, J.B., Lemaréchal, C.: Convex Analysis and Minimization Algorithms. No. 305-306 in Grund. der math. Wiss. Springer (1993). (two volumes)
Kazempour, S., Conejo, A.: Strategic generation investment under uncertainty via benders decomposition. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 27(1), 424–432 (2012)
Kelley Jr, J.: The cutting-plane method for solving convex programs. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 8(4), 703–712 (1960)
Kleywegt, A.J., Shapiro, A., Homem-de Mello, T.: The sample average approximation method for stochastic discrete optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 12(2), 479–502 (2002)
Li, X., Armagan, E., Tomasgard, A., Barton, P.I.: Long-term planning of natural gas production systems via a stochastic pooling problem. Am. Control Conf. (ACC) 2010, 429–435 (2010)
Li, X., Chen, Y., Barton, P.I.: Nonconvex generalized benders decomposition with piecewise convex relaxations for global optimization of integrated process design and operation problems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 51(21), 7287–7299 (2012)
Li, X., Tomasgard, A., Barton, P.: Nonconvex generalized benders decomposition for stochastic separable mixed-integer nonlinear programs. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 151, 425–454 (2011)
Maceira, M.E.P., Duarte, V.S., Penna, D.D.J., Moraes, L.A.M., Melo, A.C.G.: Ten years of application of stochastic dual dynamic programming in official and agent studies in Brazil: description of the NEWAVE program. Power Syst. Comput. Conf. 2008, 429–435 (2008)
Newham, N.: Power system investment planning using stochastic dual dynamic programming. Ph.D. thesis, University of Canterbury, New Zealand (2008). http://hdl.handle.net/10092/1975
de Oliveira, W., Sagastizábal, C.: Level bundle methods for oracles with on-demand accuracy. Optim. Methods Softw. 29(6), 1180–1209 (2014)
de Oliveira, W., Sagastizábal, C., Lemaréchal, C.: Convex proximal bundle methods in depth: a unified analysis for inexact oracles. Math. Program. 148, 241–277 (2014)
de Oliveira, W.L., Sagastizábal, C., Penna, D.D.J., Maceira, M.E.P.N., Damázio, J.M.: Optimal scenario tree reduction for stochastic streamflows in power generation planning problems. Optim. Methods Softw. 25(6), 917–936 (2010)
Pflug, G., Pichler, A.: A distance for multistage stochastic optimization models. SIAM J. Optim. 22(1), 1–23 (2012)
Ruszczyński, A.: A regularized decomposition method for minimizing a sum of polyhedral functions. Math. Program. 35, 309–333 (1986)
Sagastizábal, C.: Divide to conquer: decomposition methods for energy optimization. Math. Program. 134, 187–222 (2012)
Santoso, T., Ahmed, S., Goetschalckx, M., Shapiro, A.: A stochastic programming approach for supply chain network design under uncertainty. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 167(1), 96–115 (2005)
Schütz, P., Tomasgard, A., Ahmed, S.: Supply chain design under uncertainty using sample average approximation and dual decomposition. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 199(2), 409–419 (2009)
Shapiro, A., Dentcheva, D., Ruszczyński, A.: Lectures on Stochastic Programming. Modeling and Theory, MPS-SIAM series on optimization, vol. 9. SIAM and MPS, Philadelphia (2009)
Singh, K.J., Philpott, A.B., Wood, R.K.: Dantzig-Wolfe decomposition for solving multistage stochastic capacity-planning problems. Oper. Res. 57(5), 1271–1286 (2009)
Slyke, R.V., Wets, R.B.: L-shaped linear programs with applications to optimal control and stochastic programming. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 17, 638–663 (1969)
Acknowledgments
Research done during a postdoctoral visit of the third author at Instituto Nacional de Matemática Pura e Aplicada-IMPA. The authors are grateful to the reviewers for constructive suggestions that improved the original version of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruno, S.V.B., Moraes, L.A.M. & de Oliveira, W. Optimization techniques for the Brazilian natural gas network planning problem. Energy Syst 8, 81–101 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-015-0172-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-015-0172-6