Abstract
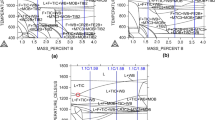
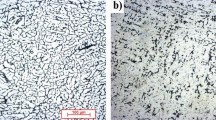
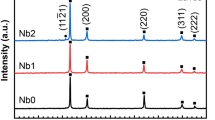
In this work, the effect of aluminum content on the crevice corrosion behavior of the magnesium alloys has been investigated. The as-cast AZ31, AM60B and AZ80 alloys were subjected to the crevice corrosion in a freely aerated 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution, and the extent of the damage was quantified using weight loss measurement and 3D surface topography using an optical profilometer. The as-cast AM60B and AZ31 alloys exhibited the lowest and highest crevice corrosion resistances, respectively. The surface investigation using a scanning electron microscopy (SEM)/energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) and analysis of the corrosion products by Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) suggested that the corrosion damage predominantly was primarily a function of the volume fraction and distribution of the Mg17Al12 precipitates. The lower corrosion resistance of the as-cast AM60B alloy (corrosion rate ~ 240 mpy) as compared to the as-cast AZ80 alloys (corrosion rate ~ 60 mpy) was attributed to the combined effect of the reduction in the barrier effect of the Mg17Al12 precipitates due to their discontinuous distribution and increase in the extent of the micro-galvanic effect due to the lower aluminum content in the α-Mg matrix in the AM60B alloy.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not Applicable.
References
Pardo A, Merino M C, Coy A E, Arrabal R, Viejo F and Matykina E, Corros Sci, 50 (2008) 823.
Makar G L, and Kruger J, Int Mater Rev 38 (1993) 138.
Song G L, and Atrens A, Adv Eng Mater 1 (1999) 11.
Staiger M P, Pietak A M, Huadmai J, and Dias G, Biomaterials 27 (2006) 1728.
Su Y, Lu Y, Su Y, Hu J, Lian J, and Li G, RSC Adv 5 (2015) 56001.
Craig B D and Anderson DS, ASM International, Materials Park (1995) 8
Weber C R, Knörnschild G, and Dick L F P, J Braz Chem Soc 14 (2003) 584.
Eliezer D, Uzan P, and Aghion E, Mater Sci Forum 419 (2003) 857.
Ghali E, Dietzel W, and Kainer K, J Mater Eng Perform 13 (2004) 7.
Gusieva K, Davies C H J, Scully J R, and Birbilis N, Int Mater Rev 60 (2015) 169.
Lunder O, Lein J E, Aune T K, and Nisancioglu K, Corros 45 (1989) 741.
Zeng R C, Zhang J, Huang W J, Dietzel W, Kainer K U, Blawert C, and Wei K E, Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 16 (2006) 763.
ASTM Standard G193–20a, NACE International/ASTM International, (2022).
Kirby C, Corros Sci 27 (1987) 567.
Shi Z, and Atrens A, Mater Sci Forum 690 (2011) 365.
ASTM Standard G78–15, ASTM International, (2015).
ASTM Standard G1–03, ASTM International, (2017).
Song G L, and Xu Z Q, Electrochim Acta 55 (2010) 4148.
Williams G, Dafydd H L, and Grace R, Electrochim Acta 109 (2013) 489.
Reddy U, Dubey D, Panda S S, Ireddy N, Jain J, Mondal K, and Singh S S, J Mater Eng Perform 71 (2021) 2209.
Marya M, Hector L G, Verma R, and Tong W, Mater Sci Eng A 418 (2006) 341.
Pawar S, Zhou X, Thompson G E, Scamans G, and Fan Z, J. Electrochem Soc 162 (2015) 442.
Prasad Y V R K, and Rao K P, Mater Des 30 (2009) 3723.
Sarvesha R, Alam W, Ghokale A, Guruprasad T S, Bhagavath S, Karagadde S, Jain J and Singh S S, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 759 (2019) 368.
Kadali K, Dubey D, Sarvesha R, Kancharla H, Jain J, Mondal K, and Singh S S, J Met 71 (2019) 2209.
Sun W B, and Liu C M, Mater Sci Forum 849 (2016) 154.
Hamu G B, Eliezer D, and Wagner L, J Alloys Compd 468 (2009) 222.
Frost R L, J Raman Spectrosc 42 (2011) 1690.
Jönsson M, Persson D, and Thierry D, Corros Sci 49 (2007) 1540.
Wang L, Shinohara T, and Zhang B P, Appl Surf Sci 256 (2010) 5807.
Xin Y, Huo K, Tao H, Tang G, and Chu P K, Acta Biomater 4 (2008) 2008.
Esmaily M, Svensson J E, Fajardo S, Birbilis N, Frankel G S, Virtanen S, Arrabal R, Thomas S, and Johansson L G, Prog Mater Sci 89 (2017) 92.
Samaniego A, Llorente I, and Feliu S, Corros Sci 68 (2013) 66.
Hu Q, Zhang G, Qiu Y, and Guo X, Corros Sci 53 (2011) 4065.
Baumgärtner M, and Kaesche H, Mater Corros 39 (1988) 129.
Lorking K F, and Mayne J E O, J Appl Chem 11 (2007) 170.
Laycock N J, Stewart J, and Newman R C, Corros Sci 39 (1997) 1791.
Dubey D, Kadali K, Panda S S, Kumar A, Jain J, Mondal K, and Singh S S, Mater Sci Eng A 792 (2020) 139.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Prof. Warren Poole at the University of British Colombia for providing as-cast AZ31 and AZ80 alloys. Authors acknowledge the financial support received from Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur. Authors also acknowledge the facilities at the Advanced Centre for Materials Science (ACMS), IIT Kanpur.
Funding
Financial support was provided by Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Neetu, Ireddy, N., Panda, S.S. et al. Effect of Aluminum Content on the Crevice Corrosion Behavior of Magnesium Alloys. Trans Indian Inst Met 77, 1265–1274 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-023-03175-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-023-03175-x