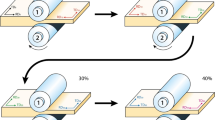
Abstract
A new vibration cast-rolling technology of “electromagnetic stirring + dendrite breaking + asynchronous rolling” was proposed with the adoption of sinusoidal vibration of crystallization roller to prepare Ti/Al laminated composites, and the effects of sinusoidal vibration of crystallization roller on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties were investigated in detail. It is indicated by the microstructure of fracture that the shear dimples surrounded by irregular torn edges in traditional cast-rolling eventually evolve into regular equiaxed dimples with honeycomb network formed by resisting shear deformation during tensile deformation. It is shown in the tensile tests that the yield strength (83.74 MPa) of cast-rolling materials with strong vibration of crystallization roller (amplitude 0.87 mm, vibration frequency 25 Hz) increased by 19% compared with that of traditional cast-rolling materials (70.41 MPa), the elongation (58.36%) decreased by 9% than that of traditional cast-rolling materials (64.34%). This is because the vibration promotes the crystal grain refinement, which leads to the increasing number of crystal grains and dislocation density. The higher the stress that needs to overcome the continuous deformation after strengthening, the more difficult it is for dislocation to migrate as a whole. The smooth and steep mountain-like interface is evolved into a regular tear ridge and dimple interface is formed by adhesive spalling aluminum layer, which can be attributed to the increasing number of crystal grains by vibration and the increase of the contact area between Al and Ti, leading to the bonding and reaction of the interface between the two metals increasing.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang M J, Li J Y, Yu X, and Nie S D, J Constr Steel Res 182 (2021) 106641.
Li S, Luo C, Bashir M U, Jia Y, Han J C, and Wang T, Rare Metals 40 (2021) 2947.
Li S, Liu X Y, Jia Y, Han J C, and Wang T, Materials 14 (2021) 4412.
Yu C, He Z B, Lv Q, Yu J R, and Xiao H, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 117 (2021) 383.
Pei Y B, Huang T, Chen F X, Pang B, Guo J Q, Xiang N, Song Z, and Zhang Y, Vacuum 181 (2020) 109596.
Cui Y, Liu D, Fan M Y, Deng G P, Sun L X, Zhang Y, Chen D, and Zhang Z W, Mater Sci Technol 36 (2020) 425.
de Godoi R P, Magalhaes D C C, Avalos M, Bolmaro R E, Sordi V L, and Kliauga A M, Mater Sci Eng A 771 (2020) 138634.
Yu C, Xiao H, Yu H, Qi Z C, and Xu C, Mater Sci Eng A 695 (2017) 120.
Haga T, Materials 11 (2021) 776.
Gladkovsky S V, Kuteneva S V, and Sergeev S N, Mater Charact 154 (2019) 294.
Huang H G, Dong Y K, Yan M, and Du F S, Trans Nonferr Metals Soc China 27 (2017) 1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60119-5
Chen P, Forming mechanism and property control of solid-liquid cast-rolling of—Ti/Al clad plate, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao, (2019), p 62.
Marc André Meyers, Krishan Kumar Chawla, Mechanical Behavior of Materials. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, (2008), p 306.
Sun MH, Study on technology and interface control mechanism of Cu/Al layered composites solid-liquid vibration cast-rolling, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao, (2020), p 122.
Zhu ZW, Cellular automata simulation and experimental research on solidification structure of twin-roll vibration cast-rolling strip, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao, (2020), p 57.
Acknowledgement
This project was sponsored by Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (No.E2017203043) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.U1604251).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Du, F. Effects of Sinusoidal Vibration of Crystallization Roller on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti/Al Laminated Composites by Twin-Roll Casting. Trans Indian Inst Met 76, 2073–2083 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-022-02795-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-022-02795-z