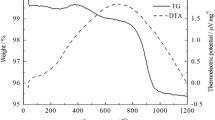
Abstract
Cathode powders of Ba0.5Sr0.5(Co1−xMgx)0.2Fe0.8O3 system (where x = 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1) were prepared by solid-state reaction route with an objective to reduce the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) by lowering Co concentration and by doping Mg for low-temperature solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) applications. The relative density of the produced cathodes was measured, and from the values, the presence of porosity was observed. With the increased sintering temperature from 900 to 1175 °C, the density was significantly increased. X-ray diffraction analysis was carried out for all the samples, and formation of no new phases was observed. The average crystallite size was measured as ~ 18 nm with perovskite type structure. The lattice parameters were calculated, and the unit cell dimension (a) was measured as increased with the increased content of Mg. The temperature-dependent electric conductivity of the prepared samples was measured from room temperature to 800 °C. Highest conductivity was observed for the cathode with Co0.08 and Mg0.12 composition. The presence of Co showed profound effect on increasing the electric conductivity of the cathode material compared with Mg. However, coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) was observed as lower (13.5 × 10–6/°C) for Mg-rich and Co-free cathode, which is favourable for SOFC applications. The results demonstrate the promising role of doping Mg ion in developing low-temperature SOFCs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saddam H, Li Y, Energy Transitions, 2021, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s41825-020-00029-8.
Mclean G F, NietT, Prince-Richard S, DjilaliN, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 27 (2002) 507.
SammesN, BoveR, Stahl K, Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 8 (2004) 372.
Zhang H, Shen P K, Chem Soc Rev 41 (2012) 2382.
Dicks A L, Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 8 (2004) 379.
Brett D J, Atkinson A, Brandon N P, Skinner S J, Chem Soc Rev 37 (2008) 1568.
SinghalS C, Kendal K, High Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells, Elsevier, Netherlands (2003)
Istomin SY, Antipov E V, Russ Chem Rev 82(2013) 686.
Lee K T, WachsmanE D, MRS Bull 39 (2014) 783.
An J, Shim J H, Kim Y, Park J S, Lee W, Gur T M, PrinzF B, MRS Bull 39 (2014) 798.
Chen Y, Zhou W, Ding D, Liu M, Ciucci F, Tade M, Shao Z, Adv Energy Mater 5 (2015) 1500537
Sun J, Liu X, Han F, Zhu L, Bi H, Wang H, Yu S, Pei L, Solid State Ionics 288, (2016) 54.
Choi S, Yoo S, Kim J, Park S, Jun A, Sengodan S, Kim J, Shin J, Jeong H Y, Choi Y, Kim G, Liu M, Sci Rep 3 (2013) 3.
Dai H, Kou H, Tao Z, Liu K, Xue M, Zhang Q, Bi L, Ceram Int 46 (2020) 6987.
Baumann FS, Fleig J, Cristiani G, Stuhlhofer B, Habermeier H U, Maier J, J Electrochem Soc 154, (2007) B931.
Wang B, Bi L, Zhao X S, Ceram Int 44 (2018) 5139.
Lee SJ, YongSM, Kim DS, Kim D K, Int J Hydrogen Energy 37 (2012) 17217.
Duan C, Hook D, Chen Y, Tong J, O’Hayre R, Energy Environ Sci 10(2017) 176.
Martinelli H, Lamas D G, Leyva A G, Sacanell J, Mater Rse Expresss 5(2018) 075013.
Abdalla A M, Hossain S, Azad AT, Petra PMI, Begum F, Eriksson SG, Azad A K, Renew Sustain Energy Rev 82 (2018) 353.
HabiballahAS, Nafisah O, Abdul MJ, Ceram Int 46(14) (2020) 23262.
Zhao S, Tian N, Yu J, J Alloys Compd 825 (2020) 154013.
Liu, D, Dou Y, Xia T, Li Q, Sun L, Huo L, Zhao H, J Power Sources, 494 (2021) 229778.
Zeng Q, Zhang X, Wang W, Zhang D, Jiang Y, Zhou X, Lin B, Catalysts 10(2) (2020) 235.
Gou M, Ren R, Sun W, Xu C, Meng X, Wang Z, Qiao J, Sun K, Ceram Int 45(12) (2019) 15696 -15704.
Li X, Liu Y, Liu W, Wang C, Xu X, Dai H, Wang X, Bi L, Sustain Energ Fuels, 5 (2021) 4261-4267.
Meffert M, Unger L S, Störmer H, Sigloch F, Wagner S F, Ivers-Tiffée E, Gerthsen D, J Am Ceram Soc 102 (2019) 4929–4942.
William D Callister Jr, David G Rethwisch, Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction, 2013, Wiley, USA.
Randall G, Sintering: From Empirical Observations to Scientific Principles, Elsevier, USA, (2014)
Kamila R, Kurniawan B, IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng 496 (2019) 012019.
Bilgili O, Acta Phys Pol A, 136 (2019) 460-466.
Chen G, Feldhoff A, Weidenkaff A et al., Adv Funct Mater, 32(6) (2022) 2105702.
Minh-Vien Lea, Dah-Shyang Tsaib, Tuan-Anh Nguyena, Ceram Int, 44 (2018) 1726.
Tatsumi Ishihara, Nigel M. Sammes, Osamu Yamamoto, High Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells 4 (2003) 83.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Subhashini, P.V.C.K., Rajesh, K.V.D. Development and Characterization of Ba0.5Sr0.5(Co1−xMgx)0.2Fe0.8O3 Cathode Materials System for Low-Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (LT-SOFC) Applications. Trans Indian Inst Met 76, 59–65 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-022-02699-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-022-02699-y