Abstract
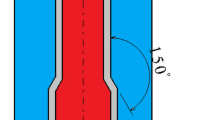
In this research, the extrusion of copper and aluminum in cylindrical forms was investigated by finite element simulation. In addition, the effect of angle and internal profile of the mold on the extrusion force and dimensional uniformity of the produced part was investigated using two types of molds with conical and curved geometry, and its effect on extrusion force was examined by changing the friction coefficient. Based on the results, increasing the conical mold's profile angle leads to an increase in dimensional non-uniformity in the piece and increases the extrusion force. Conversely, the use of curved molds lead to reduction of extrusion force and dimensional uniformity. Interchanging the material of the core and shell can also affect the extrusion force and diameter. Furthermore, curved molds use leads to close the copper core/aluminum shell extrusion product and affect the extrusion force and dimensional changes. Based on investigating the effect of friction coefficient, extrusion forces were increased by increasing the coefficient and shear stress of material flow. The results were compared and validated with similar experimental research.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcaraz J L, Gil-Sevillano J, and Martinez-Esnaola J M, J Mater Process Technol 61 (1996) 265.
Chitkara N R, and Aleem A, Int J Mech Sci 43 (2001) 2833.
Khosravifard A, and Ebrahimi R, Mater Des 31 (2010) 493.
Haghighat H, and Asgari G R, Int J Mech Sci 53 (2011) 248.
Momeni S T, Hosseinipour S J, Nourouzi S, and Gorji A H Int J Civ Eng Build Mater 2 (2012) 132.
Haghighat H, and Mahdavi M M, Trans Nonferr Met Soc China 23 (2013) 3392.
Knezevic M, Jahedi M, Korkolis Y P, and Beyerlein I, J Comput Mater Sci 95 (2014) 63.
Feizi M, and Jafari Nedoushan R, J Mod Process Manuf Prod 4 (2015) 45.
Jin T, Li G, Cao Y, Xu R, Shao S, and Yang B, Energy Build 97 (2015) 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kordeyazdi, M., Beigi Kheradmand, A., Lalegani, Z. et al. Investigating Aluminum and Copper Role in Simulating the Extrusion Process of Bimetal Tubes by Finite Element Method. Trans Indian Inst Met 74, 1179–1192 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02286-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02286-7