Abstract
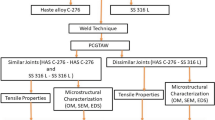
Hastelloy C-276 nickel alloy is widely preferred for nuclear power plant applications where steam generators operate at 600 °C. However, stainless steels are still used for tubes in steam gas reformers which necessitates welds between dissimilar materials. In this study, hastelloy C-276 and SS 316 L alloys were joined using GTAW process. The welding parameters of GTAW were optimized to minimize the defects in samples of similar (SS 316 L-SS 316 L, HAS C-276-HAS C-276), and dissimilar (HAS C-276-SS 316 L) joints. SEM/EDS results confirm the presence of columnar dendritic and cellular structure in fusion zone for dissimilar weldments (HAS C-276-SS 316 L). EDS results also revealed the presence of larger amount of Mo, W and lower amount of Ni in the subgrain boundary as compared to the subgrain body. Compared to the similar (HAS C-276- Has C-276) and dissimilar (HAS C-276-SS 316 L) welded joints FZs, the enrichment of Mo is lesser in SS 316 L-SS 316 L similar welded joints. Higher UTS was obtained for dissimilar (HAS C-276-SS 316 L) GTAW joints 780 MPa compared to the similar welded joints of SS316 (552 MPa) and HAS C-276 (740 MPa). The average microhardness for the dissimilar SS 316 L and HAS C-276 is 220 Hv, which is higher compared to the similar welded joints, SS 316 L and HAS C-276, i.e., 190 Hv and 210 Hv, respectively. This study shows that GTAW process is suitable to fabricate sound weld joints of similar (SS 316 L- SS 316 L, HAS C-276-HAS C-276), and dissimilar (HAS C-276-SS 316 L) alloys which are useful for the nuclear power plant boilers.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Verma, J., Taiwade, R. V., Khatirkar, R. K., Sapate, S. G., & Gaikwad, A. D. (2017). Microstructure, mechanical and intergranular corrosion behavior of dissimilar DSS 2205 and ASS 316L shielded metal arc welds. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 70(1), 225-237.
Bhattacharyya, D., Davis, J., Drew, M., Harrison, R. P., & Edwards, L. (2015). Characterization of complex carbide–silicide precipitates in a Ni–Cr–Mo–Fe–Si alloy modified by welding. Materials Characterization, 105, 118-128.
Mousavi, S. A., & Sufizadeh, A. R. (2009). Metallurgical investigations of pulsed Nd: YAG laser welding of AISI 321 and AISI 630 stainless steels. Materials & Design, 30(8), 3150-3157.
Yılmaz, R., & Tümer, M. (2013). Microstructural studies and impact toughness of dissimilar weldments between AISI 316 L and AH36 steels by FCAW. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 67(5-8), 1433-1447.
Manikandan, M., Arivazhagan, N., Rao, M. N., & Reddy, G. M. (2014). Microstructure and mechanical properties of alloy C-276 weldments fabricated by continuous and pulsed current gas tungsten arc welding techniques. Journal of Manufacturing processes, 16(4), 563-572.
Manikandan, M., Arivazhagan, N., Rao, M. N., & Reddy, G. M. (2015). Improvement of microstructure and mechanical behavior of gas tungsten arc weldments of alloy C-276 by current pulsing. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 28(2), 208-215.
Rajkumar, V., & Arivazhagan, N. (2014). Role of pulsed current on metallurgical and mechanical properties of dissimilar metal gas tungsten arc welding of maraging steel to low alloy steel. Materials & Design, 63, 69-82.
Tariq, F., Baloch, R. A., Ahmed, B., & Naz, N. (2010). Investigation into microstructures of maraging steel 250 weldments and effect of post-weld heat treatments. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 19(2), 264-273.
Dokme, F., Kulekci, M. K., & Esme, U. (2018). Microstructural and mechanical characterization of dissimilar metal welding of Inconel 625 and AISI 316L. Metals, 8(10), 797.
Sharma, S., Taiwade, R. V., & Vashishtha, H. (2017). Effect of continuous and pulsed current gas tungsten arc welding on dissimilar weldments between hastelloy C-276/AISI 321 austenitic stainless steel. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 26(3), 1146-1157.
Pandit, S., Joshi, V., Agrawal, M., Manikandan, M., Ramkumar, K. D., Arivazhagan, N., & Narayanan, S. (2014). Investigations on mechanical and metallurgical properties of dissimilar continuous GTA welds of Monel 400 and C-276. Procedia Engineering, 75, 61-65.
Sharma, S., Taiwade, R. V., Vashishtha, H., & Mukherjee, S. (2018). Microstructural characterization, mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of pulsed current GTA welded bimetallic joints between superalloy C-276 and stabilized austenitic stainless steel grade 321. Materials Research Express, 6(1), 016532.
Kumar, B. R. (2011). Weld quality analysis of TIG, laser and electron beam welded SS 304 and 316 materials with NDT techniques. In Proceedings of the National Seminar & Exhibition on Non-Destructive Evaluation NDE, Chennai (pp. 346–349).
Radha Raman, T. A. (2004). A study of Tensile Strength of MIG and TIG welded dissimilar joints of mild steel and stainless steel. Mater SciEng A, 2004, 23-32.
P. K. Taraphdar, C. Pandey, M. Mahapatra (2020). Finite element investigation of IGSCC-prone zone in AISI 304L multipass groove welds. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering 20:54
Pandeya Chandan, Mohan Mahapatrab M, Pradeep Kumara N (2018). Some studies on P91 steel and their weldments. Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 743. 332-364.
Sirohia S, Pandey C, Goyala A. (2020) Characterization of structure-property relationship of martensitic P91 and high alloy ferritic austenitic F69 steel International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping. 188, 104179.
Pandeya C, Mohan M, Pradeep Kumara N. (2017). Comparative study of autogenous tungsten inert gas welding and tungsten arc welding with filler wire for dissimilar P91 and P92 steel weld joint. Materials Science and Engineering: A. 712, 720-737.
Malarvizhi, S., & Balasubramanian, V. (2012). Influences of welding processes and post-weld ageing treatment on mechanical and metallurgical properties of AA2219 aluminium alloy joints. Welding in the World, 56(9-10), 105-119.
Ming, H., Zhang, Z., Wang, J., Han, E. H., & Ke, W. (2014). Microstructural characterization of an SA508–309L/308L–316L domestic dissimilar metal welded safe-end joint. Materials characterization, 97, 101-115.
Cieslak, M. J., Headley, T. J., & Romig, A. D. (1986). The welding metallurgy of HASTELLOY alloys C-4, C-22, and C-276. Metallurgical Transactions A, 17(11), 2035-2047.
Hosseini, H. S., Shamanian, M., & Kermanpur, A. (2011). Characterization of microstructures and mechanical properties of Inconel 617/310 stainless steel dissimilar welds. Materials characterization, 62(4), 425-431.
Ramkumar, K. D., Dev, S., Saxena, V., Choudhary, A., Arivazhagan, N., & Narayanan, S. (2015). Effect of flux addition on the microstructure and tensile strength of dissimilar weldments involving Inconel 718 and AISI 416. Materials & Design, 87, 663-674.
Pandeya C, Mahapatrab M Pradeep Kumara N. (2018). Effect of strain rate and notch geometry on tensile properties and fracture mechanism of creep strength enhanced ferritic P91 steel. Journal of Nuclear Materials. 498, 176-186.
Pandeya C, Mahapatra M. (2019). Role of evolving microstructure on the mechanical behaviour of P92 steel welded joint in as-welded and post weld heat treated state. 263: 241–55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bezawada, S., G, R. Mechanical and Microstructural Characteristics of Gas Tungsten Arc Welded Similar and Dissimilar Joints of SS-316 L and Hastelloy C276. Trans Indian Inst Met 74, 1623–1637 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02265-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02265-y