Abstract
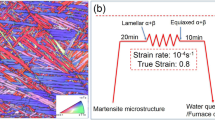
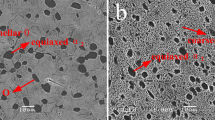
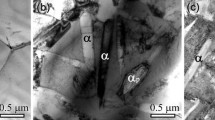
In this study, the effect of lamellar and globular α-phase on mechanical properties of strongly textured Ti–6Al–4V alloy was investigated. The strong transverse texture was developed in Ti–6Al–4V alloy via α + β rolling at 950 °C. In the following, lamellar and equiaxed microstructures have been separately promoted in the Ti–6Al–4V alloy during annealing at β- and α + β regions, respectively. According to EBSD analysis, it was revealed that deformation texture was not considerably changed during different annealing processes. Then, room temperature mechanical properties of the studied alloy including uniaxial tensile, compression and bending tests were evaluated. According to the tensile test, work hardening capacity was obtained as 1.10 and 0.64 for equiaxed and lamellar microstructures, respectively. Fracture limit curve revealed that equiaxed microstructure had more extent of homogeneous deformation in comparison with lamellar one. In addition, bending properties of the Ti–6Al–4V alloy were significantly improved as a result of equiaxed microstructure.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lütjering G, and Williams J C, Titanium, Springer, Berlin (2007), p 203.
Zhao B, Wang H, Qiao N, Wang C, and M. Hu, Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl70 (2017) 832.
Morrissey R J, and Nicholas T, Int J Fatigue27 (2005) 1608.
Barboza M, Perez E, Medeiros M, Reis D, Nono M, Neto F P, and Silva C, Mater Sci Eng A428 (2006) 319.
Nayar P, Bohm E, Petrak M, Caley W, and Cahoon J, Can Metall55 (2016) 420.
Cheng X, Li S, Murr L, Zhang Z, Hao Y, Yang R, Medina F, and Wicker R, J Mech Behav Biomed16 (2012) 153.
Gupta R, Kumar V A, Mathew C, and Rao G S, Mater Sci Eng A662 (2016) 537.
Ma X, Li F, Li J, Cao J, Li P, and Dong J, J Mater Eng Perform24 (2015) 3761.
Matsumoto H, Yoneda H, Sato K, Kurosu S, Maire E, Fabregue D, Konno T J, and Chiba A, Mater Sci Eng A528 (2011) 1512.
Ahmadian P, Abbasi S M, and Morakabati M, Mater Today Commun13 (2017) 332.
Ahmadian P, Abbasi S M, and Morakabati M, Mater Today Commun14 (2018) 263.
Ahmadian P, Morakabati M, and Abbasi S M, Int J Mater Res110 (2019) 543.
Shi X, Zeng W, Sun Y, Han Y, Zhao Y, and Guo P, J Mater Eng Perform24 (2015) 1754.
Murty S N, Nayan N, Kumar P, Narayanan P R, Sharma S, and George K M, Mater Sci Eng A589 (2014) 174.
Jiang H T, Liu J X, Mi Z L, Zhao A M, and Bi Y J, Int J Min Met Mater19 (2012) 530.
Chong Y, Bhattacharjee T, Park M H, Shibata A, and Tsuji N, Mater Sci Eng A730 (2018) 217.
Welsch G, Boyer R, and Collings E, Material Properties Handbook: Titanium alloys, ASM international, Ohio (1993), p 483.
ASTM E8/E8M-16a, Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials, (2016).
ASTM E290-14, Standard Test Methods for Bend Testing of Material for Ductility, (2014).
Chao Q, Hodgson P D, and Beladi H, Metall Mater Trans A47 (2016) 531.
Lin P, Feng A, Yuan S, Li G, and Shen J, Mater Sci Eng A563 (2013) 16.
Randle V, and Engler O, Introduction to Texture Analysis: Macrotexture, Microtexture and Orientation Mapping, CRC press, Florida (2014), p 75.
Wang Y, and Huang J, Mater Chem Phys81 (2003) 11.
Obasi G C, Variant selection and its effect on texture in Ti–6Al–4V alloy, Ph.D. thesis, University of Manchester, England (2011).
Ding R, Guo Z, and Wilson A, Mater Sci Eng A327 (2002) 233.
Hosford W F, and Caddell R M, Metal Forming Mechanics and Metallurgy, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2011), p 17.
Dieter G E, Kuhn H A, and Semiatin S L, Handbook of Workability and Process Design, ASM International, Ohio (2003), p 45.
Kulkarni G, Hiwarkar V, Patil J, and Singh R, J Nanosci Nanotechnol Res 2 (2018) 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadian, P., Morakabati, M. The Effect of Lamellar and Globular α-Phase on Mechanical Behavior of Strongly Textured Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Trans Indian Inst Met 73, 1301–1309 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-01957-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-01957-1