Abstract
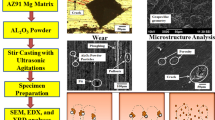
Collective outcomes of WC particle reinforcement and heat treatment on the dry sliding wear rate of AZ91 magnesium metal matrix composite have been presented. The vacuum-assisted semi-solid stir casting method was employed to fabricate the composites. Wear study was conducted on the specimens using a pin-on-disc tribometer with EN8 steel as a counter material. The experiments were designed using Taguchi L27 array, with control factors viz. applied load (20, 40 and 60 N), sliding speed (1, 2 and 3 m/s), heat treatment (no treatment, T4 and T6) and WC wt% (0, 1.5 and 3). Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy analyses were performed to study the surface of the tested specimens. T6-treated AZ91/3.0WC composite showed 63% enhanced resistance to wear due to the presence of β-phase (Mg17Al12) precipitation during the heat treatment process and WC reinforcements.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu Z, Ahmad R, Yin B, Sandlöbes S, and Curtin W A, Science (2018). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aap8716.
Joost W J, and Krajewski P E, Scr Mater (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.07.035.
Ren L, Fan L, Zhou M, Guo Y, Zhang Y, Boehlert C J, and Quan G, Int J Lightweight Mater Manuf (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijlmm.2018.05.002.
Luo A A, J Magn Alloys (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jma.2013.02.002.
Chen T J, Ma Y, Li B, Li Y D, and Hao Y, Mater Sci Eng A (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.09.112.
Wang X J, Xu D K, Wu R Z, Chen X B, Peng Q M, Jin L, Xin Y C, Zhang Z Q, Liu Y, Chen X H, and Chen G, J Mater Sci Technol (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2017.07.019.
Jayamathy M, Seshan S, Kailas S V, Kumar K, and Srivatsan T S, Mater Manuf Process (2005). https://doi.org/10.1081/AMP-200042006.
Oršulová T, and Palček P, Prod Eng Arch (2018). https://doi.org/10.30657/pea.2018.18.08.
Kumar A, Kumar S, and Mukhopadhyay N K, J Magn Alloys (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jma.2018.05.006.
Pandey K M, and Dey A, Rev Adv Mater Sci (2015).
Yang M B, Cheng R J, Bai L, Pan F S, and Shen J, Int J Cast Met Res (2008). https://doi.org/10.1179/136404608x336411.
Karuppusamy P, Lingadurai K, and Sivananth V, in Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1780-4_19.
Sánchez E, Bannier E, Salvador M D, Bonache V, García J C, Morgiel J, and Grzonka J, J Therm Spray Technol (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-010-9480-5.
Yildiz F, High Temp Mater Process (2014). https://doi.org/10.1515/htmp-2013-0018.
Banerjee S, Poria S, Sutradhar G, and Sahoo P, J Magn Alloys (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMA.2018.11.005.
Lun Sin S, Elsayed A, and Ravindran C, Int Mater Rev (2013). https://doi.org/10.1179/1743280413y.0000000017.
Zhang E, Wang G J, and Hu Z C, Mater Sci Technol (2010). https://doi.org/10.1179/174328409X443173.
Poddar P, Mukherjee S, and Sahoo K L, J Mater Eng Perform (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-008-9334-1.
Shankar G, Jayashree P K, Shetty R, Kini A, and Sharma S S, Int J Curr Eng Technol3 (2013) 922.
Powell B R, Luo A A, and Krajewski P E, Adv Mater Automot Eng (2012). https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857095466.150.
ASTM International, ASTM G99: Standard Test Method for Wear Testing with a Pin-on-Disk Apparatus. ASTM Standards (2010). https://doi.org/10.1520/G0099-05R10.2.
Dong S L, Mao J F, Yang D Z, Cui Y X, and Jiang L T, Mater Sci Eng A (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(01)01538-6.
Wang X J, Hu X S, Liu W Q, Du J F, Wu K, Huang Y D, and Zheng M Y, Mater Sci Eng A (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.11.072.
Fillot N, Iordanoff I, and Berthier Y, Wear (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2006.10.011.
Kennedy F E, J Lubr Technol (2009). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3253293.
Cho T Y, Yoon J H, Kim K S, Song K O, Joo Y K, Fang W, and Hwang S Y, Surf Coat Technol (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2008.06.106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karuppusamy, P., Lingadurai, K. & Sivananth, V. Effects of T4 and T6 Heat Treatments on the Wear Behaviour of WC-Reinforced Mg Alloy Matrix Composite. Trans Indian Inst Met 73, 521–530 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-01860-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-01860-9